Once the world’s largest iceberg, A76 was an enormous beast of a berg, 170 kilometers (105.6 miles) in length and 25 kilometers (15 miles) wide, and around 4,320 square kilometers (1,667.9 square miles) in area. Soon after its calving event it broke into three smaller – but still enormous – pieces, the largest of which set sail on quite a journey.
This massive iceberg was first captured by satellite images when it broke off from the Antarctic Ronne Ice Shelf in May 2021. It subsequently soon broke into three named pieces including A-76A, which was the largest piece, estimated to be 135 kilometers (84 miles) long and 26 kilometers (16 miles) wide. A-76A has now drifted over 2,000 kilometers (1,242 miles) and by October 2022, the satellites picked up the iceberg moving into the Drake Passage.
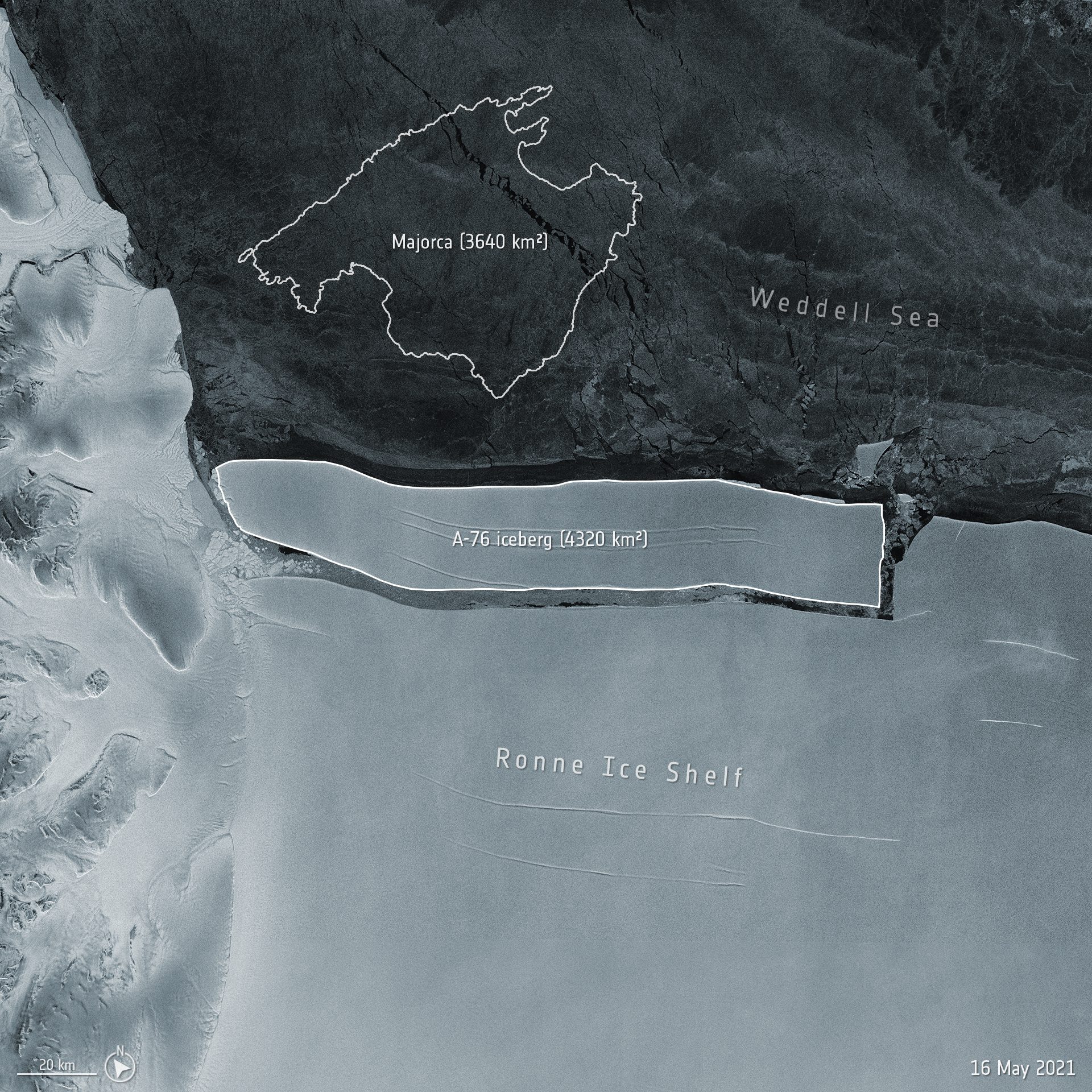
Bigger than the Spanish island of Majorca, this was one major berg.
The Drake Passage is roughly 1,000 kilometers (621 miles) long and runs between Cape Horn at the southern tip of South America and the South Shetland Isles. This water is famously extremely rough, and is where the South Pacific, Atlantic, and Southern Sea all merge.
Still, the iceberg managed to survive for quite a while before, in May 2023, new satellite images showed Iceberg A-76A and newly separated pieces near the island of South Georgia around 2,400 kilometers (1,491 miles) from the Ronne Ice Shelf where the initial calving event took place. But even this icy behemoth could not defeat the powerful currents of the Drake Passage, a stretch of water famous for strong winds and previous iceberg destruction.
