High energy photons probably originating from the birth of a black hole briefly changed the Earth’s upper atmosphere last year, despite occurring billions of light years away. A set of papers delving into the explosion astronomers dubbed the BOAT (Brightest Of All Time) reveal it far outshone anything we’ve seen before, and was accompanied by a suitably impressive afterglow.
GRB 221009A was so bright it overloaded satellites’ gamma-ray detectors. As a result, astronomers instantly knew it was very powerful, but could not measure it precisely. Telescopes operating across the electromagnetic spectrum abruptly changed direction to see what they could find. Some of the resulting work has now been released in a paper in the Astrophysical Journal Letters, while other conclusions are still working their way through peer review, but are available as preprints.
Longer Gamma Ray Bursts (GRBs) are consequences of black holes being formed, although GRBs lasting less than two seconds can have other causes. The formation of a black hole from the collapse of a giant star releases enormous amounts of energy, but GRBs are also bright because most of this radiation escapes in the form of narrow jets. If Earth falls within the beam of these jets, we get bathed in gamma rays, and if not we usually wouldn’t know anything happened.
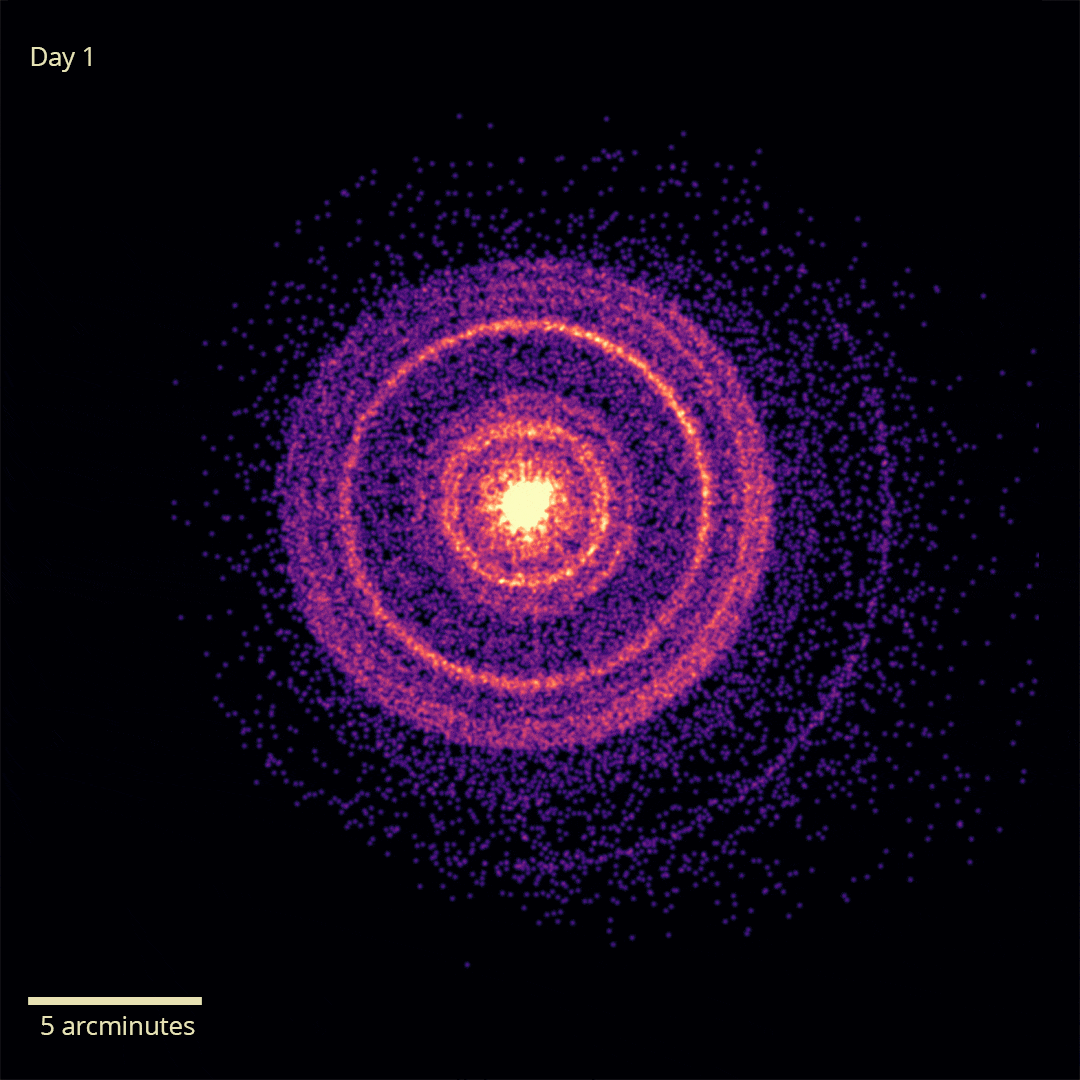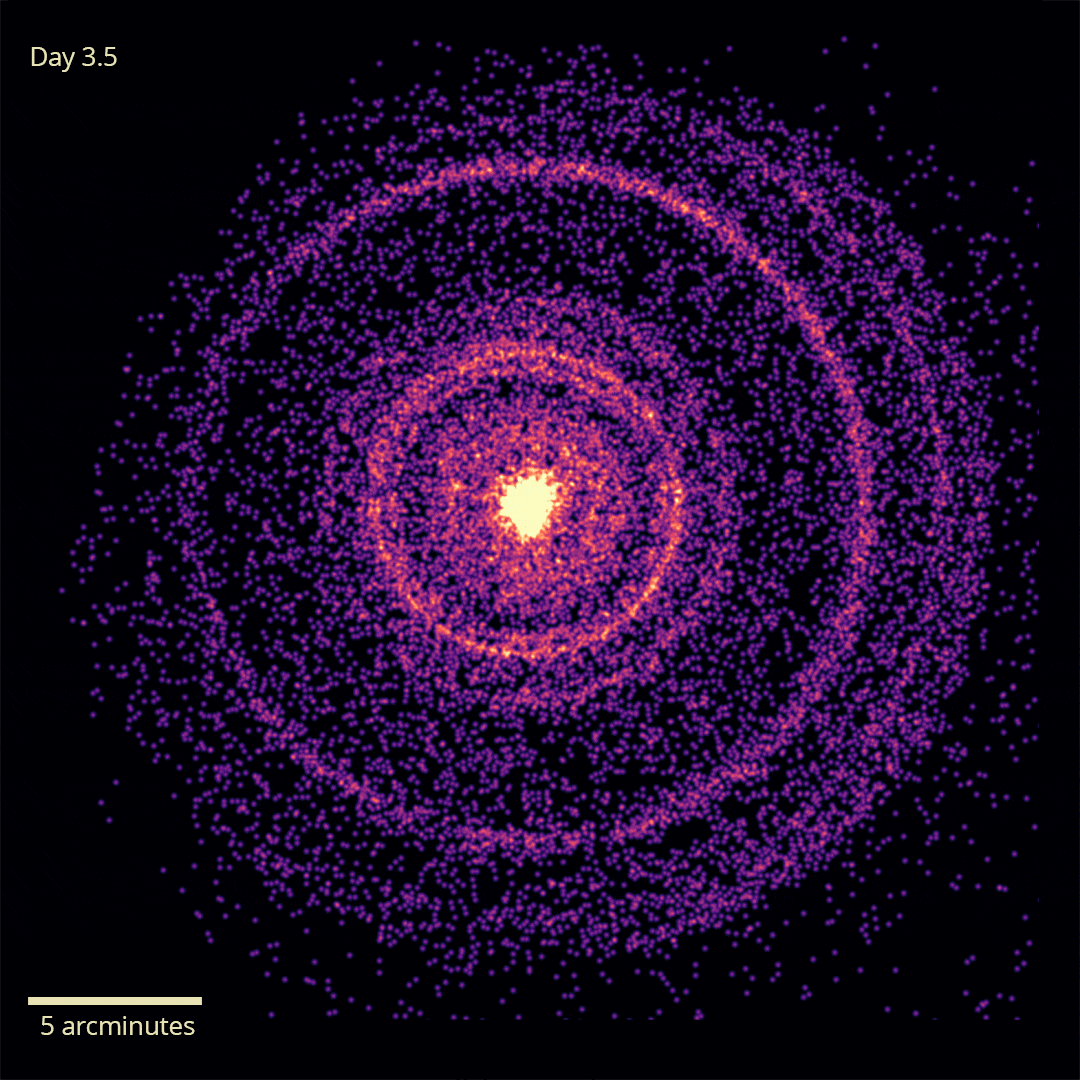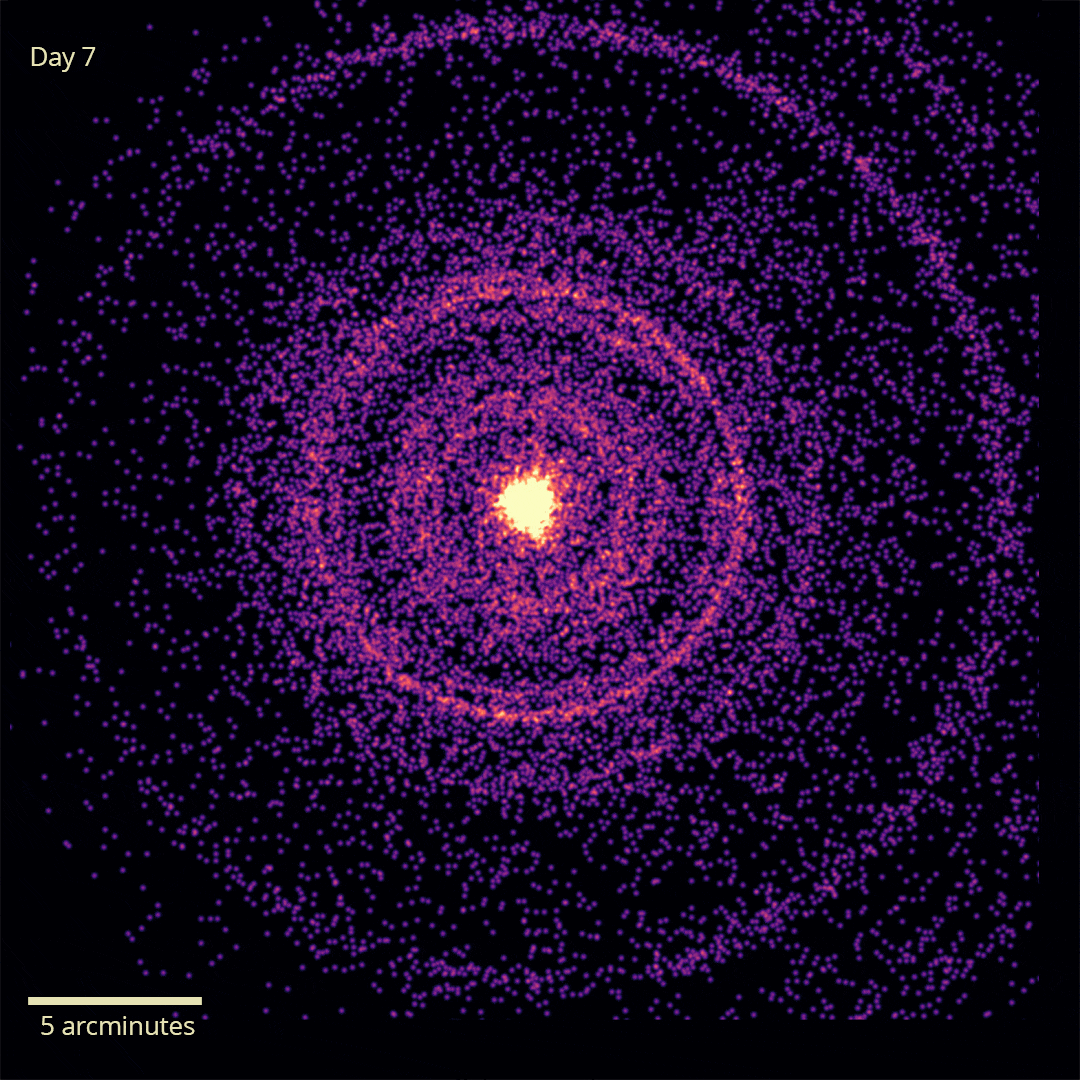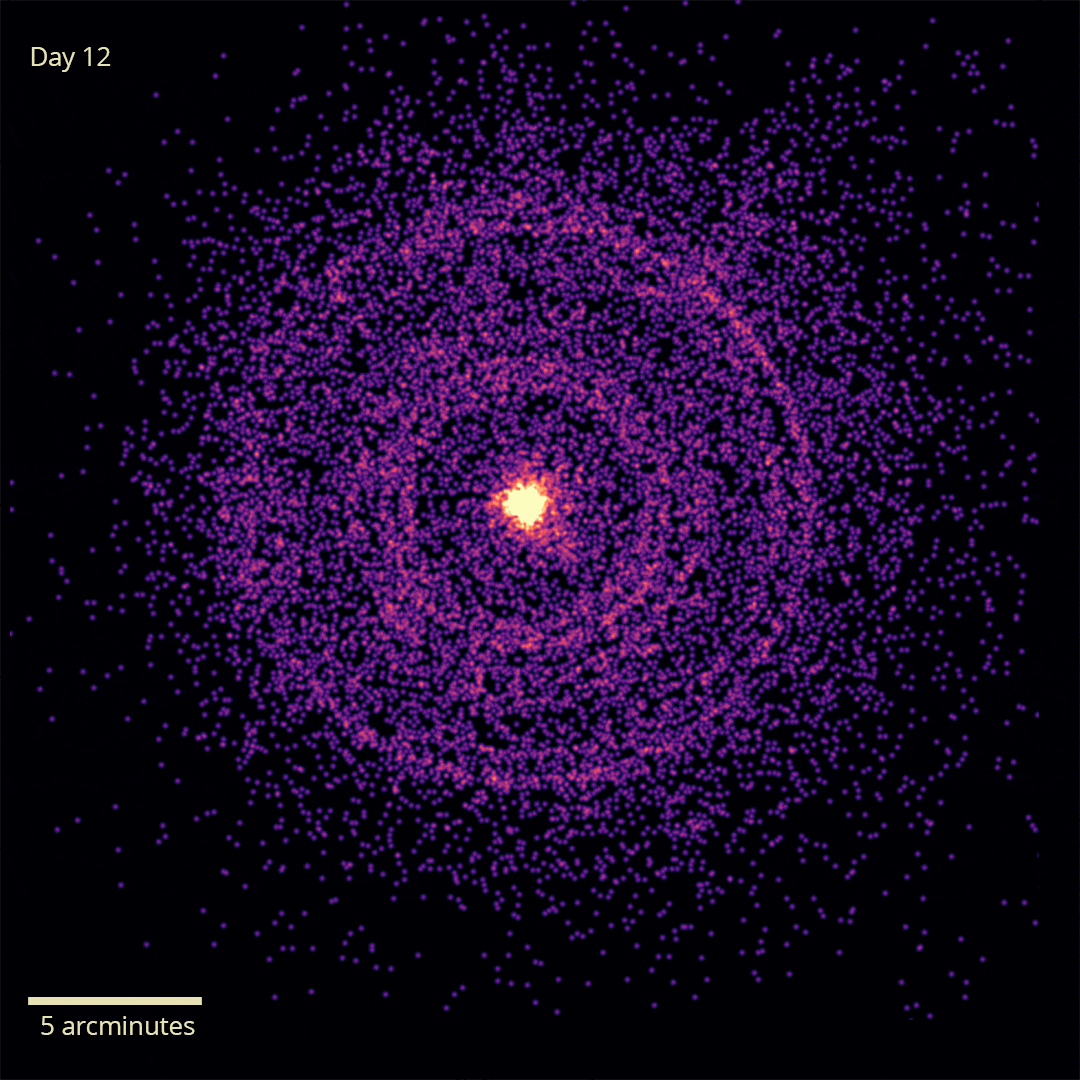
X-rays from GRB 221009A’s initial flash were reflected off dust, allowing us to see it for over a week. Image Credit: NASA/Swift/A. Beardmore (University of Leicester)
GRB 221009A definitely falls into the long-duration GRB category, lasting a whole five minutes. Indeed, as University of Sydney PhD student James Leung told IFLScience, it is thought that part of the reason it was so bright is that the mechanism powering the GRB stayed on longer than usual. In addition, Leung said, the explosion was relatively close to us; “About