The first study of bottlenose dolphins’ sensitivity to electric fields has found some can detect electric direct current (DC) fields as weak as 2.4 microvolts per centimeter, even better than the measured capacities of platypus. Although still less capable in this regard than sharks and rays, the finding suggests electroreceptivity may play a more important role in dolphins’ survival than previously suspected.
Dolphins have small pits rich in nerve endings on their face, known as vibrissal crypts. A 2022 study confirmed these allow them to detect weak electric fields, but provided no indication on how weak that can be. It makes sense for species that live in murky rivers or estuaries to develop alternatives to seeing underwater, but for those dolphins that inhabit clearer waters such capacities might prove superfluous.
However, it seems even in their frequently crystal-clear waters bottlenose dolphins find electrosensitivity useful enough they have maintained it to a considerable degree.
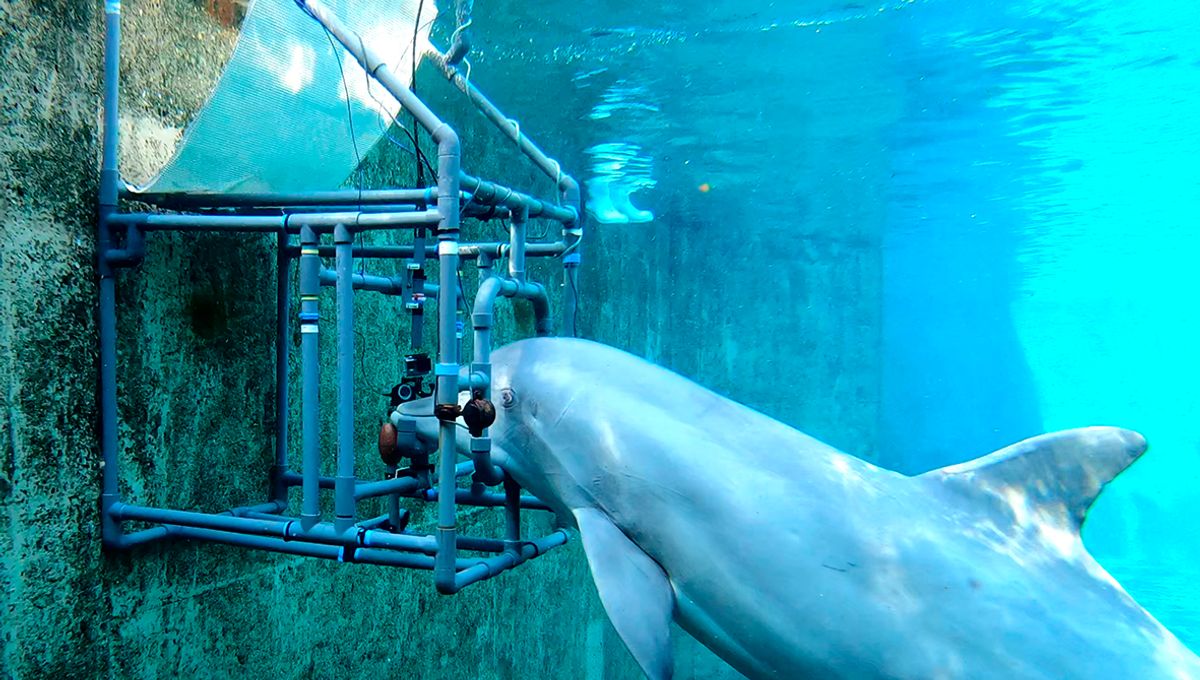
Dolphins don’t make the easiest study subjects, but a team led by Dr Tim Hüttner of the University of Rostock tested two female dolphins, Dolly and Donna, from Nuremberg Zoo. Their enclosure consists of nine pools, allowing plenty of opportunity to separate the two from each other and the rest of the pod.
Once a day each dolphin placed its nose in a headpiece with two electrodes that can produce weak electric fields in the water around them. Dolly and Donna were trained with fish rewards to leave the station when they detected an electric field, and stay when they did not.
The field strength started at 500 µV cm−1 and was gradually decreased. By comparison, platypus, the first mammals to have been found to be electrosensitive, can detect fields of 25–50 µV cm−1. It turns out the dolphins can do better than that. After achieving a 96 percent success rate at the starting field strength, the two did less well, but still much better than chance, with lower fields. Dolly’s performance reached random levels at 5.5 µV cm−, and she lost motivation to keep playing below that. Donna proved more sensitive, detecting fields down to 2.4 µV cm−1, and performing well not far above this.
Both dolphins proved less adept at detecting alternating current (AC) fields, needing field strengths up to 10 times as high at 1 Hz, and struggling even more at higher frequencies.
“Weak bioelectric fields are a reliable short-range source of information for passive electroreceptive animals as all organisms produce electric direct current (DC) fields in the water,” the authors write. These fields are created by ion flow from fish or crustaceans, and are modulated by low-frequency AC potential from muscle activity.
Predators can hunt using these fields, particularly when their other senses are blocked. For some fish, the capacity to detect electric fields is so essential they produce their own weak electric discharges, allowing them to sense a disturbance in the force created by moving prey.
More often, however, electroreception is purely passive, detecting the fields created by others. It is suspected this can also extend to the capacity to orientate oneself relative to the Earth’s magnetic field, not directly as migratory birds do, but through electromagnetic induction in sea water.
Electroreception is so useful it has evolved many times on different branches of the animal family tree, but it’s only known in mammals from platypus, echidnas and some dolphins. The last is particularly curious, since their capacity for echolocation might seem to make it unnecessary.
Guiana dolphins were the first dolphin species in which electroreceptivity was demonstrated. Living in estuaries around the South American coast, and often swimming far up-river, they face a particularly muddy environment, and much of their diet comes from fish that hide in the sediments on the sea floor. The capacity to detect electric fields these fish produce provides obvious benefits.
Bottlenose dolphins have a much more diverse diet. Just as they have developed remarkably innovative methods for safely accessing fish in traps and protecting themselves against sharp objects, it seems they have also honed their senses over many generations. If able to see, hear, taste, smell and touch the world, as well as detect it through echolocation and sense its electric fields some creatures might be overwhelmed by the surfeit of information, but it seems dolphins integrate it all. The authors suggest they use echolocation to detect prey at a distance, and electric fields for close-in work.
The study is open access in the Journal of Experimental Biology
Source Link: Bottlenose Dolphins Become One Of Few Known Mammals With A “Seventh Sense”