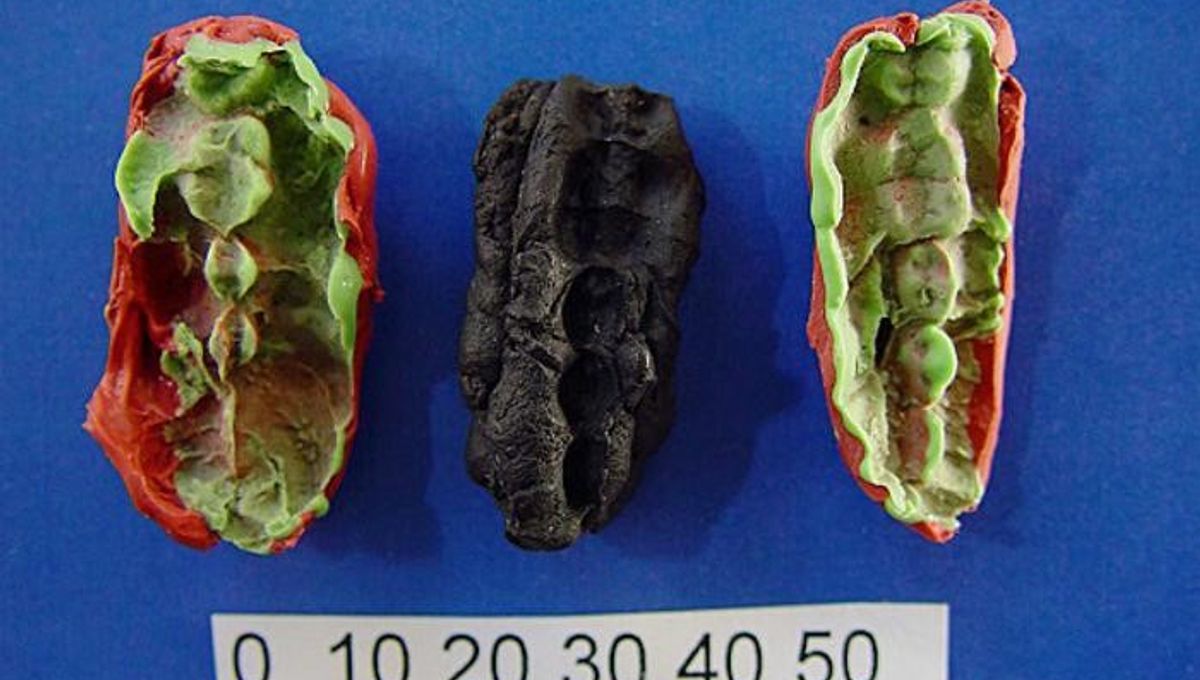
Ten millennia ago, a bunch of teenagers in what is now Sweden chewed up and spat out pieces of birch resin, in much the same way that modern kids might stick their used gum to the underside of a school desk. Little did these ancient adolescents know, however, that their discarded chewings would one day be analyzed by scientists, revealing that they had eaten deer, trout, and nuts, processed wolf and fox furs with their teeth, and suffered from gum disease.
The three pieces of chewed birch pitch – which was used as an adhesive during the Stone Age – were originally discovered in the 1990s at a site called Huseby Klev. Based on the age of the sediment in which the samples were found, researchers estimate that they are between 9,540 and 9,890 years old.
To confirm that the wrinkly specimens had indeed been chewed by humans, the study authors compared the microbial DNA sequences present in the resin with both modern and ancient salivary microbiomes. In doing so, they detected high levels of bacteria associated with periodontitis (gum disease), such as Treponema denticola, Streptococcus anginosus, and Slackia exigua.
Other bacterial species including Streptococcus sobrinus and Parascardovia denticolens – both of which are indicators of tooth decay – were also found to be abundant in the ancient chewing gum. Commenting on these findings in a statement, study author Dr Emrah Kırdök explained that “there is a richness of DNA sequences in the chewed mastic from Huseby-Klev, and in it we find both the bacteria that we know are related to periodontitis, and DNA from plants and animals that they had chewed before”.
Indeed, in addition to highlighting the poor oral health of Mesolithic Scandinavians, the genetic information extracted from the gum revealed the various different plant and animal species that had passed between the chewers’ lips shortly before they gnawed on the resin. These included food sources like hazelnuts, apples, brown trout, red deer, and limpets.
Bird species such as mallard, tufted duck, and European robin were also detected, indicating that Stone Age Scandinavians may have used their teeth to process the bones of these creatures into tools, in addition to eating them.
The researchers also identified the DNA of several canids, including red fox, arctic fox, and wolf. According to the authors, these animals were probably hunted for their furs, and people may have used their teeth at some point in the preparation of these pelts.
Among the other plants detected in the gum was mistletoe, which the researchers say might have been used medicinally or to produce poison for arrowheads.
Summing up the team’s findings, study author Professor Anders Götherström said that the DNA in the ancient gum “provides a snapshot of the life of a small group of hunter-gatherers on the Scandinavian west coast.”
“We know that these teenagers were eating deer, trout, and hazelnuts 9,700 years ago on the west coast of Scandinavia, while at least one of them had severe problems with his teeth,” he said.
The study is published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Source Link: 10,000-Year-Old Chewing Gum Reveals Stone Age Diet And Poor Oral Health