We suspect that many icy moons in the Solar System host a liquid ocean buried deep within their crusts. Plans to get to those oceans with drilling robots have been put forward, but new research suggests something even simpler could provide information about the possibility of life in those oceans. All you need is a single ice grain.
The underground oceans of both Europa and Enceladus deliver the occasional release into space, where material from the ocean is frozen in a spray of ice crystals. Research in the lab has shown that life is present in these ocean worlds, and current technology can detect it in minimal quantities.
“For the first time we have shown that even a tiny fraction of cellular material could be identified by a mass spectrometer onboard a spacecraft,” lead author Dr Fabian Klenner, from the University of Washington, said in a statement. “Our results give us more confidence that using upcoming instruments, we will be able to detect lifeforms similar to those on Earth, which we increasingly believe could be present on ocean-bearing moons.”
The team picked a simple bacterium to simulate the possible life forms inside the ocean of Europa. They used Sphingopyxis alaskensis, a bacterium that is found in the waters of Alaska – so it can survive the cold well, and can cope with few nutrients.
The team envisions how bacteria might reach the surface of the buried ocean and bubble off where the cracks connect it to the surface. Those bubbles can carry biomaterial (like the ocean scum on sea spray) and those molecules are trapped in ice grains.
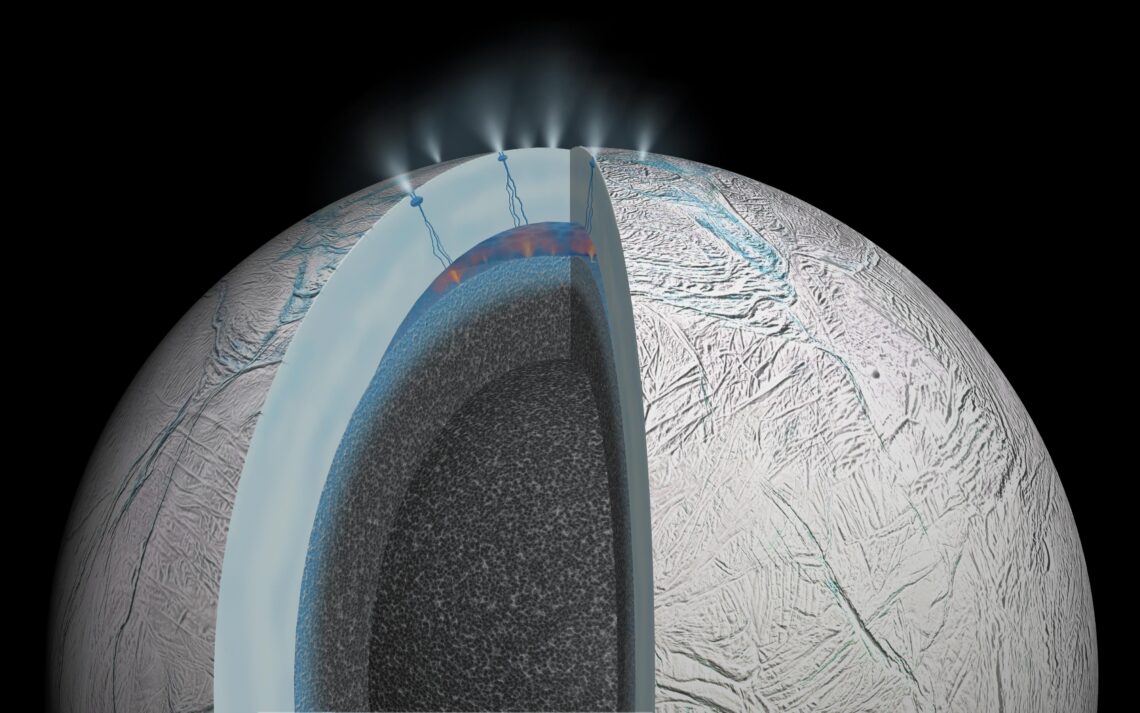
An artist’s rendition of Saturn’s moon Enceladus, depicting hydrothermal activity on the seafloor and cracks in the moon’s icy crust that allow material from the watery interior to be ejected into space.
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Instruments on NASA’s Europa Clipper, which launches in October, have the ability to detect such material, in particular lipids. These fat molecules could make up the membranes of these alien lifeforms and, as molecular structures go, they are a lot more stable than DNA.
“With suitable instrumentation, such as the SUrface Dust Analyzer on NASA’s Europa Clipper space probe, it might be easier than we thought to find life, or traces of it, on icy moons,” added senior author Frank Postberg, a professor of planetary sciences at the Freie Universität Berlin. “If life is present there, of course, and cares to be enclosed in ice grains originating from an environment such as a subsurface water reservoir.”
The study is published in Science Advances.
Source Link: A Single Ice Crystal Might Be Enough To Find Life On Europa Or Enceladus