A newly discovered species of mammal has provided a snapshot of terrestrial North America that goes back 70–75 million years ago, a time slice that’s typically not well known. Thankfully, Colorado preserves it well, and this is where a team of scientists retrieved fossil evidence of a Late Cretaceous “swamp dweller”.
The fossil remains included a jawbone and three molar teeth, belonging to an animal that lived in what’s now Rangely, Colorado, at a time when a vast inland sea covered much of the American West. Its wet surroundings are honored in the naming of the new species, Heleocola piceanus, with Heleocola roughly translating from Latin to “swamp dweller”.
When Heleocola was snuffling around, the region would’ve more closely resembled Louisiana, explained study co-author ReBecca Hunt-Foster, a paleontologist at Dinosaur National Monument in Utah and western Colorado, in a statement. “We see a lot of animals that were living in the water quite happily like sharks, rays and guitarfish.”

Oh to be a Late Cretaceous era muskrat-sized mammal splashing around a swampy version of Colorado that looks like Louisiana (pictured).
Image credit: lazyllama / Shutterstock.com
The critter was retrieved from an area of the state that’s hosted fossil digs every summer for the last 15 years, but it was in 2016 that the unusually large mammal made itself known. Its jawbone emerged from a slab of sandstone, as seen by study co-author John Foster, a scientist at the Utah Field House of Natural History State Park Museum in Vernal, Utah, who at the time – to put its size in context – said, “Holy cow, that’s huge.”
We might not have a lot of Heleocola to work with – but based on the dental morphology we have, the team was able to piece together some clues as to how the swamp dweller lived, and what living analogs we can compare it to.
“Diet-wise, and based on its teeth, Heleocola was probably a plant-dominated omnivore, meaning it ate mostly plants, but probably consumed some insects and/or small vertebrates too,” Professor Jaelyn Eberle, curator of fossil vertebrates at the University of Colorado Museum of Natural History, who led the study, told IFLScience. “It’s a large mammal by Late Cretaceous standards (with an estimated body mass similar to today’s muskrat), whereas most mammals living at this time (70 – 75 million years ago) were mouse to rat-sized.”
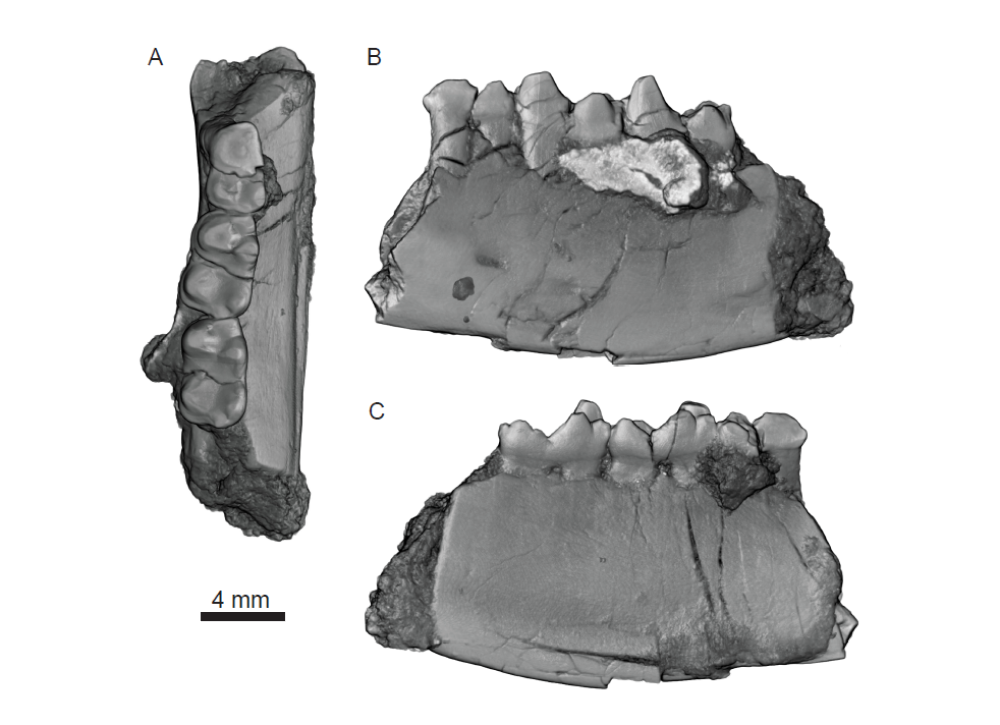
Jaw fragment of Heleocola piceanus.
“I think its larger size is one of the fascinating takeaways, as traditionally Late Cretaceous mammals have been interpreted as tiny and rather insignificant (living in the understory beneath the dinosaurs).”
Mammals didn’t really go super-sized until after the asteroid came along and killed off the non-avian dinosaurs 66 million years ago, prior to which they were all a bit mouse-like. With the arrival of the swamp dweller, we now know that there were some comparative beasts in Colorado 70–75 million years ago that were much bigger than scientists would’ve previously believed.
The study is published in the journal PLoS ONE.
Source Link: 75-Million-Year-Old "Swamp Dweller" Among Largest Late Cretaceous Mammals Ever Found