Five hundred million years ago, the Earth was a whole lot of sea. Underwater, the Cambrian Explosion was bringing a flurry of differentiation that laid the foundations for modern animal phyla. The new creatures were not just multicellular blobs, but had many of the distinguishing features of animals today: eyes, legs, shells, and mandibles. One of these creatures appears to have been not only a pioneer in body shape, but also in lifestyle. It has been called a submarine and a taco, but its name is Odaraia alata.
Odaraia had been first found 100 years ago in the Burgess Shale, a rich fossil deposit in the Canadian Rockies. It contains some of the oldest fossils of soft body parts (500 million years old!), providing many insights into what the Cambrian world looked like.
Most Cambrian animals were part of the benthos, the ecosystem of the seafloor, but Odaraia with its 20-centimeter (7.9-inch) long body may already have been swimming up the water column – to hunt. By studying 150 fossils of Odaraia, Alejandro Izquierdo-López and Jean-Bernard Caron could create a detailed reconstruction of what this arthropod would have looked like, and how it probably fed.
“The head shield of Odaraia envelops practically half of its body including its legs, almost as if it were encased in a tube,” said lead author Izquierdo-López in a statement. Its taco-like appearance is only one of the remarkable features of Odaraia. Of particular interest to the researchers are its mandibles and the many spines along its body.
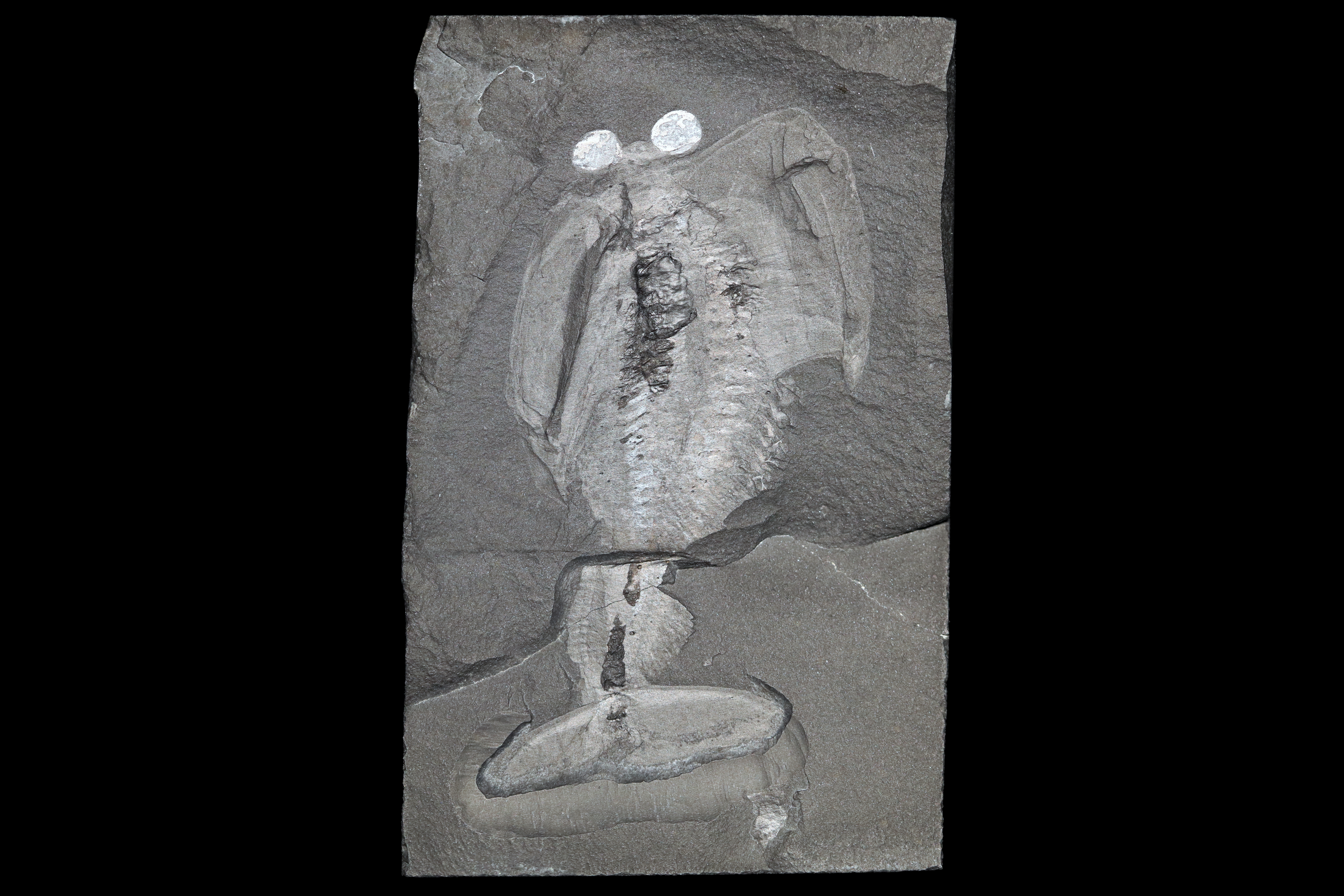
In this fossil, Odaraia reveals her taco shell.
Image credit: photo by Jean-Bernard Caron, Royal Ontario Museum.
Mandibles are ubiquitous in the world today, with almost half of all species having them, but they were a rarity in the Cambrian. The mandibles of Odaraia appear lined with teeth, and with divots for the muscles to attach and control them. This evidence secures Odaraia a spot among the pioneers of this body part.
Even more useful in prey-capture than the mandibles are the spines. Along the length of the body of Odaraia, the researchers found 30 sets of legs with small spines that could have created a mesh to capture prey with. This suggests that Odaraia could have been a suspension feeder, capturing prey similar to mesozooplankton in the net of its spines and then moving it to its mouth.
Oh, and they also found that Odaraia had a tooth shaped like a trident at its mouth opening. They suggest this resembles a gastric tooth, which amazingly is a tooth that lobster and crabs have inside their stomachs.
The authors highlight “the role of recovering anatomical information to improve ecological reconstructions”.
This study is published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences.
Source Link: 500-Million-Year-Old "Taco" Arthropod Is A Hunter With A Trident Tooth