Above and below the plane of the Milky Way lie the Fermi Bubbles, two orbs around 25,000 light-years across filled with hot gas and cosmic rays. They are a major source of gamma rays, too. Within them, there is a bright spot, the Fermi Cocoon, a mysterious feature with no clear source – until now. Astronomers believe they have found the culprit, and it’s a galaxy that is slowly being destroyed by ours.
This small galaxy is known as the Sagittarius Dwarf, a spheroidal galaxy that over a billion years has been “unspooled” by the Milky Way. The motion of this small satellite around our galaxy has stripped it of most of its gas and many of its stars, an act of galactic cannibalism.
The dwarf galaxy can be viewed right through the Fermi bubbles from the point of view of the Solar System and matches the location of the Fermi Cocoon, but without new massive stars being born and then going supernova, the gamma-ray emission is not easily explained. Astronomers put forward two ideas: either the dwarf galaxy has a population of millisecond pulsars waiting to be discovered or they were seeing the long-sought annihilation of dark matter.
According to their paper published in Nature Astronomy, the pulsar scenario is the most plausible. Pulsars are a type of neutron star, the end product of certain massive (but not too massive) stars going supernova. They rotate and emit pulses of radiation across many wavelengths including gamma rays. Millisecond pulsars, as the name suggests, spin on their axis every few milliseconds.
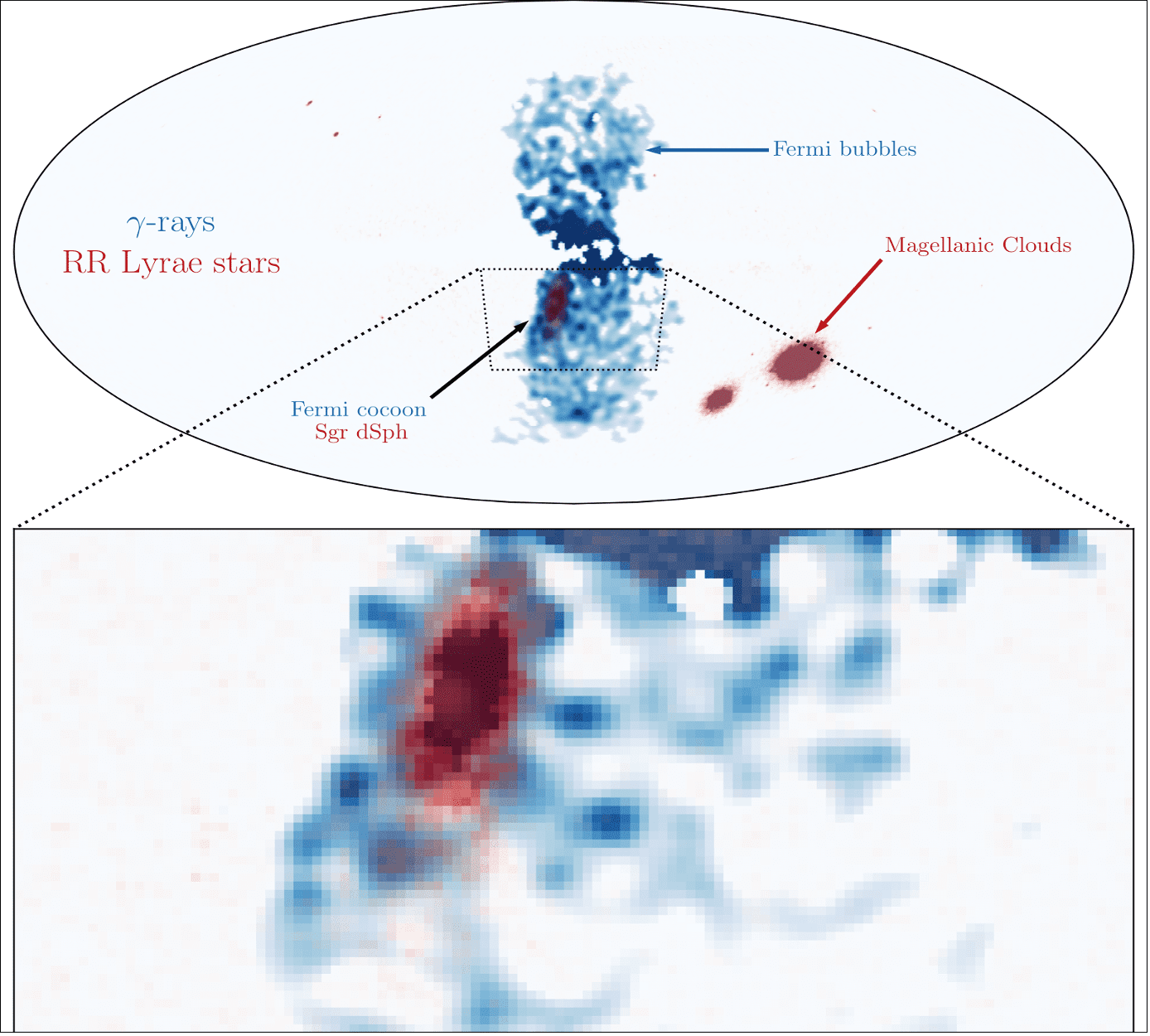
Much of the Gamma-rays from the Fermi cocoon may be coming from the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy. Image credit: Crocker, Macias, Mackey, Krumholz, Ando, Horiuchi et al. (2022)
The Fermi bubbles were actually discovered when researchers were looking for evidence that dark matter, the hypothetical substance that surrounds all galaxies, might possibly produce gamma rays. Dwarf galaxies were considered an excellent target for such searches, so this new work shifts assumptions about that.
“This is significant because dark matter researchers have long believed that an observation of gamma rays from a dwarf satellite would be a smoking gun signature for dark matter annihilation,” co-author Dr Oscar Macias, from the University of Amsterdam, said in a statement sent to IFLScience.
“Our study compels a reassessment of the high energy emission capabilities of quiescent stellar objects, such as dwarf spheroidal galaxies, and their role as prime targets for dark matter annihilation searches.”
The team believes that the production of high-energy particles around the pulsars helps accelerate the photons from the cosmic microwave background to gamma-ray energies, creating the region we see as the Fermi Cocoon.
Source Link: Astronomers May Have Found The Source Of The Milky Way’s “Fermi Cocoon”