One of the deadliest skin infections may have met its match as an exciting new family of compounds have shown unprecedented efficacy in clearing a fatal infection in mice. They target the gram-positive bacteria behind a flesh-eating disease known as necrotizing fasciitis that can be fatal in a matter of days.
Gram-positive bacteria are characterized by their cell wall, setting them apart from gram-negative bacteria. Which group a bacterium falls into matters when it comes to allocating an antibiotic to someone’s illness, as some drugs will be more effective on one type than the other.
Necrotizing fasciitis is a rare but life-threatening infection that can happen when bacteria get in through a break in the skin, be that a bite, burn, or scratch. It’s more commonly associated with gram-positive bacteria, with Streptococcus pyogenes being the most likely culprit.
Limb amputation is often required to control the spread of necrotizing fasciitis, and about 20 percent of people die. Getting on top of this fatal infection by tackling the culprit, which is responsible for many other potentially life-threatening diseases, could save hundreds of thousands of lives each year. This latest study focused on S. pyogenes necrotizing soft tissue infections in mice, to see how treatment with a novel family of compounds influenced the progression of disease.
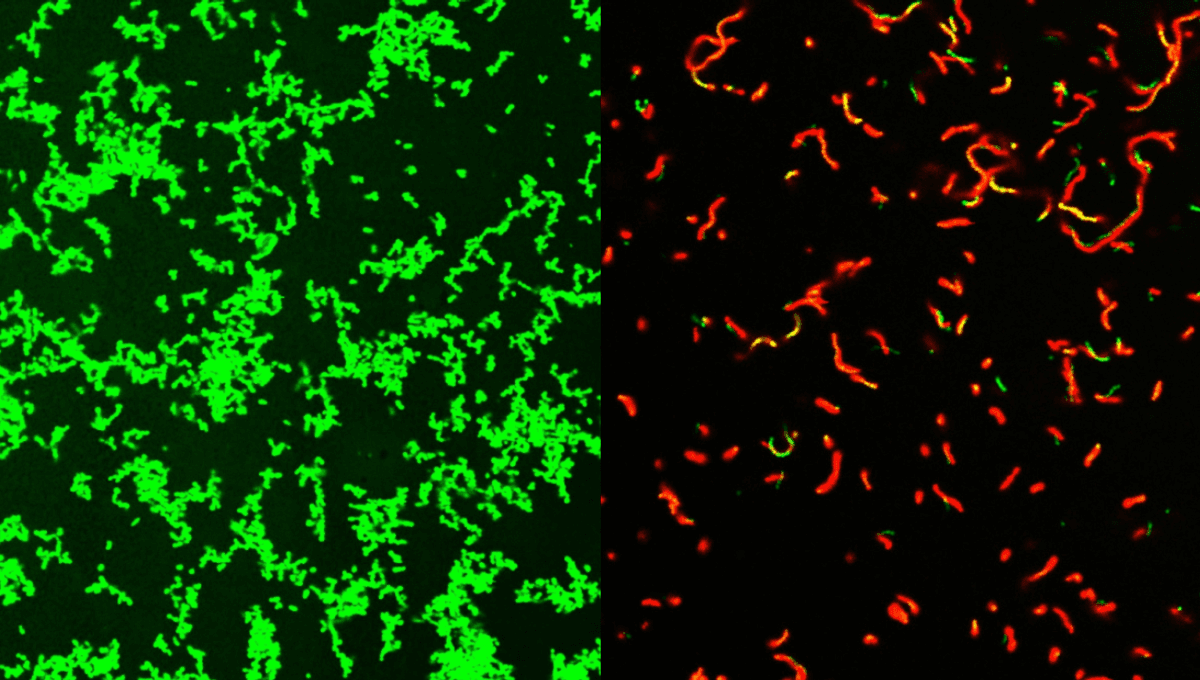
The compounds are called GmPcides (for gram-positive-icide) and had already proven their efficacy on bacteria in a Petri dish. The mouse model revealed that the compound was once again effective, both in reducing the virulence of the bacteria and even speeding up post-infection healing.
It’s not entirely clear how it’s able to do this just yet, but it’s thought that the GmPcide may affect the bacteria’s cell membranes.
“One of the jobs of a membrane is to exclude material from the outside,” said study co-author and professor of molecular microbiology Dr Michael Caparon in a statement. “We know that within five to ten minutes of treatment with GmPcide, the membranes start to become permeable and allow things that normally should be excluded to enter into the bacteria, which suggests that those membranes have been damaged.”
As well as letting in things the bacteria would sooner keep out, permeating the cell membrane can make it less able to harm the host, and less resistant to the human body’s immune response. And in case that’s not quite enough good news for you, it also proved to be effective across a range of bacteria.
“All of the gram-positive bacteria that we’ve tested have been susceptible to that compound. That includes enterococci, staphylococci, streptococci, C. difficile, which are the major pathogenic bacteria types. The compounds have broad-spectrum activity against numerous bacteria.”
So far the compound has been tested in mice, who are a common research subject because they are genetically so similar to us humans. So, while we can’t necessarily generalize findings from mouse studies to humans, it’s a very promising step in the fight against a deadly foe.
The study is published in Science Advances.
Source Link: A Deadly Skin Infection That Can Kill In Days May Have Met Its Match