Relics of the distant past, as well as recent tragedies, dwell within the cerulean depths of the Great Blue Hole in Belize.
The Great Blue Hole is a large marine sinkhole in the Caribbean Sea, some 70 kilometers (43 miles) from the coast of Belize. With a diameter of 318 meters (1,043 feet) and a depth of 124 meters (407 feet), it’s one of the largest marine sinkholes.
Blue holes like this are relics from the Quaternary Glaciation when sea levels were over 100 meters (330 feet) lower than the present day – it started life as a limestone cave but became flooded as the seawater rose. Eventually, the ceilings collapsed under the weight of the water to reveal a pit within the seabed.
The Great Blue Hole is part of the Belize Barrier Reef Reserve System, a UNESCO World Heritage Site described by Charles Darwin “as the most remarkable reef in the West Indies.” Home to a wealth of unique coral species – not to mention other animals like the West Indian manatee, green turtle, hawksbill turtle, loggerhead turtle, and the American crocodile – the area has become magnetic for tourists, scuba divers, and snorkeling explorers.
Descending into the sinkhole, it’s possible to see the remains of stalactites, geological features from when this was a cave exposed to the open air. However, it’s said that there’s not much to see inside the Great Blue Hole in terms of wildlife – at least that’s alive.
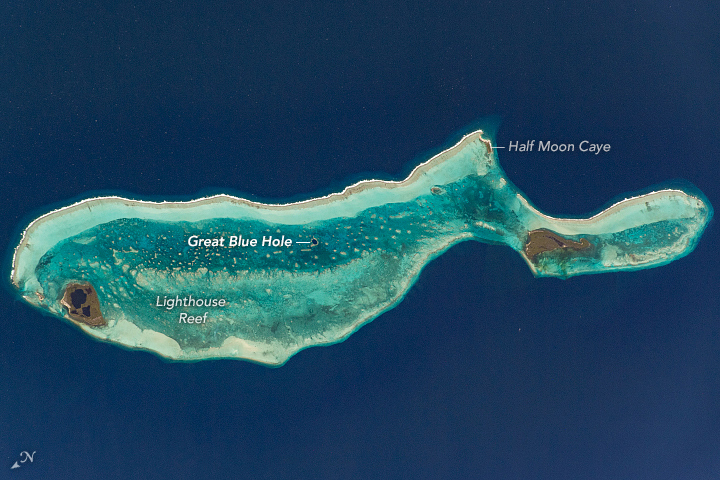
A photograph of Belize Barrier Reef Reserve System, featuring the Great Blue Hole, seen from the International Space Station March 5, 2020.
Image credit: ISS/NASA Earth Observatory
The bottom of the blue hole is devoid of oxygen. Dissolved oxygen levels drop to zero below the layer of hydrogen sulfide that lies around 90 meters (295 feet) deep in the hole, effectively creating an invisible barrier in the hole. As a result of these uninhabitable conditions, the seafloor is littered with a “graveyard” of dead sea creatures that likely went too deep and asphyxiated.
One of the most publicized expeditions of the Great Blue Hole was carried out in 2018 by British billionaire Richard Branson, oceanographic explorer Fabien Cousteau, and National Geographic Explorer Erika Bergman.
Writing on his blog about the trip, Branson commented how the geology of the blue hole served as a vivid reminder of the potential devastation that climate change and rising sea levels could bring to the world.
“At 300 feet [91 meters] down you could see the change in the rock where it used to be land and turned into sea. It was one of the starkest reminders of the danger of climate change I’ve ever seen,” Branson wrote.
He also noted that the team saw some evidence of another scourge of the modern world: plastic pollution.
“Sadly, we saw plastic bottles at the bottom of the hole, which is a real scourge of the ocean,” he added.
It’s not known how many people have lost their lives in Great Blue Hole, but Bergman has previously suggested that three people are known to have gone missing while exploring it. Tragically, she believes they saw two of these bodies during the 2018 expedition with Branson. The skeletons remain there to this day.
“We did encounter two of the probable three people who have been lost in the Blue Hole, so we found kind of the resting place of a couple folks, and we just sort of very respectfully let the Belize government know where we found them, and everyone decided that we would just not attempt any recovery. It’s very dark and peaceful down there, just kind of let them stay,” Bergman told Business Insider in a 2020 interview.
Source Link: At The Bottom Of The Great Blue Hole, Divers Find Wonderful And Worrying Sights