“It is impressive to think it ‘sailed’ that far in about two years,” said Christopher Shuman, a University of Maryland, Baltimore County, glaciologist based at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, in a statement. “That obviously speaks to the force of powerful currents in this part of the Southern Ocean.”
This new image showed the iceberg to only measure 78 kilometers (48 miles) long and 11 kilometers (6.8 miles) wide, a much smaller, reduced version of its former self. The Drake passage is thought to be responsible, as the comparatively warmer waters and rough conditions melt and splinter icebergs apart.
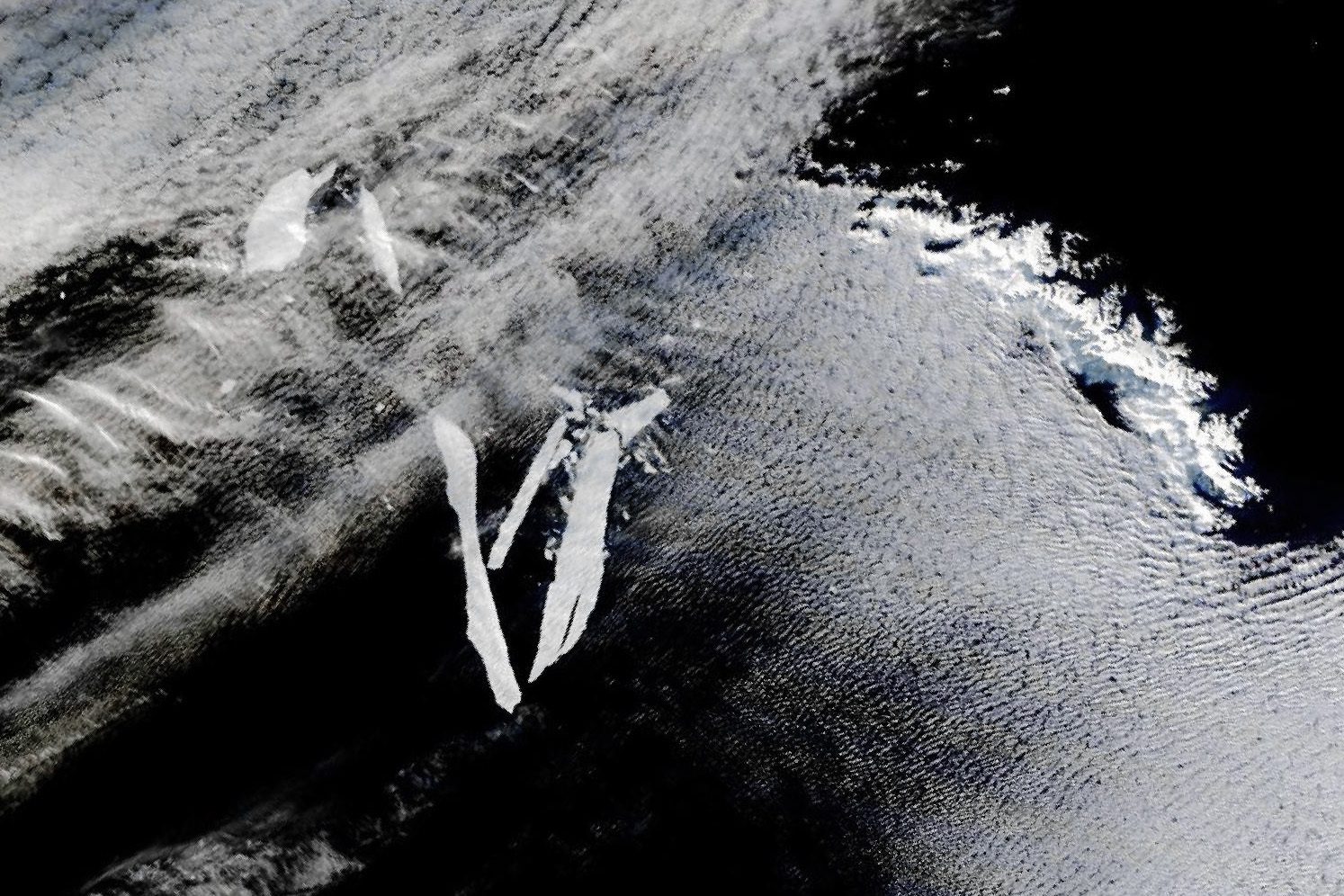

RIP A-76A, the Drake Passage’s latest victim.
Image credit: NASA Earth Observatory image by Wanmei Liang, using MODIS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE and GIBS/Worldview
The Drake Passage was also responsible for destroying the previous title holder, A-68A. It calved from Antarctica’s Larsen C Ice Shelf in July 2017, before it was ripped apart by the rough ocean currents and broke apart near South Georgia in February 2021.
If you’re feeling down at the thought of these icebergs being ripped apart, cheer yourself up with these spectacular images of rare striped icebergs instead.
Source Link: Biggest Piece From World's Largest Iceberg Destroyed In Notorious Iceberg Graveyard