Welcome to 2025! A lovely year, filled with excellent things. Obviously, we’re not talking about the state of the planet – that’s pretty terrible, all things considered. But the math? That is delectable.
The geometry of 2025
Let’s start with arguably the simplest fact about this new year: 2025 is a perfect square. It’s equal to 45 × 45, meaning that if we drew a big old square with side length 45 units, the total area would be 2025 units squared.
Go on, count them if you don’t believe us.
Image credit: ©IFLScience
That’s not all, though: because it’s an odd square, it’s also a centered octagonal number – which, much like with square numbers, is precisely what it sounds like: it means we can draw a perfect octagon using exactly 2025 pieces.
We can get even more complex: 2025 is an enneadecagonal number (for the few among you who aren’t professional shape-name-knowers, that is of course a 19-sided shape). Unfortunately for us, it’s a negative enneadecagonal number – the -15th – so it’s a bit impossible to draw.
We know it’s right, though, because all enneadecagonal numbers are given by the following formula:
Nm = m(17m – 15)/2
and plopping m = -15 into this recipe gives us 2025.
The names of 2025
Along with square, octagonal, and enneadecagonal, 2025 has a few pretty names. It’s a powerful number: an integer m such that if p|m, then p2|m. The reason for that is fairly simple – it’s 452, which is equal to (32)2×52 – or in other words, every prime factor of it turns up at least twice.
It’s also a refactorable number, or tau number, which means it’s divisible by the number of divisors it has. To take a simpler example, think of 18: it has six divisors – 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18 – and it’s divisible by six. Similarly, 2025 has 15 factors, and one of them is indeed 15 – the entire list, for the record, being 1, 3, 5, 9, 15, 25, 27, 45, 75, 81, 135, 225, 405, 675, and 2025.
The theorems of 2025
Let’s get onto the good stuff, shall we? We’ve already seen that 2025 is a perfect square, but dig a little deeper and we see some even prettier patterns. Forty-five, the number’s square root, is also a triangular number, and that means we can write it as a sum of consecutive numbers. Like this:
45 = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9.
That means that
2025 = (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9)2,
which is nice for sure, but that’s not all. Thanks to Nicomachus, an ancient Greek follower of Pythagoras who lived between around 60 CE and 120 CE, we know that numbers that can be written like this – the squares of triangular numbers – also have another interesting property: they can be rewritten as the sum of the cubes of those same numbers. In other words, because
2025 = (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9)2,
we also know that
2025 = 13 + 23 + 33 + 43 + 53 + 63 + 73 + 83 + 93.
Ain’t that cool?! There’s a few ways to prove this – one of the nicest is this proof without words:
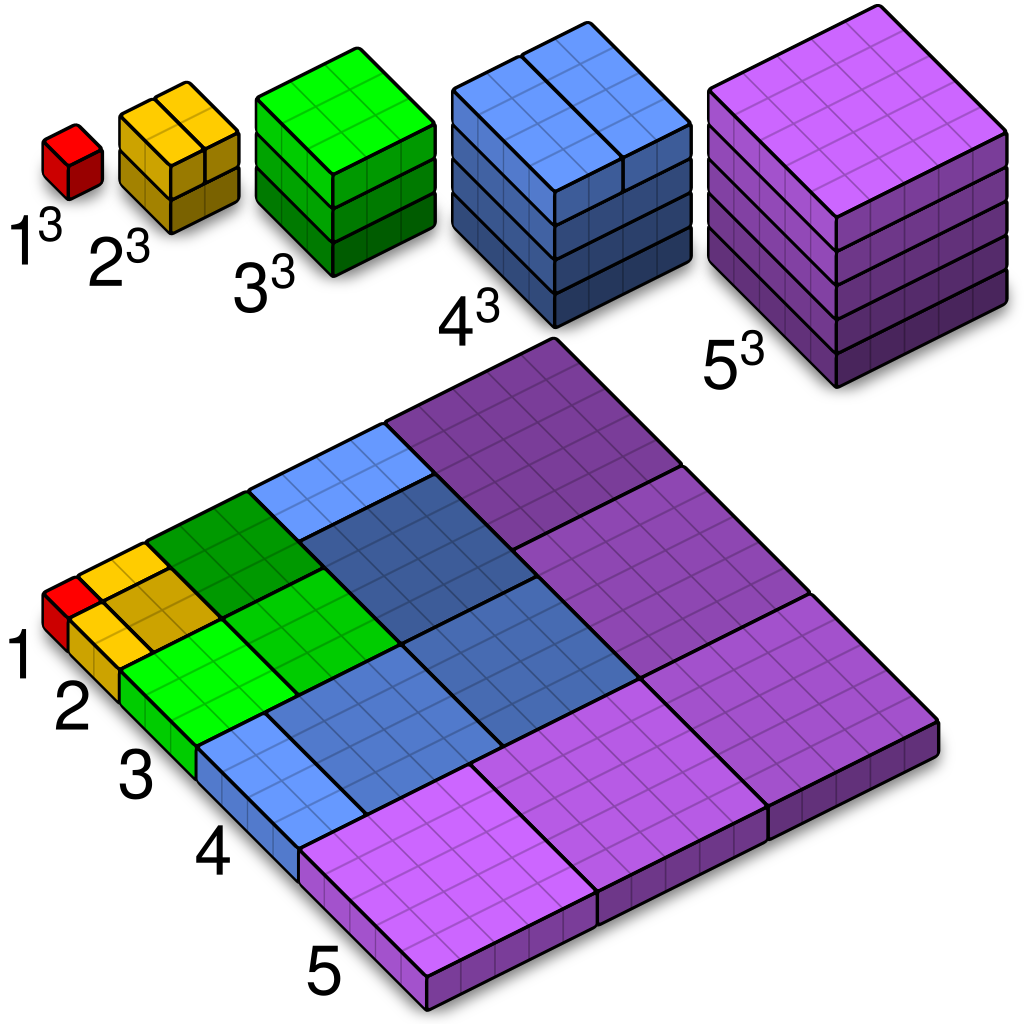
Neat, huh?