a thousand times as distant as the Andromeda Galaxy,” or 2.4 billion light years away. Immense as that distance is, it’s still closer than 97 percent of GRBs.
The University of Sydney’s Professor Tara Murphy said in a statement that “One of the fascinating things about gamma ray bursts is, although they are over quite quickly – in just a matter of seconds – they leave afterglow emissions across the light spectrum in surrounding matter that echo for months and years afterwards.” The afterglow is produced by the jets colliding with gas thrown off by the former star.
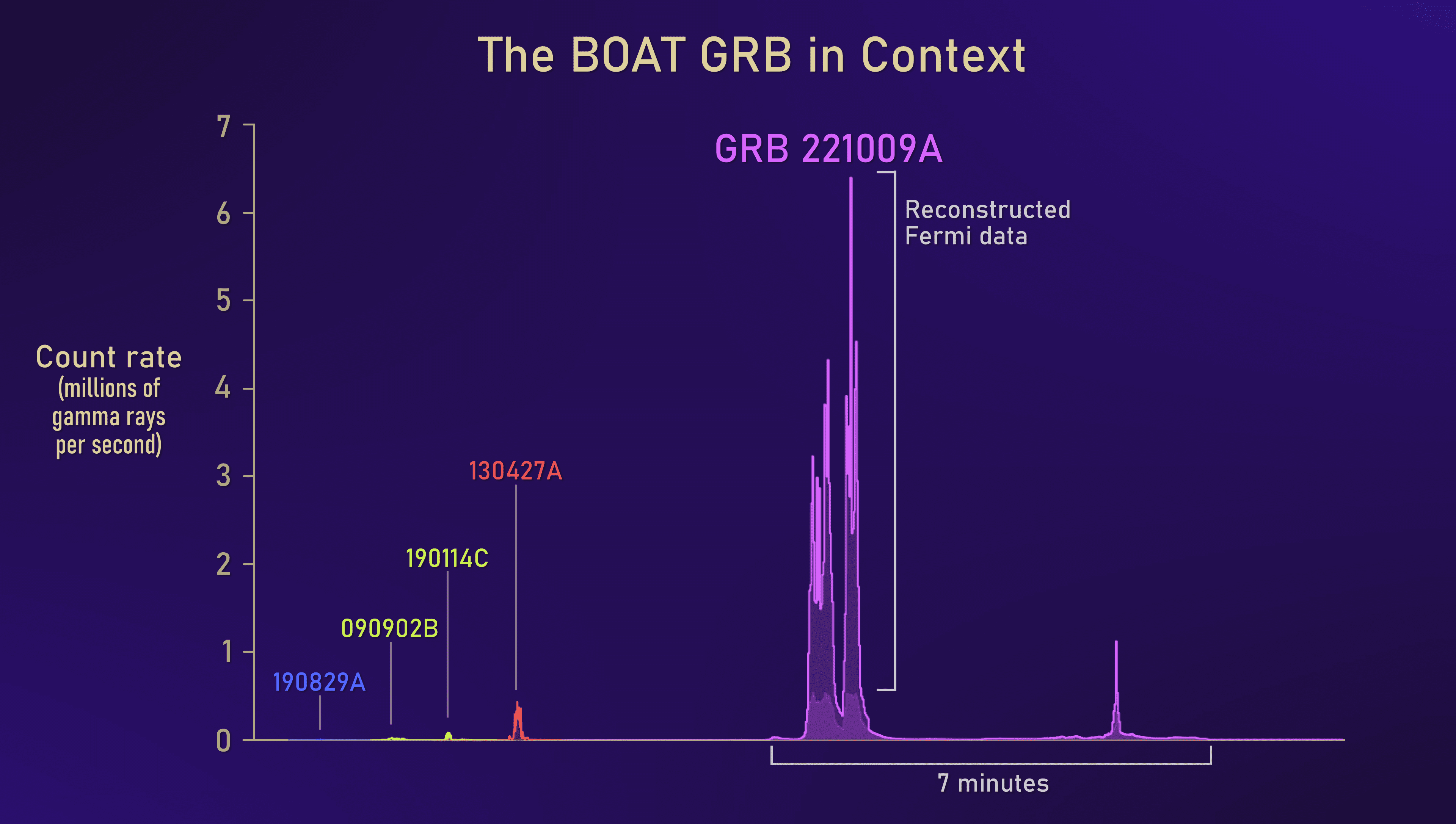
Gamma rays detected from GRB 221009A compared to the previous five record holders. Even the afterburst outshone anything before. Image Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center and Adam Goldstein (USRA)
GRB 221009A’s afterglow was bright, but also puzzling. The visible and X-ray parts of its spectrum were unusually faint relative to the extraordinary strength of its radio and millimeter waves. “A few GRBs in the past have shown a brief excess of millimeter and radio emission that is thought to be the signature of a shockwave in the jet itself, but in GRB 221009A the excess emission behaves quite differently than in these past cases,” said Dr Yvette Cendes of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophsyics, in a statement.
Leung told IFLScience that GRB models will need to be reworked to account for this example. Although ideas are being considered, no final conclusions have been reached.
We’ve only been observing GRBs since we could put detectors on satellites, but astronomers estimate GRB 221009A was a one-in-a-thousand-year event, if not rarer. GRBs’ intrinsic brightness are determined by factors such as the mass and rate of spin of the star before it collapsed. Leung told IFLScience that some researchers have also found evidence GRB 221009A’s jet was unusually tightly focussed, contributing to its extraordinary brightness, but this remains contested.
