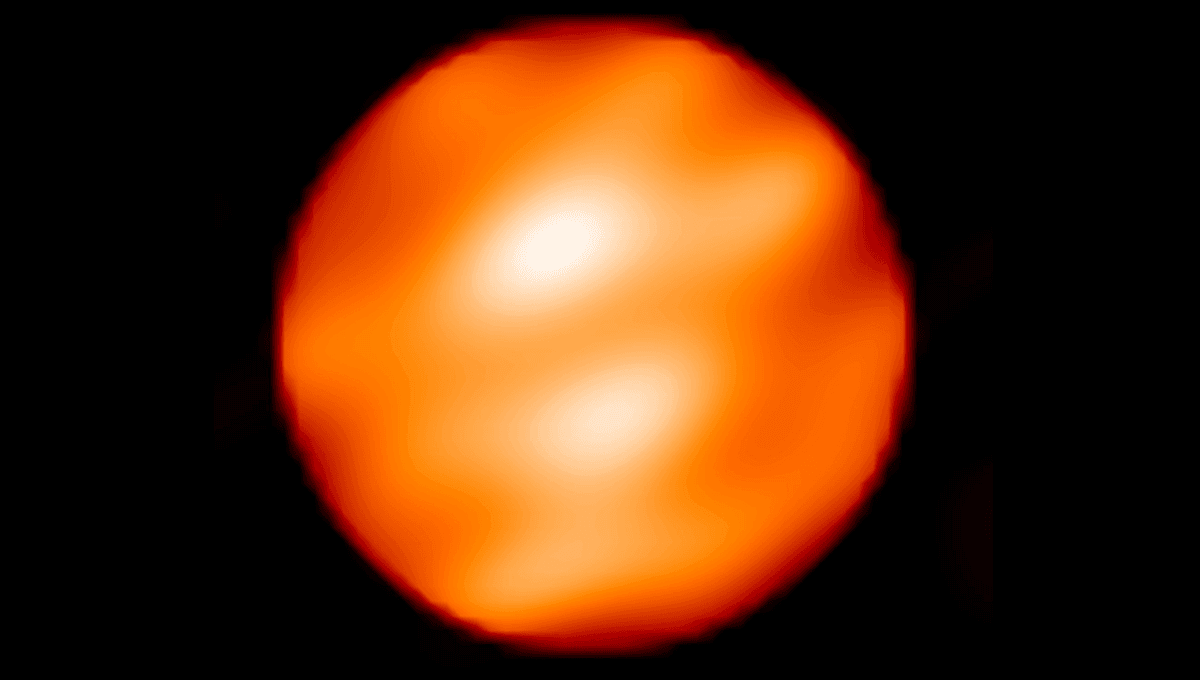
When Betelgeuse finally collapses, the star – currently a red supergiant – will likely shine as brightly as the Moon in the sky for about two weeks, and be visible during the day time for 6-12 months after that.
It will be a spectacular event, but calculating when it will happen is a tricky business. Every now and then in recent observations, Betelgeuse has grown dimmer or brightened, prompting speculation that the star may end up going supernova in a very short amount of time, measured in human lifespans or decades rather than astronomical timetables.
It’s still unclear when the star will undergo collapse into a supernova, and muddying the picture somewhat is that stars like Betelgeuse constantly expel dust and gas, which can obscure our observations and make it appear as though the star is dimming or getting brighter. To make it even more complicated, a new preprint paper suggests that the star may have a “buddy”, which could mean that the star is a lot further from going supernova than we thought.
The team, motivated by studies that put Betelgeuse’s 2019/2020 dimming down to dust clouds, looked at patterns in the star’s light-curve – or the amount of light that reaches our viewing point over time. Red giants like Betelgeuse have been found to have “long secondary periods“, or variations in brightness over long time periods. Long secondary periods have been put down to several causes, with the most favored hypothesis being that they are caused by companion stars. Based on observations of Betelgeuse, the team proposes that it may actually be a binary system, explaining the “great dimming” event of 2019/2020.
“We predict the existence of α Ori B, a low-mass companion orbiting Betelgeuse. This is motivated by the presence of a 2,170-day Long Secondary Period (LSP) in Betelgeuse’s lightcurve, a periodicity ≈ 5 times longer than the star’s 416 day fundamental radial pulsation mode,” the team explains in the paper, which has not yet been peer reviewed. “While binarity is currently the leading hypothesis for LSPs in general, the LSP and the radial velocity variation observed in Betelgeuse, taken together, necessitate a revision of the prevailing physical picture.”
According to the team, the most plausible explanation for the varying light seen from Betelgeuse is that α Ori B, as they have dubbed it, “impacts the dust in its vicinity, corresponding to a brightness increase when the companion is in view”. The team attempted to put constraints on the orbit and mass of such a companion, if it exists, assuming it to be low-mass so that it would not deform Betelgeuse significantly as they orbit one another.
If correct, it would mean that the star is less likely to go supernova any time soon, with the dimming and brightening being explained by Betelgeuse’s “buddy” as they also term it in the paper. For now, more observations of Betelgeuse, and further analysis, will be needed to assess whether Betelgeuse is approaching supernova, or simply orbiting with a friend.
The study has been submitted to the American Astronomical Society journals and is posted to preprint server arXiv.
Source Link: Betelgeuse May Not Be On The Edge Of Supernova. It Might Just Have A Buddy