Once upon a time, half a million people perhaps lived on a vast archipelago that stretched out of Australia’s north coast. Unfortunately, the prehistoric homeland was eventually lost to the ocean waves due to intense sea level rise that hit the globe some 14,000 years ago.
Scientists led by Griffith University have recently been studying the ocean floor topography on the Australian northwest continental shelf to understand how this area appeared in an era before the oceans rose.
They conclude that this long-lost land could have potentially been home to a substantial population of humans, perhaps as many as 500,000 people at its peak.
The new research revealed that the region, which is now submerged by seawater, was an extensive archipelago between 71,000 to 59,000 years ago. It then transformed into a fully exposed shelf between 29,000 to 14,000 years ago, featuring an inland sea and a huge freshwater lake, encircled by high cliffs and deep gorges.
This timespan includes a pivotal moment in human history. People first set foot in Australia around 65,000 years ago after migrating southwards from Wallacea, the region of modern-day Indonesia. When they first arrived, the landmass would have included the since-submerged landscapes identified in this new study, suggesting that early human settlers roamed here.
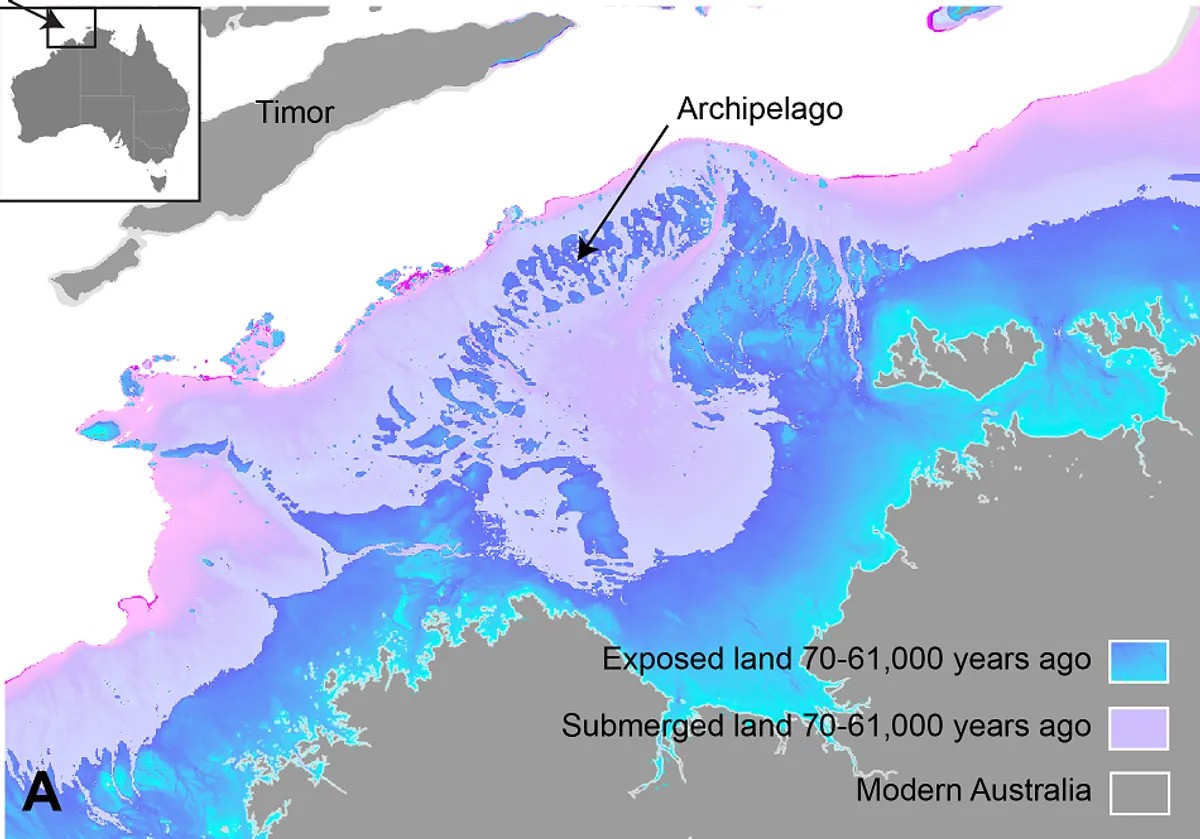
During lower sea levels, a vast archipelago formed on the Australian northwest continental shelf.
Image credit: K Norman, et al./Quaternary Science Reviews (2024)
The study notes that “Australia has traditionally lagged behind many parts of the world with respect to exploration of the archaeology of submerged continental shelves,” adding that marine archaeology has kicked off in other parts of the world, most notably around the Mediterranean.
However, archaeological evidence has shown that northernmost Australia was the host of many dynamic cultures before the last Ice Age.
Furthermore, the researchers note that the time of global sea level rise is directly linked to a significant uptick in the amount of rock art and human-made stone artifacts found in the Kimberley and Arnhem Land regions. This, they say, could imply that human populations were retreating inland away from the since-submerged area.
Based on the size of the sunken land and the number of archaeological discoveries in Northern Australia, the team speculated that the long-lost archipelago could have potentially supported human populations ranging from 50,000 to 500,000 people at various times.
“The temptation to overlook the continental shelf margins of Late Pleistocene Sahul in discussions of early peopling and expansion risks oversimplification and misunderstanding of this pivotal period in history,” Kasih Norman, lead researcher from the Australian Research Centre for Human Evolution at Griffith University, said in a statement.
“Our demographic modeling showed a peak in population size at the height of the last ice age ~20,000 years ago, when the entire extent of the Northwest Shelf was dry land. This finding has now been supported by new genetic research showing very large populations for the Tiwi Islanders – located just to the east of the study region – at the height of the last glacial period,” added Norman.
The discovery has been dubbed the “Aussie Atlantis”, but that might be a little misleading. Researchers are yet to find extensive long-lost settlements here, nor even the physical remains of tools, fire, or other hints that humans were once here.
Besides anything, the discovery of any submerged human settlements is regularly branded as that nation’s own “long-lost Atlantis”. There’s been “Egypt’s Atlantis“, “England’s Atlantis”, and “the Welsh Atlantis”. It’s a great hook to get people interested in a discovery, but not always accurate.
After all, serious archaeologists aren’t even convinced that the original Atlantis spoken about in ancient Greek texts was a real place.
The new study is published in the journal Quaternary Science Reviews.
Source Link: 500,000 People May Have Once Lived On Australia's Long-Lost Landmass