NASA has shared an image of a truly bizarre-looking galaxy, believed to be surrounded by a “halo” of dark matter.
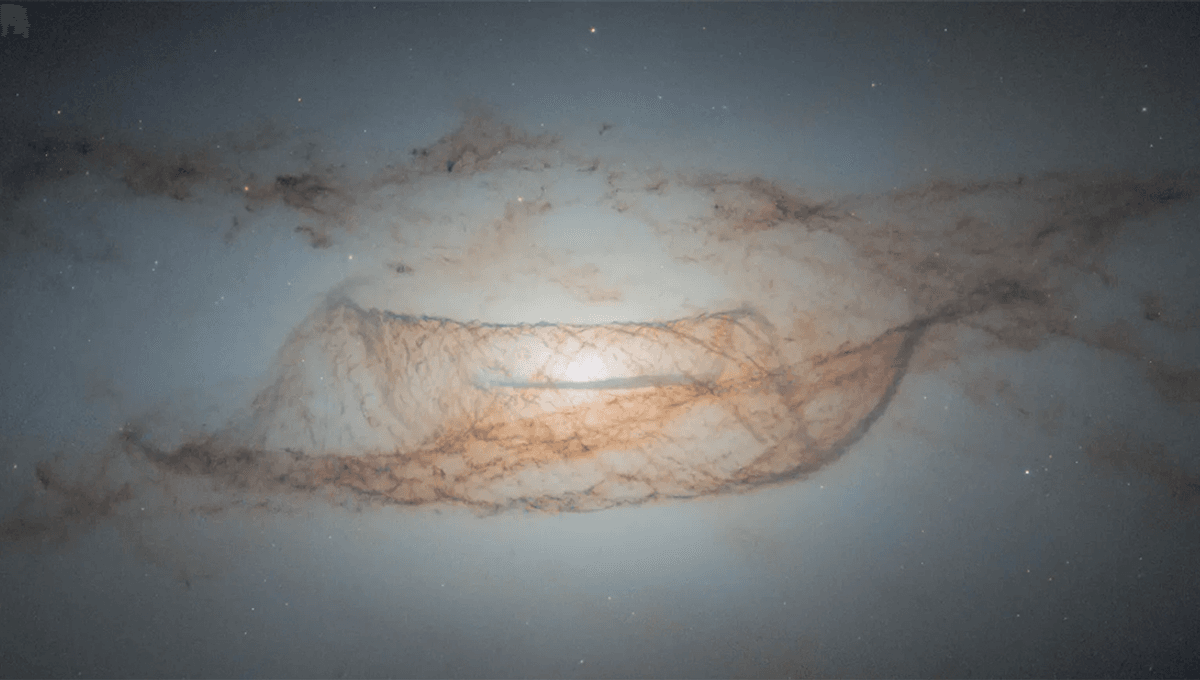
The image – taken by the aging but still extremely useful Hubble Space Telescope – shows lenticular galaxy NGC 4753, part of the Virgo II Cloud of around 100 galaxies and galaxy clusters. Lenticular galaxies are unusual in themselves, appearing to have the central bulge of spiral arm galaxies (like the Milky Way) but without their distinctive arms. There are a few theories about how these galaxies evolved, including that they are older spiral galaxies whose spiral arms have simply faded over time, and that they form during mergers of spiral galaxies.
NGC 4753 is particularly twisted, but part of this comes from our viewing angle. Modeling the galaxy, one team found that from “above”, it would take on a much more familiar shape.
“If the twisted disk is viewed nearly face-on, then the galaxy may be misidentified as a barred or grand-design spiral,” the team wrote in a 1992 paper. “Since approximately half of all viewing orientations produce spiral or bar-like features, we wonder whether some galaxies which have experienced accretion events have been misclassified as ‘normal’ spirals.”
Looking closer at the galaxy, the team determined that the galaxy likely got its shape from an accretion event – attracting more nearby matter through the galaxy’s gravitational pull.
“This galaxy is likely the result of a galactic merger with a nearby dwarf galaxy roughly 1.3 billion years ago,” NASA explains, alongside the latest image of the galaxy. “NGC 4753’s distinct dust lanes around its nucleus probably accreted from this merger event.”
Studying the visible matter was not enough to explain the galaxy’s shape, however. For the galaxy to take its shape, dark matter is likely involved.
Dark matter is invisible matter that doesn’t emit, reflect, or absorb light, and only interacts with normal matter through gravity. We have never detected it directly, but physicists are very confident of its existence due to precise measurements of the movements and shape of galaxies and galaxy clusters. In fact, physicists believe that there is about five times as much of it in the observable universe than regular matter which makes up the stars, planets, dust, and everything else we enjoy (e.g. Danny DeVito).
In this case, astronomers believe that most of the galaxy’s mass is in a slightly flattened, spherical halo of dark matter, twisting it – along with visible matter – into the strange and beautiful shape captured by the Hubble Space Telescope.
Source Link: Bizarre "Lenticular" Galaxy Surrounded By Dark Matter Captured In New Hubble Image