One of the slowest art heists in history is currently going down in the Negev desert, where a host of hardy fungi and lichens are destroying ancient artworks before our very eyes. The petroglyphs carved by ancient humans have endured for 5,000 years, but they’re now at risk of being lost forever.
The desert is in the south of Israel where rocks can be found marked with petroglyphs of ibexes, goats, horses, donkeys, camels, and the odd abstract form. If this is the first you’re hearing of petroglyphs, they’re defined as prehistoric rock carvings – in this case, created by hunters, shepherds, and merchants who roamed the Negev since at least the third millennium BCE.
The petroglyphs have lasted for thousands of years, but a new study has revealed that the few species that live on these rocks may represent a monumental problem. Sampling of the rock surfaces showed they host a comparatively low species diversity compared to the surrounding soil, but the species that are present are known to be destructive.
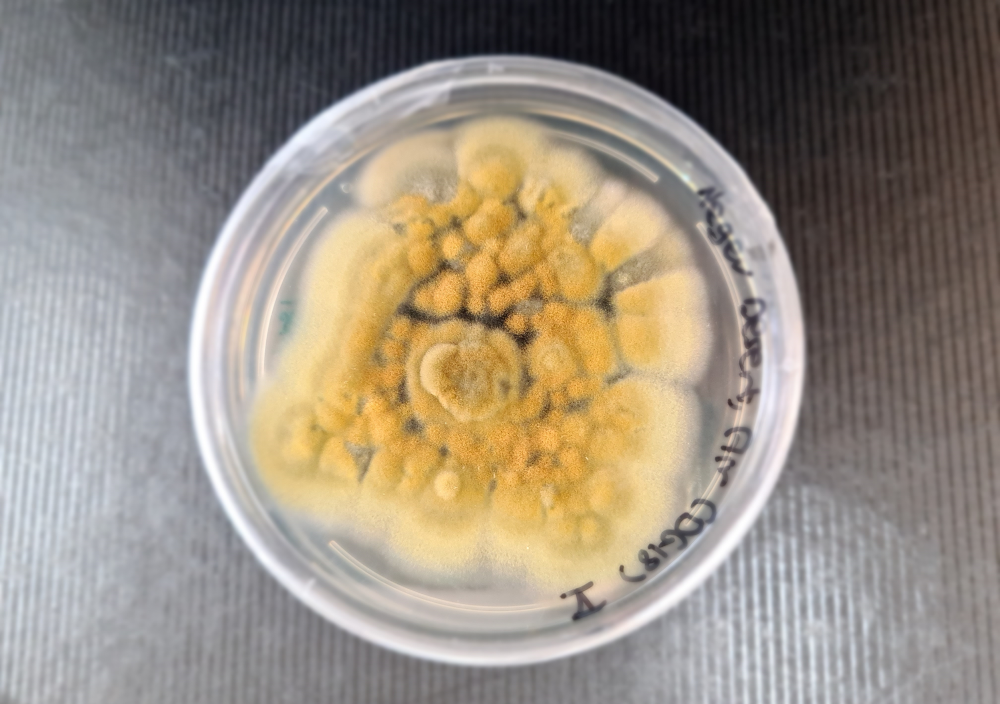
A fungus culture of one of the species threatening the petroglyphs: Cladosporium limoniforme.
Image credit: Dr Irit Nir, Ben Gurion University of the Negev
On the roster of culprits are multiple species of fungi within the Alternaria, Cladosporium, Coniosporium, Vermiconidia, Knufia, Phaeotheca, and Devriesia genera, as revealed by DNA barcoding and direct sequencing. Of those, all of them are microcolonial fungi other than Alternaria and Cladosporium, a group that is famous for setting up camp in desert environments. They’re also known wrong’uns when it comes to rock art.
“Microcolonial fungi are considered highly dangerous for stone artifacts,” said first author Laura Rabbachin, a PhD student at the Academy of Fine Arts Vienna in Austria, in a statement. “For example, they have been implicated as a probable cause of the deterioration of stone cultural heritage in the Mediterranean. Lichens are also well known to cause rocks to deteriorate and thus to be a potential threat to stone cultural heritage.”
