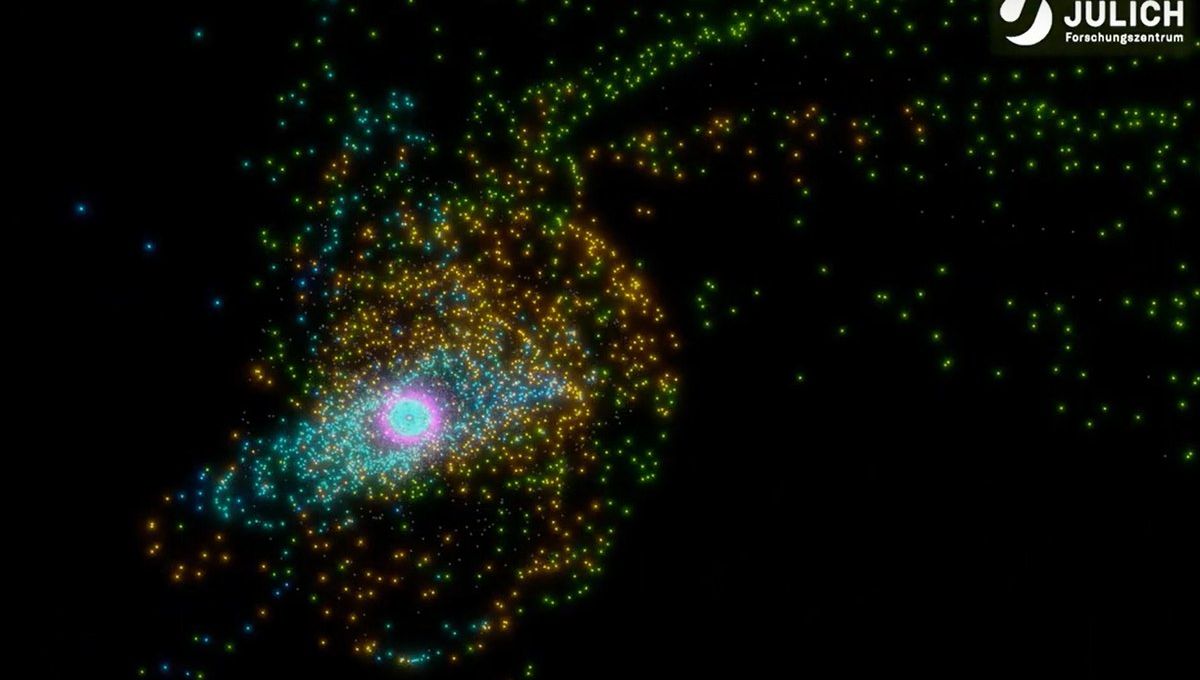
A new study suggests that the Sun may have had a close encounter with another star, explaining the unusual orbits of objects in the outer Solar System.
“When we think of our Solar System, we usually assume that it ends at the outermost known planet, Neptune. However, several thousand celestial bodies are known to move beyond the orbit of Neptune,“ Susanne Pfalzner, astrophysicist at Forschungszentrum Jülich, explained in a statement. “It is even suspected that there are tens of thousands of objects with a diameter of more than 100 kilometres [62 miles]. Surprisingly, many of these so-called trans-Neptunian objects move on eccentric orbits that are inclined relative to the common orbital plane of the planets in the Solar System.“
It is a bit of a mystery why these objects are inclined the way they are. The strange orbits of some of these Trans Neptunian Objects (TNOs) has led some teams to suggest they are being shepherded by an elusive ninth planet, that our understanding of gravity is incorrect at low accelerations, or that the larger planets in our Solar System shepherded them into these orbits as they migrated through the early Solar System. But the new team believes they have an explanation for these unusual orbits: a star passing by our own Sun several billion years ago in our history.
The team ran 3,000 simulations of scenarios where stars of various masses passed by our own at different distances. Though we have only discovered an estimated 1-10 percent of TNOs, making further observations and study of their orbits necessary for a full explanation, the team found that a close flyby of a slightly smaller star than our own could produce a Solar System that looks remarkably similar to how it looks today.
“The best match for today’s outer Solar System that we found with our simulations is a star that was slightly lighter than our Sun – about 0.8 solar masses,“ Amith Govind, co-author on the paper, explained. “This star flew past our sun at a distance of around 16.5 billion kilometres [10.3 billion miles]. That’s about 110 times the distance between the Earth and the Sun, a little less than four times the distance of the outermost planet Neptune.“
The simulation produced a number of TNOs in retrograde orbits. At first, this worried Pfalzner, as it suggested that the simulation may not have produced a Solar System that looks like our own.
“Only later did I learn that a few retrograde TNOs have indeed been discovered recently,” Pfalzner told Sky & Telescope.
Close encounters are more common in the very early days of star formation, when stars are still part of their “birth cluster”, sometime in the first 10 million years.
“Even in low-density clusters, ∼1% of solar-type stars experience such an encounter,” the team wrote in their study. “Putting this number in perspective, in the first 10 Myr of their lives, at least 140 million solar-type stars in the Milky Way (possibly ten times more) have experienced an encounter similar to the Sun’s.”
Later close encounters are possible, however, and the team estimates that there is a 20-30 percent chance that the Sun had such an encounter in the 4.5 billion years since the Solar System’s formation.
One problem is that there’s a good chance Neptune’s orbit would have been affected by such a close encounter, though the team found that in a quarter of scenarios the ice giant could have been “shielded” from the effects of the other star by essentially flying behind it.
It is an interesting idea, and hopefully one that can be tested further. When the Vera C. Rubin Observatory begins work in 2025 it will provide more information on TNOs as it discovers them, allowing the team to test their hypothesis further.
The study is published in Nature Astronomy.
Source Link: A Close Encounter May Explain The Strange Orbits Of Objects Beyond Neptune