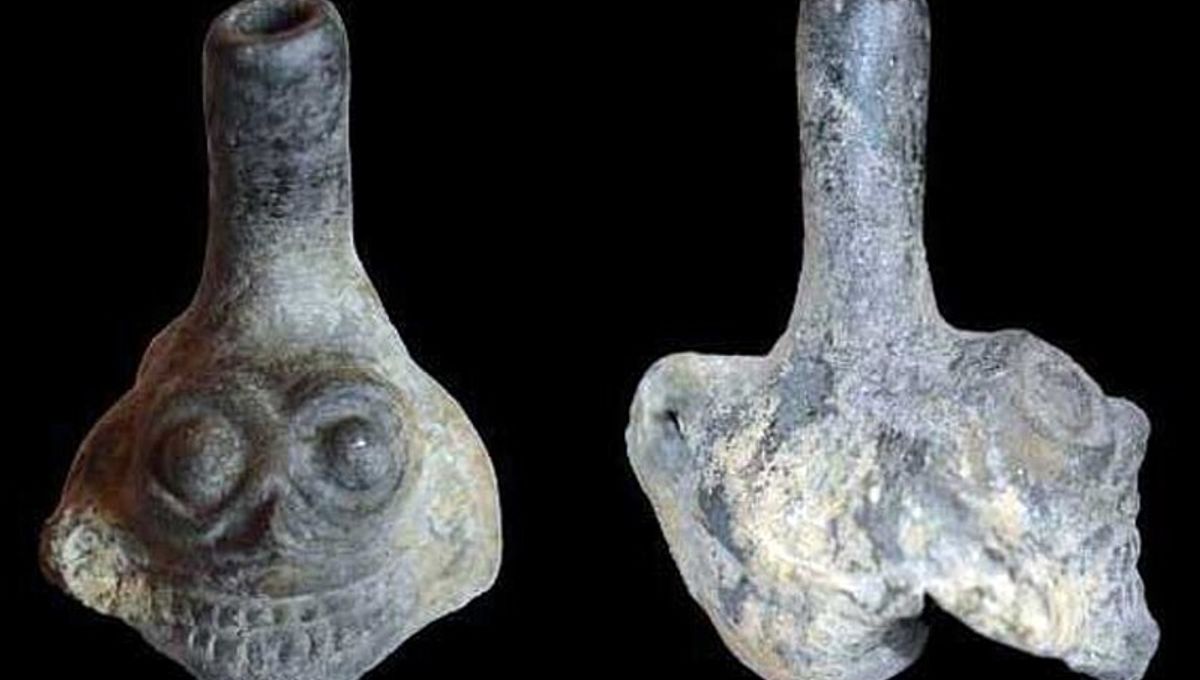
With a love of human sacrifice, warfare, and towers made out of human skulls, the ancient Aztecs certainly knew how to have fun. Just to add to the excitement, the pre-Columbian empire-builders may have conducted some of their favorite activities to the sound of skull-shaped whistles, which produced a horrifying “death scream” that sent chills down the spines of all who heard it.
For the first time, researchers have now analyzed the effect of these ghastly pipes on modern listeners’ brains, finding that the sound puts the auditory cortex on high alert.
“Human listeners in our experiments rated skull whistle sounds as very negative and specifically labeled them largely as scary and aversive, which potentially also trigger urgent response tendencies and interfere with ongoing mental processes,” write the study authors. Using a series of neuroimaging techniques, the researchers found that this subjective experience was linked to “very specific brain activity” within low-order auditory cortical regions that respond to scary noises.
Numerous examples of Aztec skull whistles have been found in graves dated between 1250 and 1521 CE. Made of clay, these small instruments are typically crafted into the form of a human skull and are designed to allow for the collision of numerous airstreams, resulting in a “shrill, piercing, and scream-like sound quality.”
Sometimes called “death whistles”, the ancient shriekers are speculated to have been used in warfare to terrify opponents on the battlefield. The fact that they are regularly found alongside the skeletons of sacrifice victims, meanwhile, has fuelled suggestions that the whistles might have had more of a ceremonial function.
For instance, some experts believe the death whistles were intended to mimic the razor-sharp winds of Mictlan, the Aztec underworld to which sacrificial tributes were believed to descend. Others think the sound was meant to represent Ehecatl, the Aztec God of the Wind, who created humanity from the bones of the dead.
To gain a deeper insight into how the whistles might have been used, the study authors conducted a series of psychoacoustic experiments using modern-day European volunteers. Recording participants’ neural and psychological responses to hearing the death scream, the researchers found that the brain struggles to classify the sound, which was perceived as as “having a hybrid natural-artificial origin.”
“Skull whistle sounds attract mental attention by affectively mimicking other aversive and startling sounds produced by nature and technology,” write the authors. “We furthermore found that skull whistle sounds received a specific decoding of the affective significance in the neural auditory system of human listeners, accompanied by higher-order auditory cognition and symbolic evaluations in fronto-insular-parietal brain systems,” they write.
In other words, the terrifying ambiguity of the death whistle apparently ignites the imagination as the brain struggles to pinpoint the symbolic meaning of the sound. The researchers therefore conclude that the whistles’ “usage in ritual contexts seems very likely, especially in sacrificial rites and ceremonies related to the dead.”
For instance, they speculate that “skull whistles might have been used to scare the human sacrifice or the ceremonial audience.”
The study is published in the journal Communications Psychology.
Source Link: Aztec Death Whistles Have A Terrifying Effect On Listeners’ Brains