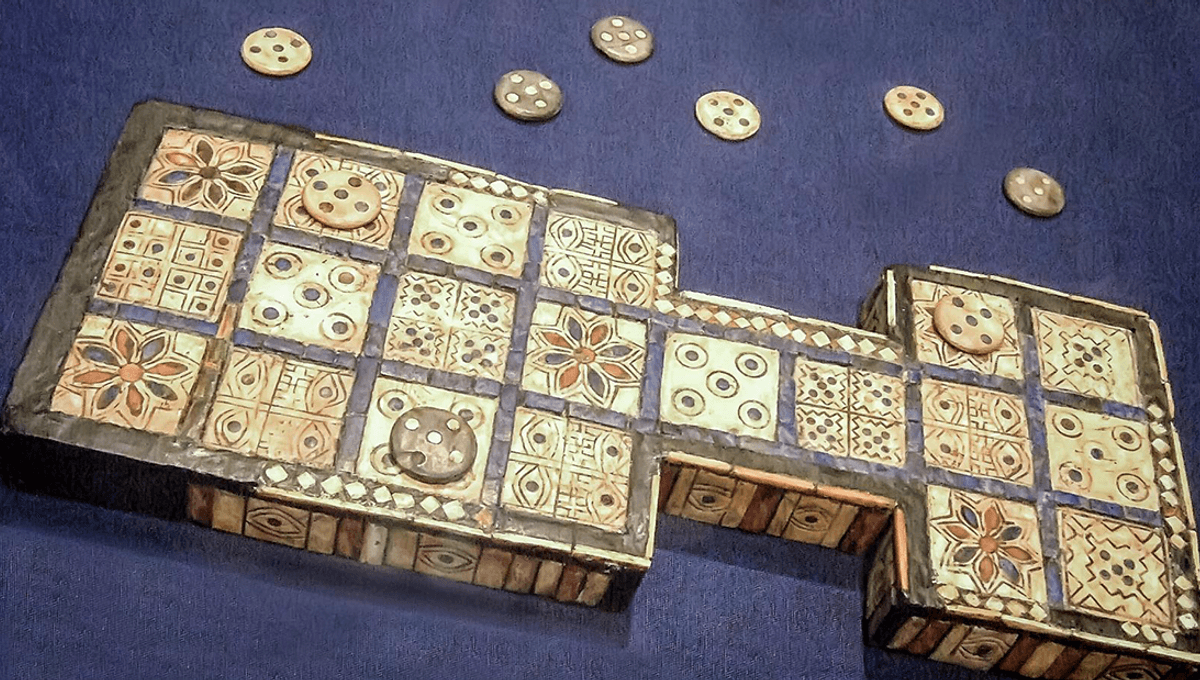
After thousands of years, we may finally know how to play an ancient board game, or at least a decent approximation of it.
In 1977, Italian and Iranian archaeologists were excavating a cemetery in Shahr-i Sokhta in the south-eastern region of Iran when they discovered an unusual item in grave number 731. Inside the pseudo-catacomb grave was an ancient board game, coming from around 2600–2400 BCE based on radiocarbon dating.
Somewhat unhelpfully, the board game was not buried with a copy of the rules, and so thousands of years later we have a (hopefully) complete board game with no idea how to play. But we do have a few clues, helping researchers to try and pin down some likely rules.
Other similar board games have been found, including the Royal Game of Ur, played in Mesopotamia at a similar time. For this game, the rules were written down on a cuneiform tablet. Deciphering the tablet allowed British Museum curator Irving Finkel to pin down a good understanding of the rules, making it playable once again thousands of years after it was invented. However, it is still open to interpretation what the rules exactly were, though it is assumed to be a racing strategy game played with dice.
The team investigating the Shahr-i Sokhta game attempted to propose rules for it based on what we know of other ancient board games, including the Royal Game of Ur, and the historical evidence. In doing so, they suggest that the board game was similar to the Royal Game of Ur, though slightly more strategic due to the variety of pieces and blockers.
“The blocker pieces cannot attack the opponent’s blockers, as the core of the gameplay is racing, and the rules must focus on the racing aspect. Moreover, the blocker pieces should be able to move more strategically,” the team writes in their study, giving a taste of the rules.
“A possible option in ancient rules is to move runner pieces and blocker pieces with the rolling of a die. However, the blocker pieces can move with special numbers, when rolled and players decide whether to move them.”
The game, which is available to play online, is described as a “really old version of backgammon”.
“The primary purpose of this game is to get all 10 pieces off the board before the other player does,” the team explains of the overall goal, with players able to eliminate their opponent by attacking them. “When the opponent attacks a piece, it must be returned to the board from the starting point.”
The game was put to the test on 50 experienced players, who were asked to evaluate the gameplay, and also compare it to the Royal Game of Ur. The result is a game that is playable thousands of years after its invention, even if we can’t be sure we’ve got the rules exactly right. But, if you’re really honest with yourself, you probably aren’t playing Monopoly by the rules set out by Hasbro, either.
The study is accepted for publication in the Journal of the British Institute of Persian Studies and is posted as a pre-print to SocArXiv.
Source Link: After Losing The Rules For 4,000 Years, We May Know How To Play This Ancient Board Game