Something strange is occurring in the skies over Antarctica. Each winter, a blisteringly cold ring of wind rapidly circulates clockwise in the stratosphere above Antarctica, forming a polar vortex around the icy continent. This year, however, the polar vortex isn’t acting like its usual self.
Models produced by NASA’s Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO) show the southern vortex above Antarctica has become unusually elongated, warm, and weak over this winter period.
The rotating mass of cold air typically has a circular shape that fits nicely around the continent, but this year it’s shaped like a stretched-out peanut and packs significantly less punch in terms of wind velocity.
It’s also surprisingly warm up there. Temperatures in the stratosphere above Antarctica in July are typically around -80°C (-112°F). However, the past July saw temperatures in the middle of the stratosphere soar to 15°C (27°F), setting a record. Temperatures then cooled briefly, before rocketing to 17°C (31°F) on August 5.
“The July event was the earliest stratospheric warming ever observed in GMAO’s entire 44-year record,” Lawrence Coy, an atmospheric scientist and modeling expert at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, said in a statement.
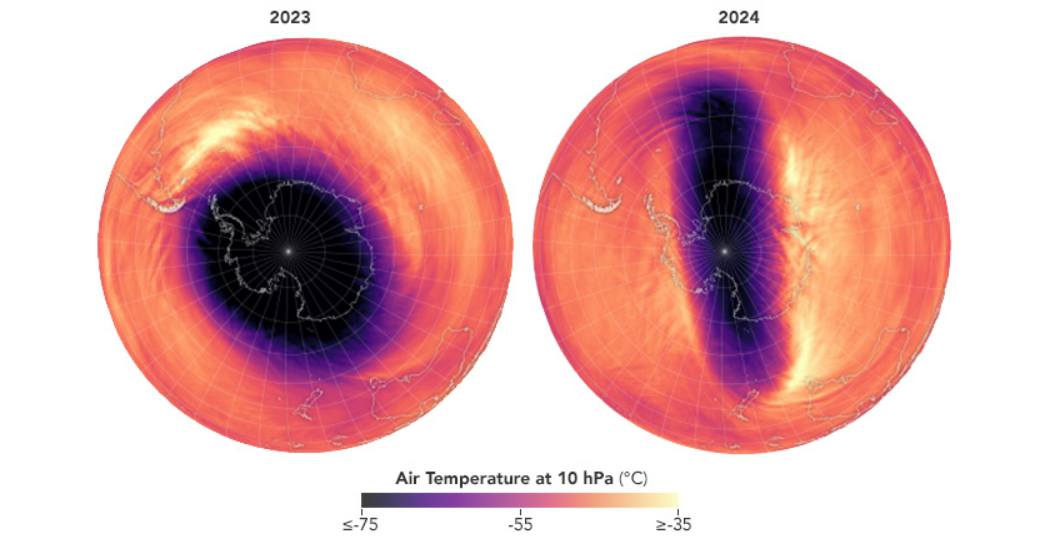
The southern polar vortex in August 2023 vs. August 2024.
Image credit: NASA Earth Observatory
The instability over Antarctica is so severe that scientists have raised concerns that the polar vortex could collapse or even change direction to anticlockwise. The last time this occurred was 2002 following a spate of unseasonably hot weather.
Likewise, the strange goings-on in the stratosphere have a relationship to a wider heatwave in Antarctica. In late July 2024, the southernmost continent experienced temperatures that were 10 to 12°C (18 to 21.6°F) above average for this time of year, compared to the 1991-2020 reference period. Brief spikes in heat aren’t unusual, but this heatwave was worryingly long and widespread.
While there appears to be a link between the unusual conditions at the surface and those in the stratosphere, the exact nature of the relationship is deeply complex and not fully understood.
“Variations in sea surface temperatures and sea ice can perturb these large-scale weather systems in the troposphere that propagate upwards. But the attribution of why these systems develop is really difficult to do,” explained Paul Newman, the Chief Scientist for Earth Sciences at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in the Earth Sciences Division.
You might also be aware that the ozone layer is a component of Earth’s stratosphere, acting as a shield that protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet light.
Interestingly, warming events draw ozone gas from other parts of the stratosphere toward the polar region, which means the ozone hole over the Southern Hemisphere is currently very small. In fact, the hole in the ozone layer has undergone a monumental “recovery” in recent years and is on track to be fully healed in a few decades.
Source Link: Antarctica's Polar Vortex Is Looking Worryingly Peanutty At The Moment