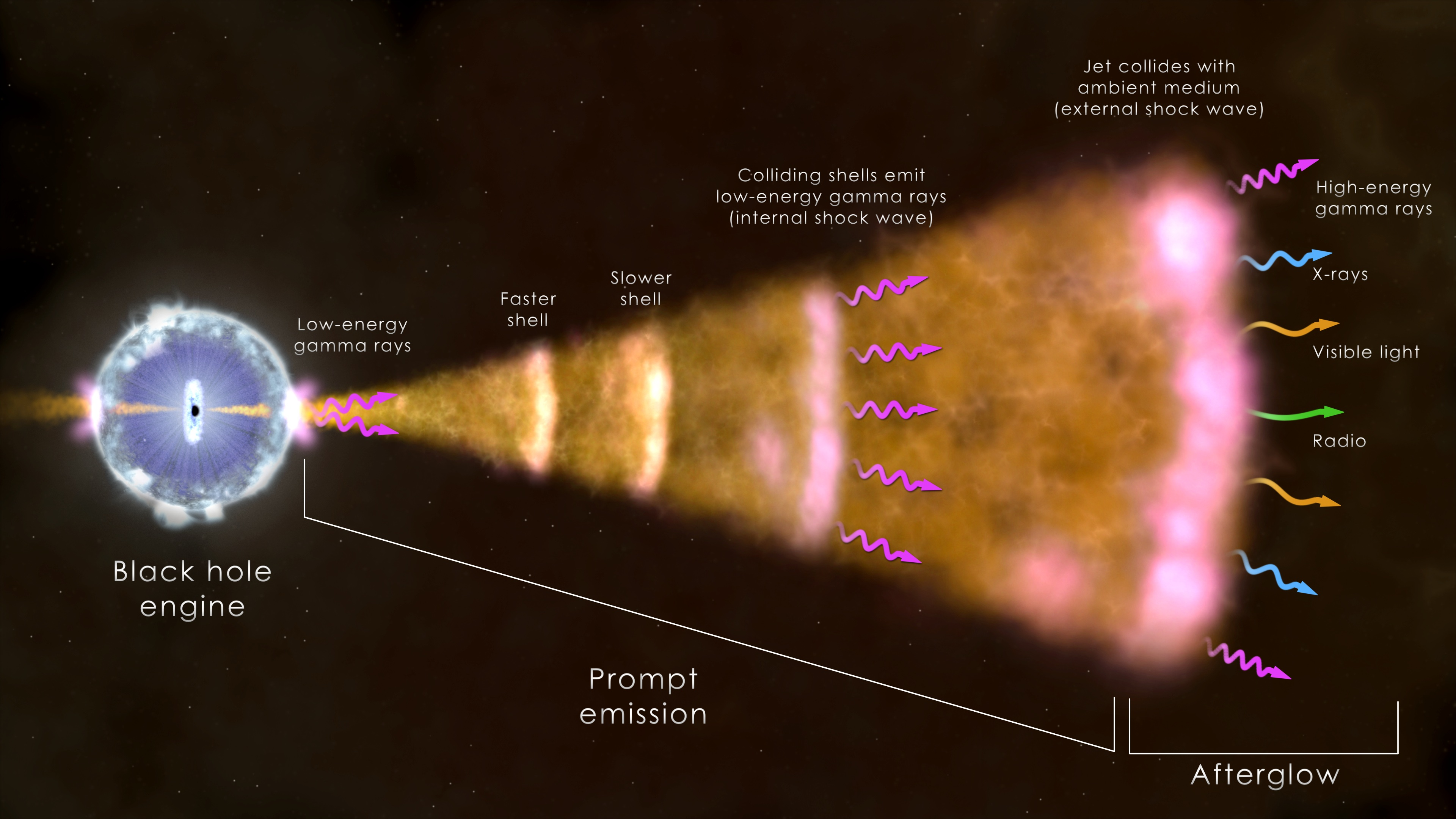
Schematic of long gamma-ray burst. A giant star collapses into a black hole, releasing a few minutes of gamma rays, which collide with surrounding gas and dust to produce an afterglow lasting days. Image Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Astonishing as this event was, it has left astronomers wanting more. Leung told IFLScience that long-GRBs’ cause was confirmed because some were found to be co-located with supernovas. However, in the case of GRB 221009A, “The supernova has proven elusive.” The reason for this is unknown, but Leung said some astronomers attribute it to dust blocking out visible light from the direction of the explosion. “Another theory is the black hole formed so fast there was not time for a significant supernova contribution,” Leung added.
Some of the work discussed here is open access in The Astrophysical Journal Letters
Leung and Murphy’s work has been submitted to Nature Astronomy, and is currently available on ArXiv.org
Source Link: Brightest Cosmic Explosion Humanity Has Ever Seen Was Seventy Times Previous Record