Astronomers have confirmed the existence of a star with one of the shortest life expectancies imaginable, having formed dangerously close to the supermassive black hole known as Sagittarius A*. It accompanies the announcement of a mysterious object being destroyed by the same giant black hole, published in the same edition of The Astrophysical Journal.
If you want excitement, the center of the galaxy is definitely the place to be. It’s filled with bright, short-lived stars and their highly energetic remains, as well as things we can’t see clearly enough to determine. At the heart of it all is Sagittarius A*, with a mass 4.6 million times that of the Sun and feeding on anything that gets too close – including the suspected small gas cloud X7 described in the accompanying paper.
The area is also hot and rife with high-energy radiation and powerful gravitational and magnetic fields, all of which prevent star formation. Consequently, astronomers were very puzzled upon discovering clumps that appear to be protostars two light years from Sagittarius A*. It had been thought any stars that close would be old ones that drifted into dangerland.
There are lots of other objects in the area whose nature is hard to determine at this distance, including one known as X3, about 0.4 light years from Sagittarius A*. By combining 25 years of data from telescopes operating at different wavelengths, a team of astronomers has concluded that at the heart of X3 lies a star younger than the human species, which they call X3a.
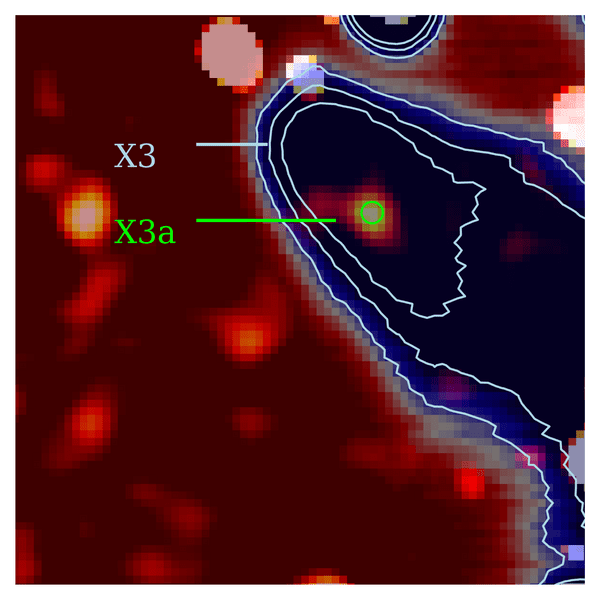
X3a in its envelope, X3 (blue). Intense stellar windscreate a cigar-like shape. On timescales of less than 10 years, clumps can form, which in turn are swallowed by X3a, explaining its impressive size. Image Credit: Florian Peißker
“It turns out that there is a region at a distance of a few light years from the black hole which fulfils the conditions for star formation. This region, a ring of gas and dust, is sufficiently cold and shielded against destructive radiation.” First author Dr Florian Peißker of the University of Cologne said in a statement.
Objects in this star formation ring would need to get themselves together quickly. Clouds of gas and dust with masses hundreds of times that of the Sun can form there, smaller versions of star-forming regions like the Orion Nebula in which most stars form. However, instead of having millions of years to coalesce into stars, collisions within the clouds cause them to lose angular momentum and sink toward the black hole in a few tens of thousands of years.
The authors think a cloud temporarily shielded from the local radiation must have become dense enough to collapse into a star while at the outer edge of the dust and gas ring.
In this scenario, X3a continued to develop as over tens of thousands of years as it fell towards Sagittarius A*, leading to the object we now see, which is well on the way to becoming a mature star. “The so-called fall time approximately corresponds to the age of X3A,” Peißker said, indicating the process got started almost as soon as it possibly could.
X3a has a mass approximately 15 times that of the Sun – no record-breaker, but certainly a tiny minority in a galaxy where most stars are red dwarfs less massive than our own. This not only proves that the hostile conditions in the area don’t prevent star formation, but also that they don’t stop growth to an unusual size. The authors propose it snapped up passing hot clumps of gas as it fell toward Sagittarius A*.
Smaller objects in the same region would be too faint for us to see. Since lower-mass stars evolve more slowly, they might also not reach mature star status before being swallowed.
Most galaxies contain their own supermassive black holes. The authors hope planned studies of the areas around nearby examples by the JWST and giant Earth-based telescopes will reveal whether X3a is a freak, or represents a class of young stars unfortunately born in very bad neighborhoods.
The paper is published in The Astrophysical Journal
Source Link: A Giant Baby Star Is Forming In The Galaxy’s Most Dangerous Location