We may have been able to point the finger at the offending microbial saboteurs, but unfortunately, identifying the issue hasn’t brought us any closer to a solution.
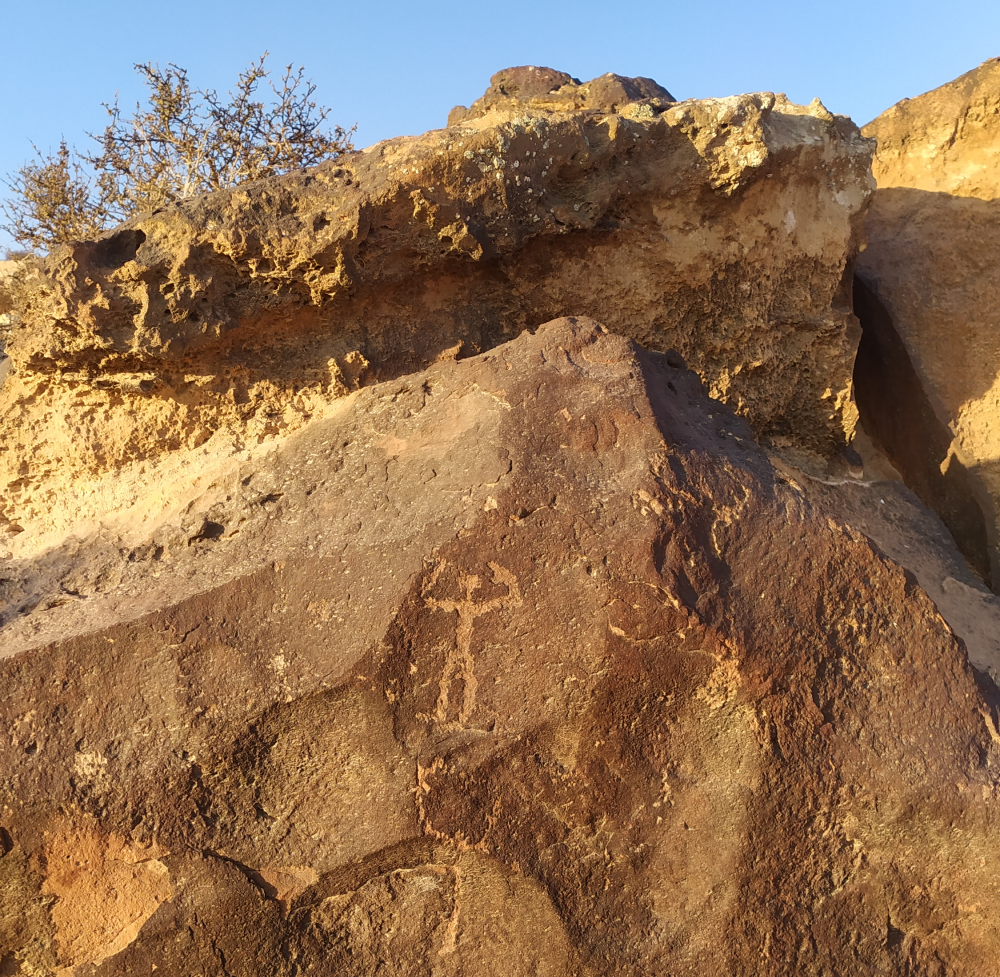

One of the Negev desert petroglyphs showing a human figure.
Image credit: Laura Rabbachin, INTK, Academy of Fine Arts, Vienna
“These natural weathering processes cannot be stopped, but their speed of the weathering process depends heavily on whether and how the climate will change in the future,” added study senior author and Rabbachin’s academic supervisor, Prof Katja Sterflinger. “What we can do is to monitor the microbial communities over time and most importantly, document these valuable works of art in detail.”
Sketchbooks at the ready, I guess.
The study is published in Frontiers In Fungal Biology.
Source Link: Attack Of The Lichens: 5,000-Year-Old Rock Art Is Under Deadly Threat