What scientists believe to be a Bronze Age lipstick with a deep red color – and possibly a hint of shimmer – has been discovered in Iran, suggesting that ancient Iranians may have been rouging their lips since the second millennium BCE.
The lip paint was contained in a small, ornately decorated chlorite vial, which was discovered in the Jiroft region of southeastern Iran in 2001. Recent radiocarbon dating has revealed it was made somewhere between 1936 and 1687 BCE, which would make this “probably the earliest [lipstick] analytically reported,” the team behind the find report in their paper.
As impressive as almost-four-millennia-old makeup may sound, the researchers add that the lipstick’s advanced age isn’t all that surprising “considering the long-standing, well known technical and aesthetic tradition in cosmetology in ancient Iran.”
Foundations, eye shadows, and black kohl eyeliners have all previously been identified in the ancient Near East and Egypt. However, deep red pigments such as those found in the lipstick have remained elusive – until now.
Chemical analysis of the residue left in the vial, which by now resembles a fine purple powder, revealed it contains predominantly hematite, known for its intense red color, darkened with manganite and braunite, and complete with traces of galena, anglesite, and other organic substances. Vegetal fibers were present in the archaic cosmetic concoction too, possibly for their aromatic properties, which may have been utilized to scent the lipstick.
The researchers also identified quartz particles, from ground sand or crystals, which they suggest might have been included to add a bit of shimmer – although a much less glamorous explanation is that the quartz flaked off the decaying container.
Glittery or not, the mixture “bears a striking resemblance to the recipes of contemporary lipsticks,” the study authors write. It seems the cosmetologists of ancient Iran walked so that modern pout-enhancers could run.
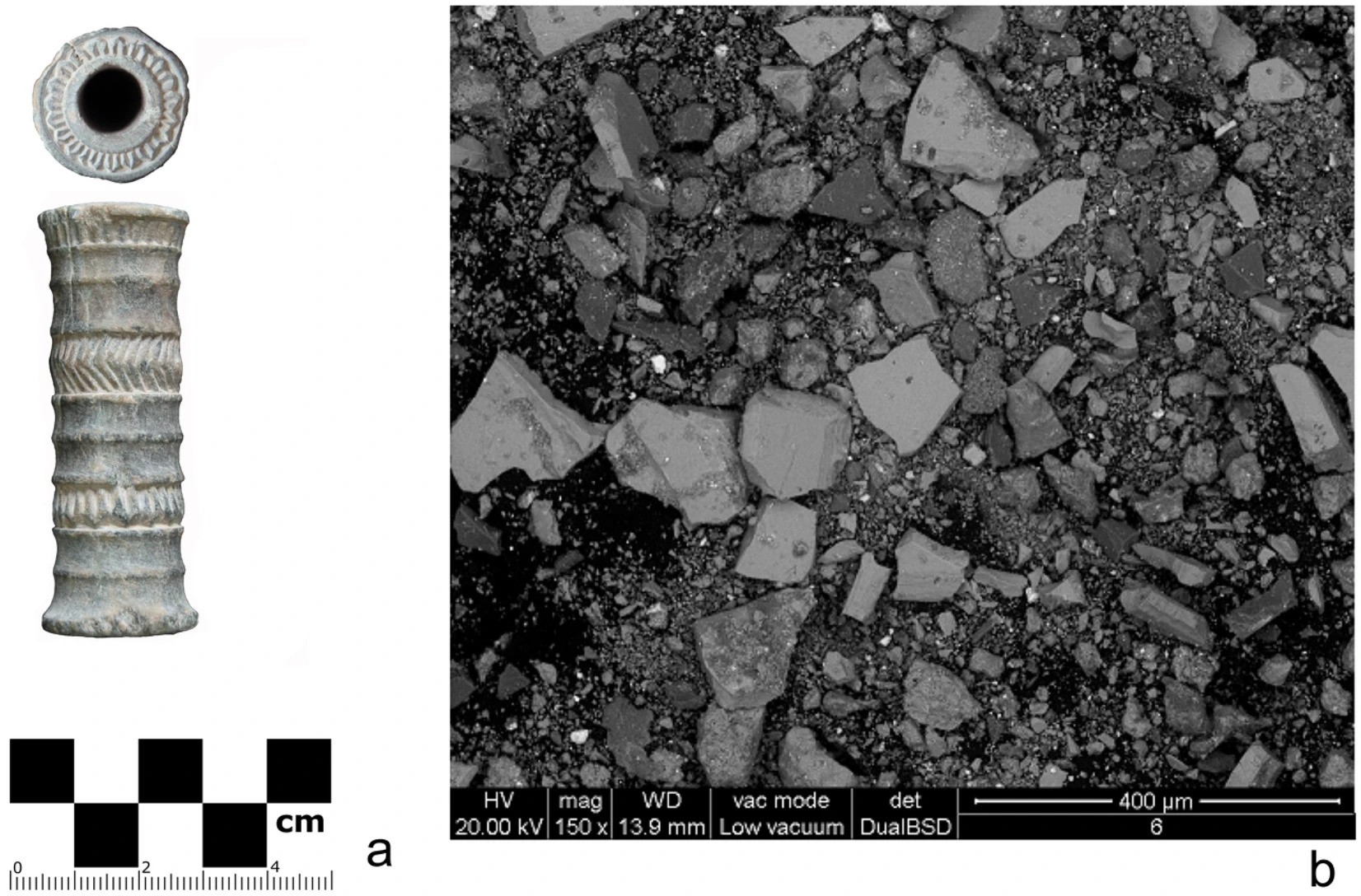
The chlorite vial (left) and its contents (right).
The vial itself is intricately decorated with fine incisions, and is “unlike any other similar object currently known”. Because of this, and the fact of its unusual contents, the researchers write that it “supports the idea that cosmetic products in ancient times were branded, packaged and traded in standard types of containers with specific forms allowing for easy visual identification,” as is the case with contemporary cosmetics and perfumes.
While it’s not possible to know who the owner and wearer of the lipstick was, the find nonetheless offers some insight into the often-overlooked Bronze Age cosmetics industry.
Study author Professor Massimo Vidale told Smithsonian Magazine: “It was a costly expression of luxury that played a crucial role in shaping social interaction in the hierarchies of the early cities.”
The study is published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Source Link: 3,700-Year-Old Red Lipstick Unearthed In Iran May Be Oldest Ever Found