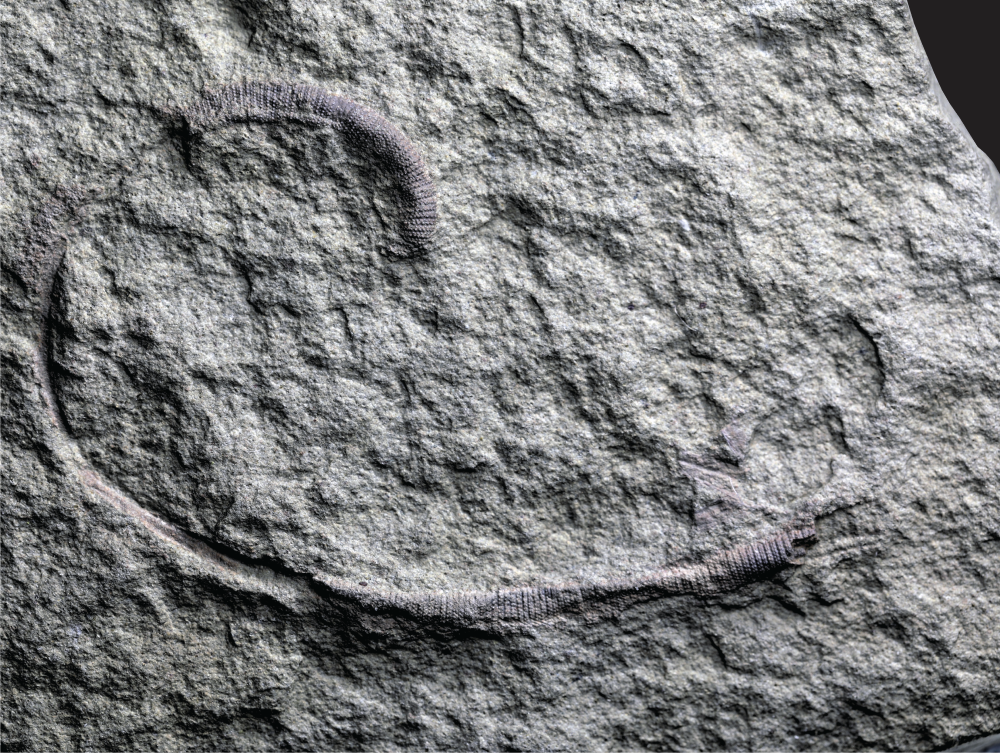
A remarkable fossil of a worm has been described, estimated to be around 425 million years old and marking the youngest species of its group to have been classified. The carnivorous burrowing predator was retrieved from Leintwardine in Herefordshire and has been named Radnorscolex latus by scientists at the London Natural History Museum.
Radnorscolex is thought to have moved along the seafloor like an accordion, using a set of sharp teeth and hooks on its head to anchor itself as it shuffled along. Its feeding mechanism has been compared to that of Dune’s sandworms, consuming anything unlucky enough to be in its path.
“We believe anything that happened to be close by when they shoved their throat outwards into the sediment would have been grabbed,” said lead author Dr Richie Howard, Curator of Fossil Arthropods at the London NHM, in a statement emailed to IFLScience. “They weren’t too dissimilar to the sandworms in Dune in that respect!”

“We know this fossil was studied in 1920, but without the advanced technology we have today using state-of-the-art imaging techniques they weren’t able describe them as accurately and precisely as we can now.”
Image credit: Richie Howard & Luke Parry
The description is new to science, but the fossil has been kicking around for a while – retrieved sometime back in the 1920s from a disused Victorian quarry site in Herefordshire, UK. It was studied at the time of its discovery, but without the advanced technology available in scientists’ arsenal today, the researchers of the time weren’t able to get to the bottom of what they were looking at.
With the aid of advanced scanning technology, today’s team of scientists have been able to describe the worm and uncover clues about its position in the ecosystem. Turns out that Radnorscolex was remarkable even in its heyday.
“What we’ve found is quite rare in that we may be looking at today’s equivalent of a living fossil, but from the perspective of the Silurian,” explained Howard. “Like how we see coelacanths or horseshoe crabs today, groups which have been around for such a long time they exist as very ancient fossils but also show up as low-diversity groups relatively unchanged millions of years later in the present day.”
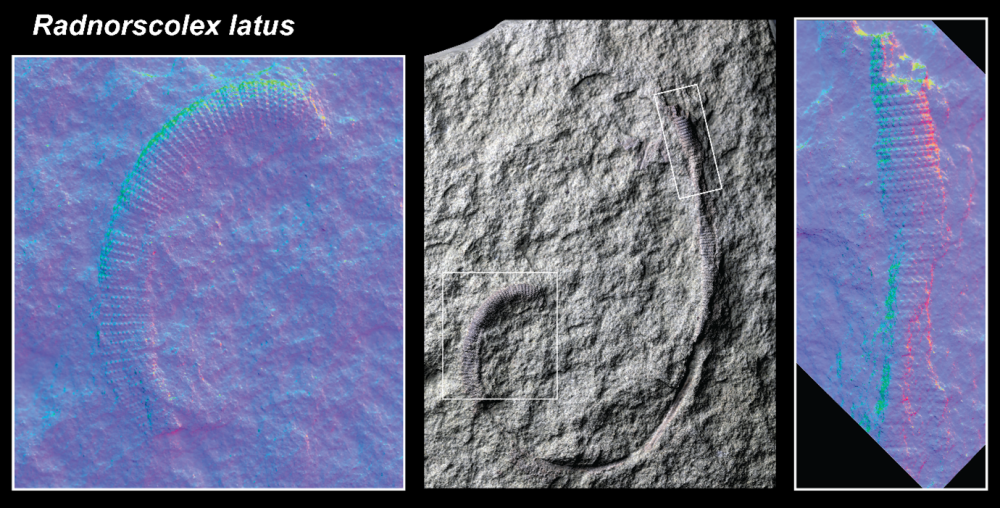
Closeups reveal the pattern of armor plates on the prehistoric worm Radnorscolex latus.
Image credit: Richie Howard & Luke Parry
“We know this fossil was studied in 1920, but without the advanced technology we have today using state-of-the-art imaging techniques they weren’t able describe them as accurately and precisely as we can now. We hope this study lays the groundwork for the research people will do in the future on Silurian palaeoscolecids.”
The study is published in the journal Papers in Palaeontology.
Source Link: A 425-Million-Year-Old Predatory Worm That Moved Like An Accordion? Why Not