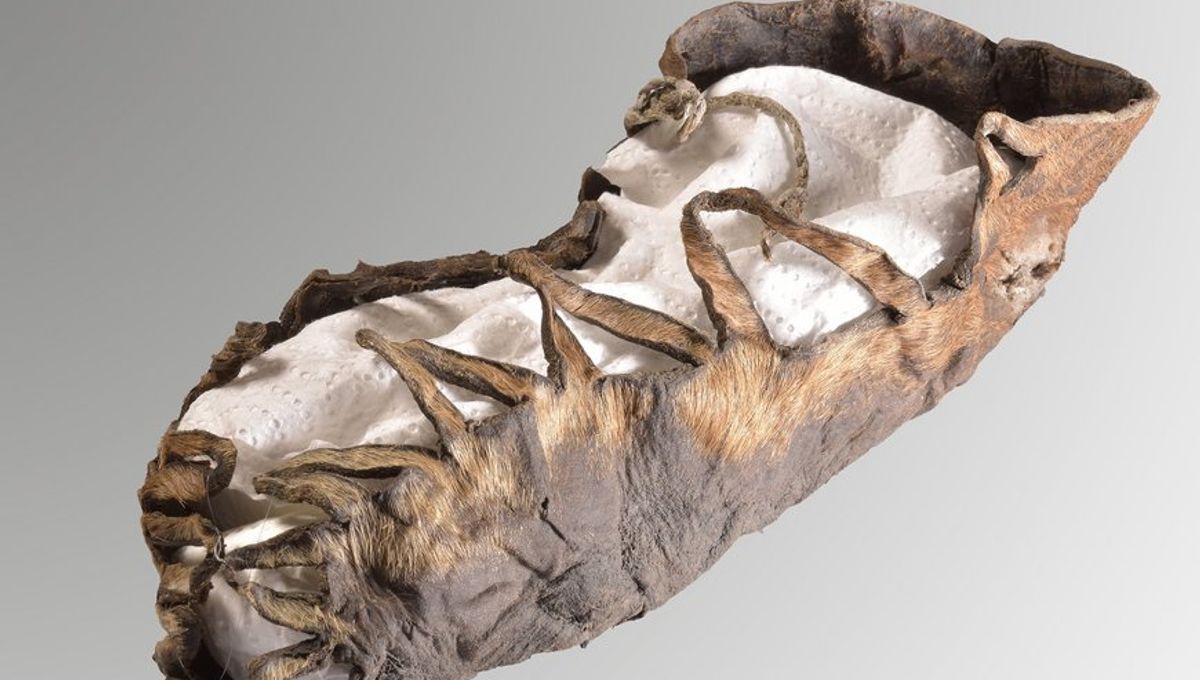
Archaeologists at an old mining site in Dürrnberg, near Salzburg, Austria, have recovered a perfectly preserved child’s shoe that is thought to be over 2,000 years old. The specimen is so well preserved that remnants of the fine materials used to lace it have also survived.
Since 2001, researchers with the German Mining Museum Bochum, Leibniz Research Museum for Georesources, have been investigating an ancient mine in Dürrnberg (otherwise known as Bad Dürrnberg). This site is known for containing rock salt (halite), and was mined as early as the Iron Age (between 1200 and 600 BCE).
The reason why the child’s shoe is so well preserved is because of the salt at the site. Salt helps prevent organic materials from decomposing as they would in other locations.
According to the researchers, the shoe would be equivalent to an EU size 30 (13 US or child’s 11.5 UK) today.
“Our research activities at Dürrnberg have been providing us with valuable finds for decades in order to scientifically explore the earliest mining activities. The condition of the shoe found is outstanding,” Professor Dr Thomas Stöllner, of the German Mining Museum Bochum (Deutsches Bergbau-Museum Bochum), said in a translated statement.
This is not the only shoe recovered from the site, but it is significant because it proves children were present deep in the mine.
In addition, part of the material used to lace the shoe has also survived the centuries. This is extremely rare, especially as the lace appears to be made of flax or linen. This allows researchers to draw conclusions about how this early footwear was tied up. Judging by its overall design, Stöllner and his colleagues believe the shoe was made in the second century BCE.
Excavations have also recovered other organic remains in locations near to where the shoe was found. These include fragments of a wooden shovel, as well as the remains of what is thought to have been a fur hood with lacing.
“Organic materials generally decompose over time”, Stöllner added. “Finds like this child’s shoe, but also textile remains or excrement like those found on Dürrnberg, offer an extremely rare insight into the life of Iron Age miners. They provide valuable information for our scientific work.”
The excavation of the mining site is set to continue for several more years. In that time, the team hope to explore the whole area and to reconstruct a comprehensive image of what life was like in an Iron Age mine. The finds here are helping to address gaps in the historical record that cannot be filled through other sources.
Source Link: 2,000-Year-Old Child’s Shoe Recovered In Ancient Austrian Salt Mine