Around the deep sea vents of Earth’s deepest waters, it’s possible to find colonies of bacteria that are neatly pointed toward the invisible magnetic field lines of Earth, just like a compass needle. These strange life forms are known as magnetotactic bacteria, living microorganisms capable of “sensing” magnetic fields. While their kind have been found on land and in shallow water, they are rarely discovered in ocean water as deep as this.
The “living-magnets” were collected from a sample scooped up in 2012 during an expedition by the University of Tokyo in the southern Mariana Trough of the western Pacific Ocean. In a study published earlier this year, the team genetically analyzed these samples and managed to identify the mysterious magnetotactic bacteria.
This particular sample was gathered from the rim of a chimney from a hydrothermal vent field, some 2,787 meters (9,143 feet) below the water’s surface. Conditions can get pretty extreme around these sites. They are essentially cracks in the seafloor where superheated water from Earth’s depths rises up along with rich deposits of minerals and metals.
“We discovered magnetotactic bacteria living on the chimney, which we didn’t expect. Due to the chimney’s shape, it lacks a clear, vertical chemical gradient which these bacteria typically prefer,” Yohey Suzuki, study author and Associate Professor from the Graduate School of Science at the University of Tokyo, said in a statement.
“The bacteria we collected contained mainly ‘bullet’-shaped magnetosomes, which we see as a ‘primitive’ form and so inferred that they have not changed much over many millennia. Indeed, the environment we found them in is similar to early Earth about 3.5 billion years ago, when the ancestor of magnetotactic bacteria is estimated to have emerged,” Suzuki added.
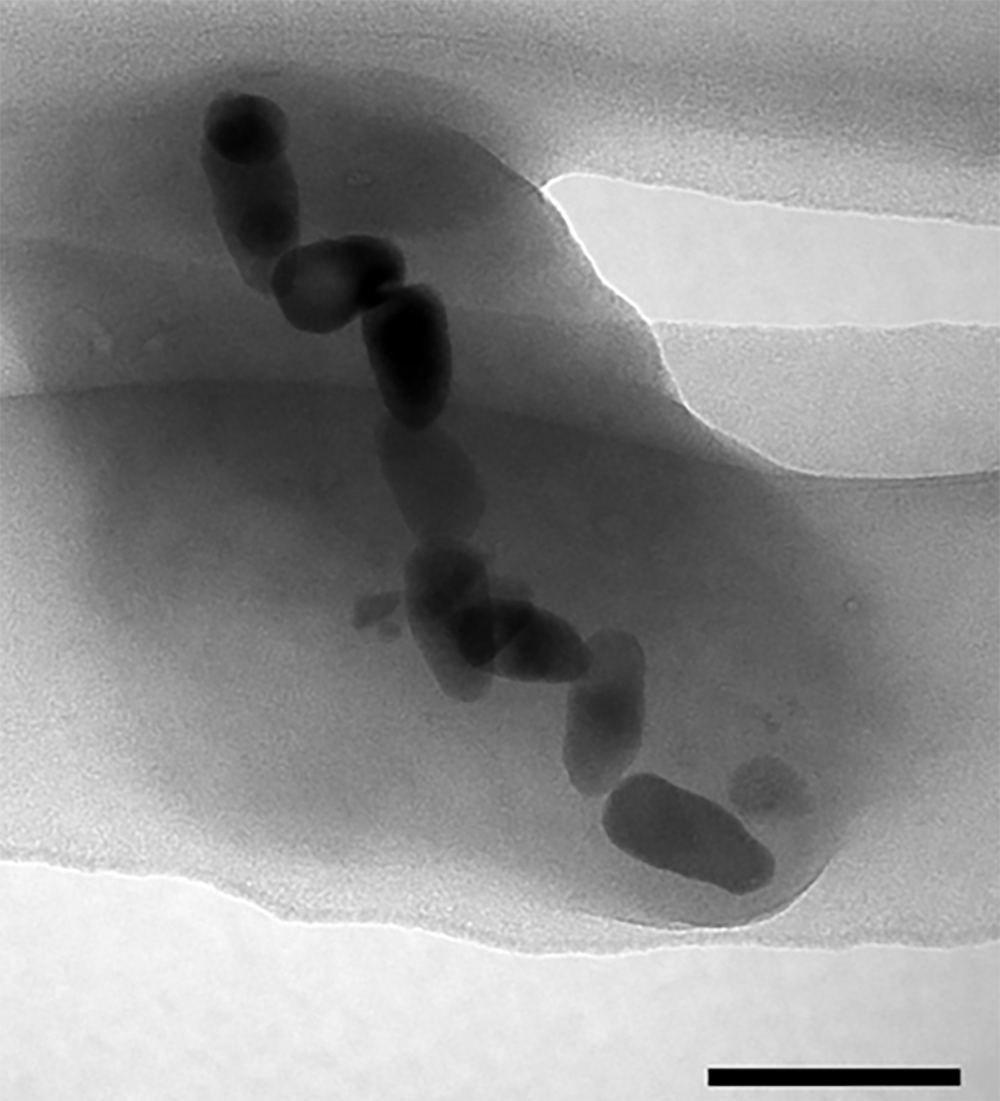
Microscopic image of the magnetosomes in magnetotactic bacteria.
Image credit: © 2017, Toshitsugu Yamazaki
Magnetotactic bacteria were first described by microbiologist Richard Blakemore in 1975, although it turned out another scientist, Salvatore Bellini, had already discovered them in the previous decade to little fanfare.
Their magnetic superpowers are thanks to organelles called magnetosomes that contain iron crystals wrapped in a membrane.
Plenty of living things have a sensitivity to magnetic fields, including turtles and birds, which helps them navigate the world. The magnetotactic bacteria are no different, although their migrations tend to be much simpler. The leading theory is that they evolved this ability to help them navigate in areas of low oxygen concentration. Their flagella arm-like appendages can help them swim fairly well, but the magnetic pull gives them a much-needed nudge in harsh environments.
There’s even some fascinating speculation that magnetotactic bacteria might underlie the magnetic sensing capabilities of animals, although that’s yet to be proven.
Like any unusual bacteria living in an extreme environment, the researchers on this project believe that their magnetotactic bacteria could help our understanding of extraterrestrial life. Since the hydrothermal vents of the deep ocean have similarities to otherworldly environments, perhaps the magnetotactic bacteria could teach us about possible candidates for life elsewhere in the Solar System beyond our own Earth.
“Deep-sea hydrothermal vents attract attention not only as the birthplace of unique underwater life, but also as a potential analogous habitat for extraterrestrial life. The environment where we sampled the bacteria is similar to what we think Mars was like when there was still flowing water on its surface, about 3 billion years ago,” explained Suzuki.
“Magnetotactic bacteria provide clues for the early diversification of bacteria and we hope they will be found beyond Earth, maybe on Mars or icy moons. For now, we will continue to look for more evidence of them in various types and ages of rocks on Earth where they were not previously thought to inhabit,” he added.
The study is published in Frontiers in Microbiology.
Source Link: Bacteria Living In The Deep Sea Can "Sense" Earth's Magnetic Fields