The natural world is full of things that glow, but there’s more than one way that they can do so. Some are biofluorescent and others are bioluminescent – but what’s the difference between the two?
What is biofluorescence?
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
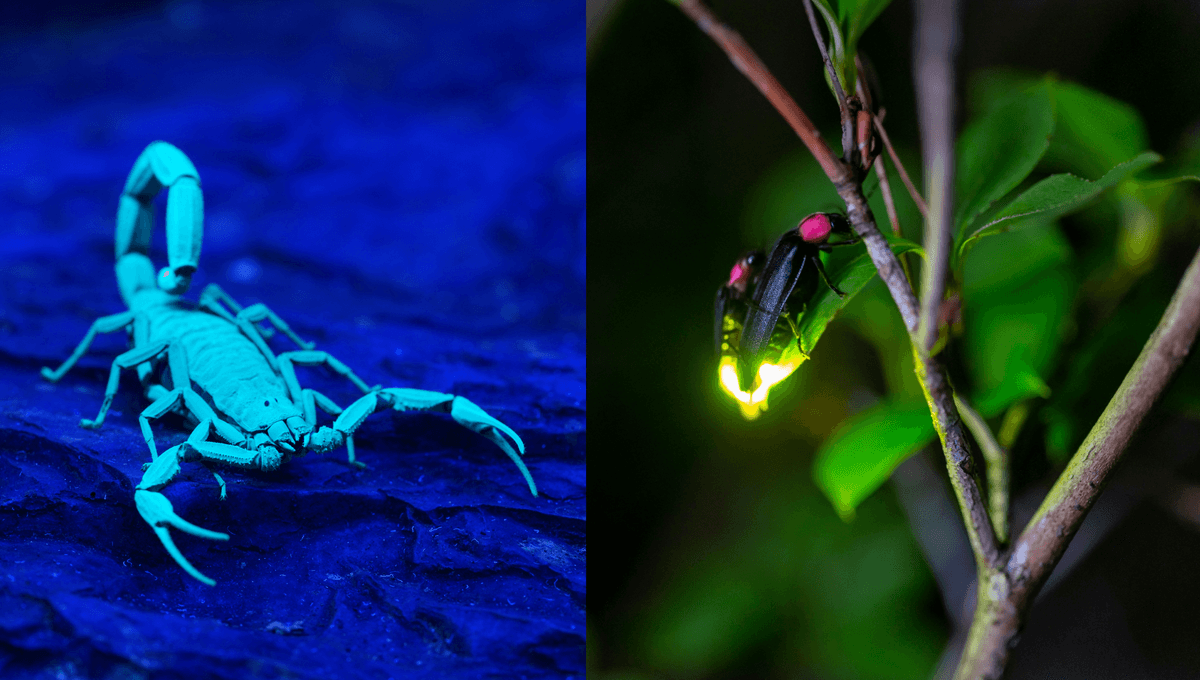
Biofluorescence is a phenomenon in which an organism absorbs light at a certain wavelength and then emits it at a different wavelength, seen as a different color from the light that was absorbed.
At the microscopic level, this involves some kind of fluorescent biomolecule. Certain shark species, for example, have tiny metabolites within their skin that are responsible for their biofluorescence.
However, the best-known biomolecules behind the glow are proteins, and perhaps the most famous of all is green fluorescent protein (GFP). It was first observed in 1962 in the jellyfish species Aequorea victoria and as the name suggests, glows bright green under ultraviolet (UV) light.
Not only did the discovery help us to understand more about how some organisms glow, but GFP has also become an invaluable tool in cell biology, allowing scientists to understand the inner workings of cells in previously unseen detail. It’s perhaps unsurprising then that three of the leaders behind its discovery and development were awarded a Nobel Prize back in 2008.
What plants and animals are biofluorescent?
Marine animals like jellyfish and sharks are far from the only biofluorescent critters out there; chameleons, squirrels, and even our favorite fake-looking animal, the platypus, have all been found to be biofluorescent.
Just recently, a new study identified for the first time that some birds-of-paradise can biofluoresce too, with researchers suspecting that their glowing feathers might have developed to help out during courtship displays.
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
On the darker side of attraction, it’s thought that some carnivorous plant species – including the Venus flytrap – make use of biofluorescence to lure in unsuspecting insect prey, having been found to glow blue under UV light.
What is bioluminescence?
Unlike biofluorescence, bioluminescence involves a chemical reaction that releases energy as light, though it too takes place within a living organism. The reaction occurs between oxygen and a group of small compounds called luciferins, and is catalyzed – the scientific term for “sped up” – by an enzyme called luciferase.
What plants and animals are bioluminescent?
Bioluminescence isn’t particularly common in animals that live on land, though some well-known examples include glowworms and, of course, fireflies and their little light-up butts. Under the waves, however, bioluminescence is far more widespread. It’s often seen in deep-sea species in particular, such as in the bacteria that reside in the glowing lure of the anglerfish.
Plants, on the other hand, are not naturally bioluminescent – but the power of science has allowed for some workarounds. Gene editing has been used to create “glow-in-the-dark” tobacco plants, while researchers have also been able to make wood glow by infiltrating it with bioluminescent fungi.
Source Link: Biofluorescence Vs Bioluminescence: What's The Difference?