An ancient oceanic plate under modern-day Iraq is breaking off horizontally, researchers have shown in a new study. This huge underground tear, stretching from southeast Turkey to northwest Iran, is affecting the way Earth’s surface bends and shifts, reshaping the landscape as it changes.
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
For millions of years, as the Arabian and Eurasian continental plates have drifted toward each other, the underground ancient seabed that lay between them – called the Neotethys oceanic plate – has been forced deeper into the Earth. When the plates finally collided, their edges crumpled and rose, forming the Zagros Mountains.
But the story doesn’t quite end there – the team of researchers behind the new study has examined how the Zagros Mountains in Iraq’s Kurdistan region have continued to morph over the past 20 million years.
The weight of the Zagros Mountains causes the Earth’s surface to bend, forming depressions that fill with sediment, one example of which is Mesopotamia. However, the researchers found that the 3 to 4-kilometer (1.8 to 2.4-mile) depression filled with sediment in the southeastern area is deeper than expected.
This suggests the sinking oceanic plate beneath the region is also helping to pull down the Earth’s surface, along with the mass of the hefty mountains.
“Given the moderate topography in the northwestern Zagros area, it was surprising to find out that so much sediment has accumulated in the part of the area we studied. This means the depression of the land is greater than could be caused by the load of the Zagros Mountains,” Dr Renas Koshnaw, lead author and Postdoctoral Researcher at Göttingen University’s Department of Structural Geology and Geothermics, said in a statement.
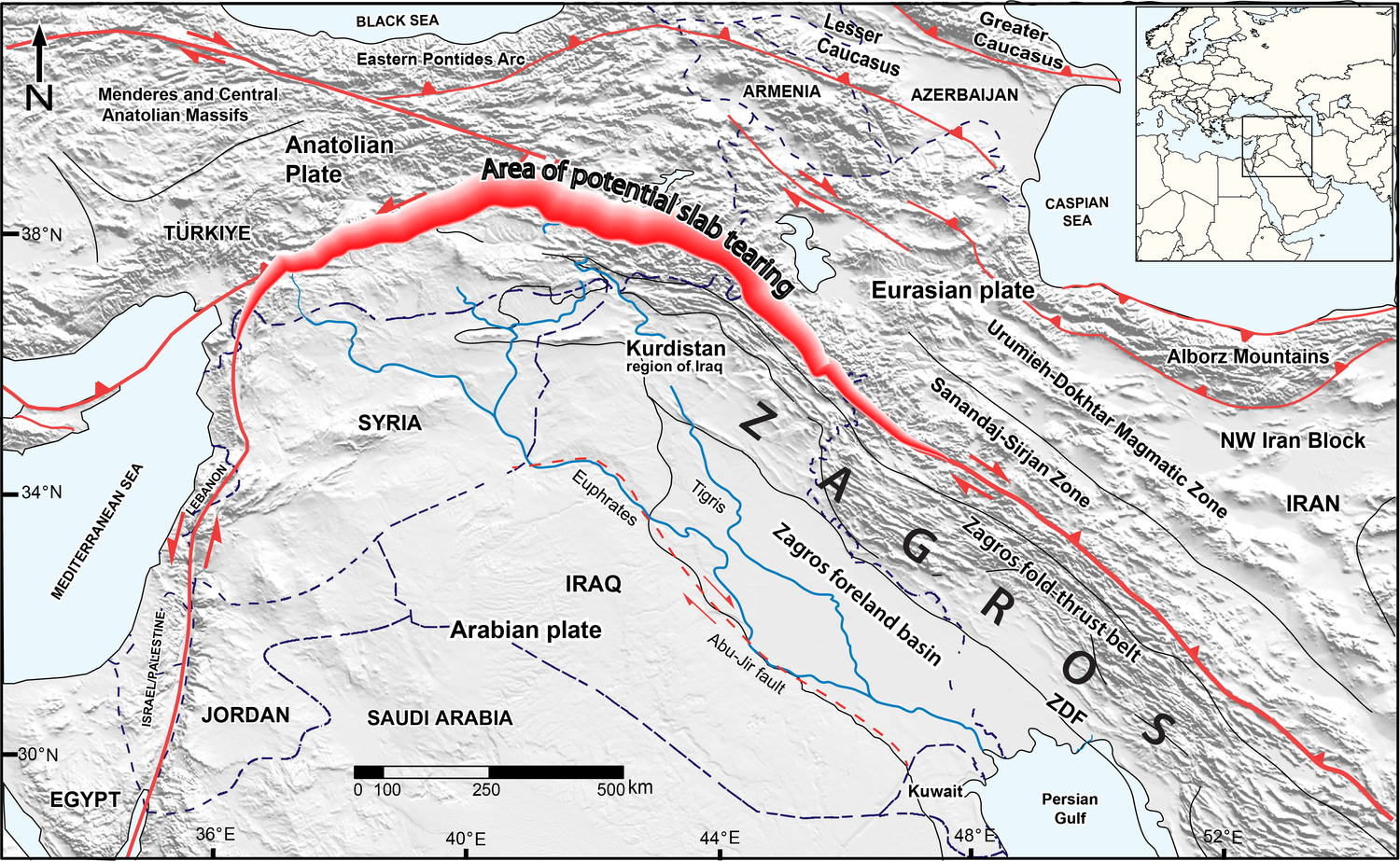
Map of the northern Middle East showing the Arabian and Eurasian plates and their collision zone, as well as the study area, the Kurdistan region of Iraq.
“This plate is pulling the region downward from below, making space for more sediment accumulation. Towards Turkey, the sediment-filled depression becomes much shallower, suggesting that the slab has broken off in this area, relieving the downward pull force,” explained Koshnaw.
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
It’s likely that the Neotethys oceanic plate is effectively sinking into Earth’s mantle, the thick layer of rock that sits between the crust and core. By looking at how the inner workings of the planet are impacting the Zagros Mountain region, scientists hope to understand how deep-Earth processes shape geological features on the surface.
“This research contributes to understanding how the Earth’s rigid outer shell functions,” added Koshnaw.
It takes a hell of a long time, but few things in Earth’s geology remain constant. Some of the most dramatic changes over recent times can be found along the East African Rift System (EARS), one of the largest rifts in the world that stretches downward for thousands of kilometers through several countries in Africa. In 5 to 10 million years, it is possible that part of East Africa split from the rest of the continent, creating a new ocean between the divorced landmasses.
The study is published in the journal Solid Earth.
Source Link: Beneath The Middle East, An Ancient Seabed Is Splitting From The Continental Plates