Another way is to use the properties of the square and cube numbers themselves – in fact, this is where old Nicomachus actually gets the credit, rather than noticing the theorem itself. His eponymous result is a step back, and technically says this:
∀n∈N>0 : n3 = (n2 − n+1) + (n2 − n+3) + … + (n2 + n−1).
That might look… well, like it’s written in another language, and it sort of is, but really it just means that any number n cubed can be written as the sum of n consecutive odd numbers beginning at (n2 − n+1). Like this:
1 = 1
8 = 3 + 5
27 = 7 + 9 + 11
64 = 13 + 15 + 17 + 19
125 = 21 + 23 + 25 + 27 + 29
and so on.
Now, written out like that, you can probably see a nice pattern already, right? If you sum up the first k cubed numbers, you’re going to get
13 + 23 + 33 + … + k3 = 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11 + … + (k2 − k+1) + (k2 − k+3) + … + (k2 + k−1).
But now let’s take a look at the square numbers. They have a similar sort of pattern going on as well – they can be written like this:
1 = 1
4 = 1 + 3
9 = 1 + 3 + 5
16 = 1 + 3 + 5 + 7
25 = 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9
and so on – that is, the square of n is equal to the sum of the first n odd numbers.
But guess what? That sum we found before is precisely that – it’s the sum of the first (k2 + k)/2 odd numbers! In other words,
1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11 + … + (k2 − k+1) + (k2 − k+3) + … + (k2 + k−1) = ((k2 + k)/2)2.
So there’s just one thing left to prove, and that’s that (k2 + k)/2 is equal to the sum of the first k natural numbers. Luckily, that’s pretty easy – it’s the definition of a triangular number (or, if you prefer, you can do it visually:
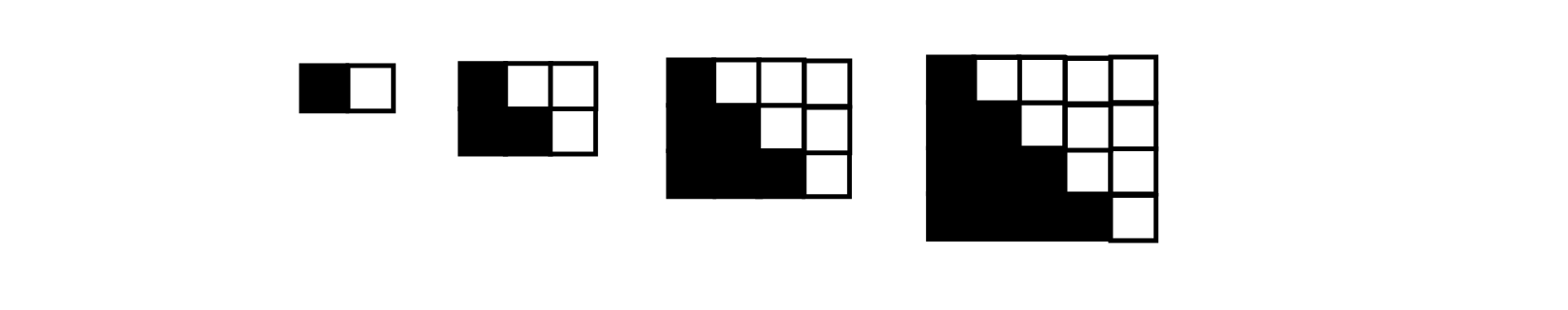
The triangular number – the shaded section – is half of the n x (n+1) rectangle.
Image credit: ©IFLScience
However you prove it, though, the math doesn’t lie: the sum of (n cubes) equals the (sum of n) squared. And now is as good a time as any to rave about this nice little result, since 2025 proves it perfectly. Happy New Year!
Source Link: All The Cool Math Of 2025 (Including Two Proofs Of One Ancient Greek Theorem)