The use of echolocation is one of the defining characteristics of toothed whales and dolphins, allowing them to navigate, communicate, and hunt in their underwater home. Now, a new study has provided fresh insight into how these creatures evolved to get their “built-in sonar”.
To find out more about how dolphins and whales developed the ability to emit and locate high-pitched sounds, researchers analyzed a large collection of Xenorophidae fossils, an extinct family of animals belonging to the same group as all living echolocating whales and dolphins, Odontoceti.
Within this collection, they found two ancient species belonging to the genus Xenorophus, including a species entirely new to science. Creatures in this genus lived in the waters surrounding eastern North America around 25 to 30 million years ago, and whilst they had more molar-like teeth, they otherwise resembled modern dolphins from the outside. At around 3 meters (10 feet) long, they were about the same length as some common bottlenose dolphins.
The clues to the evolution of echolocation also lay in similarities between these ancient odontocetes and their modern relatives – primarily, in the structures of their jaws and around their blowholes. Similar to living toothed whales and dolphins, Xenorophus were found to have asymmetry in the skull near the blowhole; this “lopsidedness” is what allows their descendants to produce high-pitched sounds.
The researchers also discovered that Xenorophus had a distinct snout bend, with the snout shifted and twisted several degrees to the left. Previous studies have suggested that this could have affected the placement of fat in the lower jaw. This structure in modern whales and dolphins helps to conduct sound waves to the internal ear, in a way that they can locate where sound is coming from – aka directional hearing.
Though Xenorophus was found to have less pronounced asymmetry near the blowhole – which suggests it may not have been as good as living whales and dolphins at producing and hearing high-pitched sounds – the researchers believe the snout structure demonstrates the 30-million-year-old creatures as a key transition point in the evolution of echolocation.
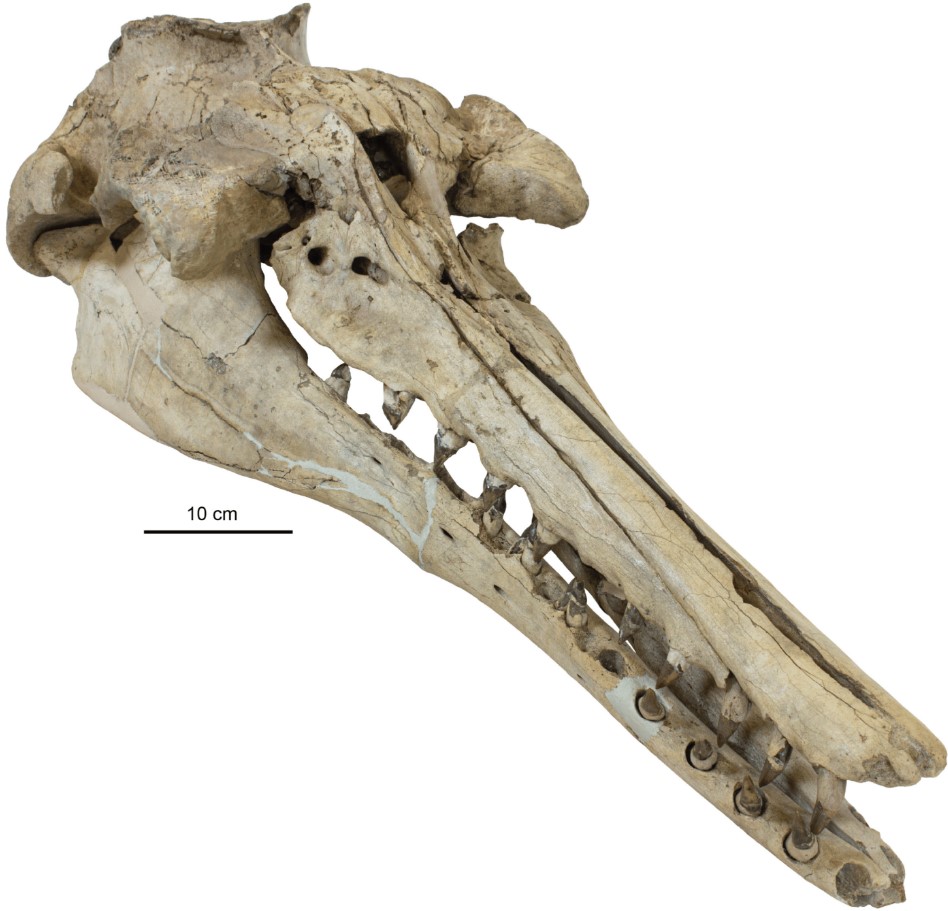
The skull of a Xenorophus.
“While this asymmetry is seen in other ancient whales, Xenorophus displays the strongest of any whale, dolphin, or porpoise, living or extinct,” said first author Robert Boessenecker in a statement. “In addition, although the blowhole-focused asymmetry in today’s odontocetes can be traced back to Xenorophus and other relatives, the twisting and shifting of the snout is no longer seen today. This suggests that Xenorophus is a crucial puzzle piece in understanding how whales and dolphins evolved their echolocation abilities.”
The researchers also believe the study demonstrates that scientists should not dismiss the importance of asymmetry. “Biological symmetry, or the mirror-imaging of body parts across anatomical planes, is a major feature in the evolutionary history of animals and humans,” said co-author Jonathan Geisler.
“However, our research shows the important role of asymmetry in adapting to different environments, and that asymmetry should be closely investigated in fossils, instead of being dismissed as individual variation or assumed to be caused by geological distortion.”
True to their word, the team are planning to look for the snout bend in other odontocetes, in hopes of determining if the feature was widespread.
The study is published in Diversity.
Source Link: 30-Million-Year-Old Whale Ancestor Sheds Light On Early Evolution Of Echolocation