While many modern humans opt for a vegetarian or vegan diet, new research suggests that our ancestors obtained the majority of their nutrition from meat, and only diversified their food intake to include more plants at the very end of the Stone Age. Published in the American Journal of Physical Anthropology, the new study indicates that humans were apex predators for around 2 million years, with numerous species within the Homo lineage engaging in “hypercarnivory”.
Determining the trophic level – or position within the food web – of ancient humans is tricky, as we can’t directly observe the feeding behaviors of our early ancestors. Most attempts to do so have therefore focused on present-day hunter-gatherer groups, assuming that the practices of such cultures reflect those of primitive humans.
However, the authors of this latest study explain that such comparisons are highly problematic, as changes to the ecological landscape will inevitably have forced humans to alter their hunting and gathering preferences over time. For instance, the loss of megafauna like mammoths and other large animals produced a major shift in human diets.
The researchers therefore attempted to reconstruct the diet of ancient humans and determine the trophic level of our ancestors throughout the Pleistocene, which began 2.5 million years ago and ended around the time of the agricultural revolution, some 11,000 years ago. Taking a multidisciplinary approach, the team examined over 400 scientific studies covering areas such as genetics, metabolism, morphology, archaeology, and paleontology in order to determine whether early humans were specialized carnivores or more general omnivores.
Their investigation yielded 25 sources of evidence that strongly suggest that our predecessors were hypercarnivores. For instance, stomach acidity is a hallmark of carnivorous animals, as this ensures that any pathogens lurking in meat are killed. The fact that modern humans’ stomachs are more acidic than most carnivores’ points to the fact that our ancestors were well adapted to consume the meat of large animals they hunted, which would have fed a community for days or even weeks and would therefore have been full of bacteria.
This is backed up by the fact that several archaic hominids were morphologically adapted to hunt megafauna. Homo erectus, for instance, was equipped with shoulders that were ideal for throwing spears but unsuitable for tree climbing, suggesting that the species probably ate more meat than plants.
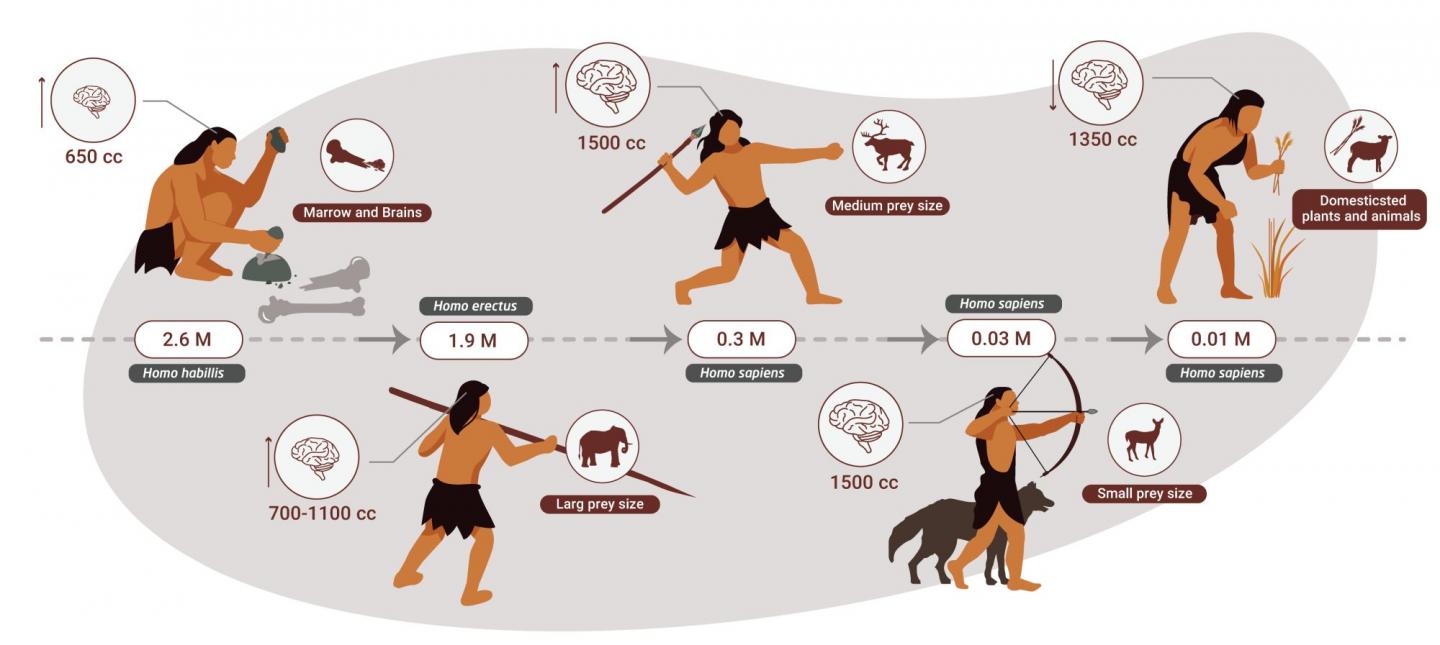
How the diet of ancient humans changed as our brains evolved. Image credit: Dr Miki Ben Dor
Furthermore, genes that facilitate the digestion of plant acids and starch did not become widely expressed within the human genome until late in the Pleistocene. According to the study authors, this indicates a lack of evolutionary pressure to switch to a plant-based diet while the hunting was good. Yet as animal sources become scarcer, humans that consumed more vegetation enjoyed higher survival rates.
According to the researchers, this late switch to a more omnivorous diet provided the spark for the advent of agriculture, leading to a change in the types of stone tools used by ancient humans. Looking through the archaeological records, they found that tools associated with processing plants only appear around 40,000 years ago and increase in frequency around the time of the agricultural revolution. Prior to this, most tools were designed for hunting, with the same types of artifacts found across all areas inhabited by humans.
“Archaeological evidence does not overlook the fact that stone-age humans also consumed plants,” explained study author Miki Ben-Dor in a statement. “But according to the findings of this study plants only became a major component of the human diet toward the end of the era.”
A version of this article first appeared in April 2021.
Source Link: As “Hypercarnivores", Humans Were Apex Predators For 2 Million Years