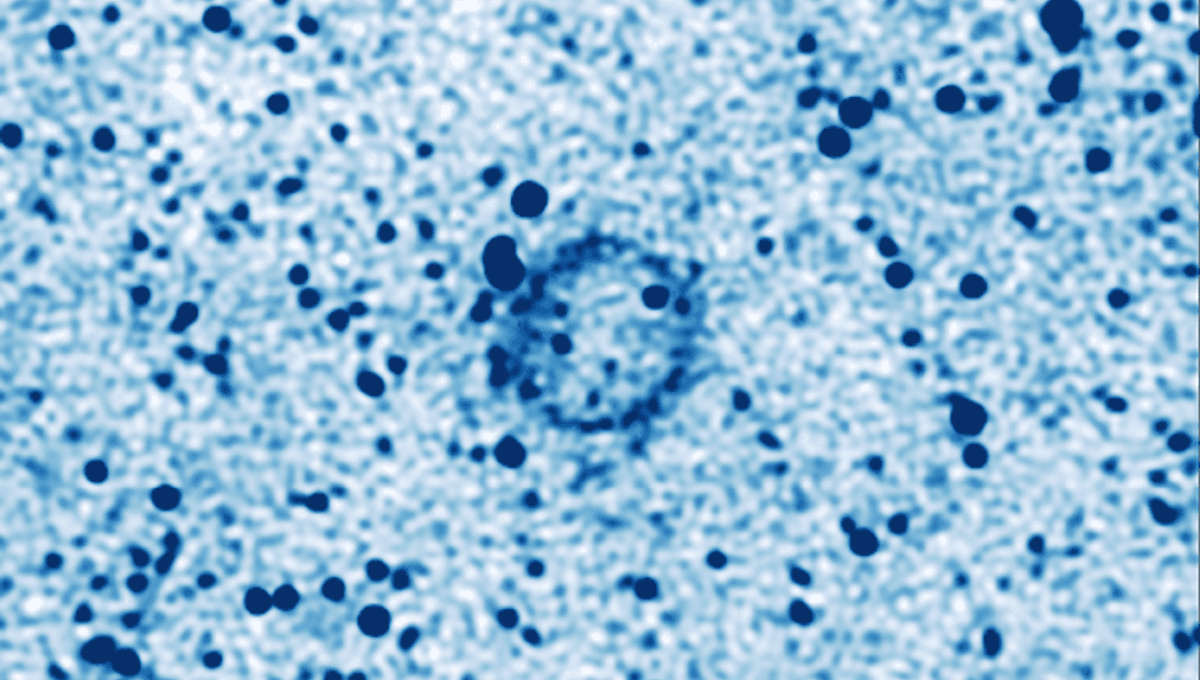
It will be sad when the universe can no longer surprise us, but today is not that day. South Africa’s MeerKAT radio telescope has detected a faint ring almost in the direction of the center of the galaxy – but what it is and where it came from are mysteries we get to explore.
In 2020, astronomers using the Australian Square Kilometer Array Pathfinder Telescope (ASKAP) found strange objects they named Odd Radio Circles (ORCs). They’d never been noticed before because they were too big – faintly taking up such large areas of the sky they didn’t stand out to telescopes with tiny fields of view.
At first sight, MeerKAT’s new discovery J1802–3353, which the finders have nicknamed Kýklos (circle in Greek), looks similar but fainter. As with ORCs, it’s unusually circular and apparently not visible at nonradio wavelengths. However, ORCs have only been found surrounding galaxies, and almost certainly lie hundreds of millions of light years beyond the Milky Way.
Kýklos, on the other hand, lies just 6 degrees from the plane of the Milky Way, and has no distant galaxy it appears to be associated with. Although enormous by human standards, it’s probably thousands of times smaller and closer than an ORC, and possibly quite close to our own galactic center. If we discover any more of them, maybe we should call the class goblins.
Even assuming we are right about where it is, however, doesn’t mean we know what Kýklos is. So far all we really know is that it shows up as a faint, almost circular ring a little over one minute of a degree wide, about the apparent size of a largish lunar crater. Being presumed to be millions of times further away, however, Kýklos is probably several light-years across, at least. There’s a bright blue star in a similar direction, but it could easily be much closer or more distant. Various other objects could be associated, but could also just happen to be in the same part of the sky, including some unexplained infrared sources.
Even MeerKAT, which can observe at a range of frequencies, only detects Kýklos in some.
Thin spherical shells show an effect known as limb-brightening, where their outer edges look more intense because we are seeing more of the material. Kýklos’s discoverers suspect that is why we see a ring, not a disk. Clumpiness could be the product of it expanding into space that is not evenly occupied.
After several years of bewilderment, some astronomers concluded ORCs are the product of numerous supernovae from starburst galaxies blasting gas into space almost in unison. It’s probably still too early to declare this question settled. As the paper reporting Kýklos states; “The origin of these structures remains elusive and continues to be a topic of debate.”
ORCs identity may not help explain Kýklos, anyway. We know what a single supernova remnant within our galaxy looks like – we’ve seen plenty of them. Not only are they usually easily seen by optical telescopes, but they’re mostly much smaller, unless very close to us by astronomical standards.
The paper describing Kýklos’ discovery includes a number of possible explanations, but most seem a poor fit with what we know. The most plausible answer the authors can offer is that Kýklos is the product of mass loss from a very large star, most likely the rare category known as Wolf-Rayets, suspected of many astronomical oddities.
HD 164455, the bright star mentioned previously, is probably too small and close. Three more distant stars are candidates, but at this stage we don’t know enough about any of them, or how far away Kýklos is, to be sure.
Perhaps the most remarkable aspect of all this is that MeerKAT, like ASKAPF, was intended mainly as a practice run for the Square Kilometer Arrays (SKAs) to be built in Australia and South Africa. Instead of just helping test the design and specifications for the giant telescopes before construction, the two have revealed classes of objects we never expected. It’s not hard to understand why astronomers are so excited about what the SKAs themselves will reveal.
Whatever Kýklos is, it’s not related to Earth’s new ring, caused by the recent bursts of solar storms, but it does feel like the universe is big on them these days.
The discovery is announced in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics.
[H/T Phys.org]
Source Link: A Strange Radio Ring Could Be From A New Class Of Astronomical Object