Biological microorganisms are energy efficient, proliferate easily, and move autonomously. This makes them ideal sources of power for biohybrid machines. Scientists have now designed the first micromotors powered by algae. If you thought animals driving cars was impressive, get a load of this.
The alga in question is called Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, a single-celled green alga. Thanks to their two long flagella (the tails of cells), they can swim at 100 micrometers per second – quite impressive when your body is only 10 micrometers long. This inspired student Naoto Shimizu and co-authors to try to harness their abilities… by fitting them with a harness.
Haruka Oda and colleagues designed two micromachines to be powered by C. reinhardtii. The machines consist of small baskets (10 micrometers in diameter, 1/100th of a millimeter!) in which the algae are trapped. The basket holds the cell, while still allowing it to freely move its flagella. The baskets are attached to each other leading to the unwitting cooperation of several individuals, a necessary step to generate enough propulsive force to move a mechanism larger than a single cell.
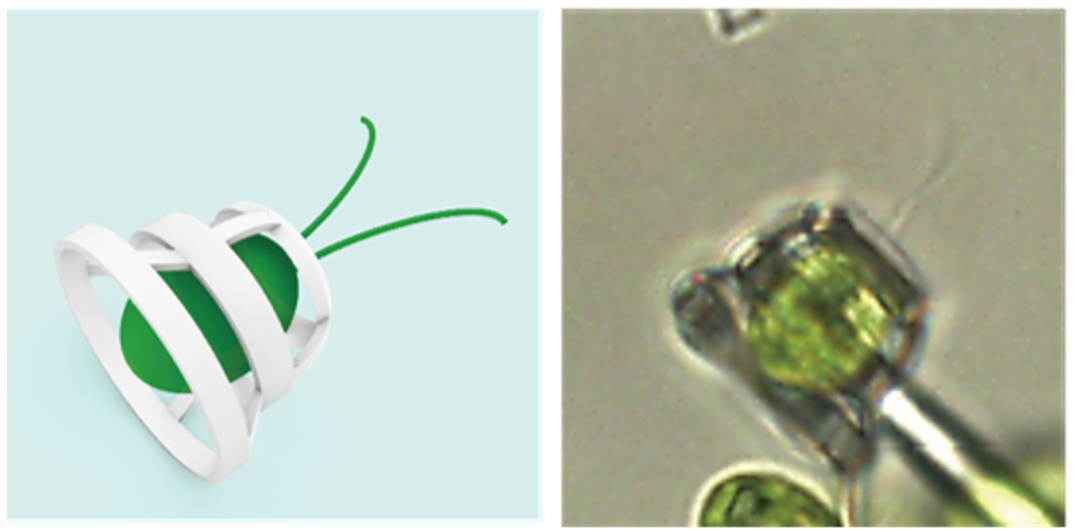
A diagram of the basket trap design, and a microscope image of the real thing in action.
Image credit: © 2024 The Shoji Takeuchi Research Group at the University of Tokyo
The two micromachines are a “scooter” and a “rotator”. In the rotator, four algae sit in baskets at the end of four arms, with the center pinned down. Swimming enthusiastically, the algae could spin the rotator at 20-40 micrometers per second.
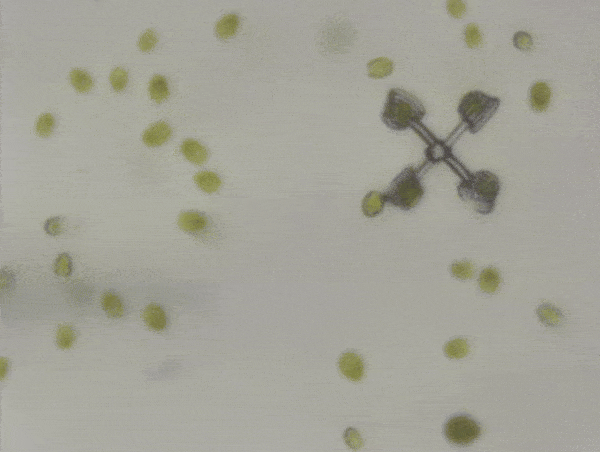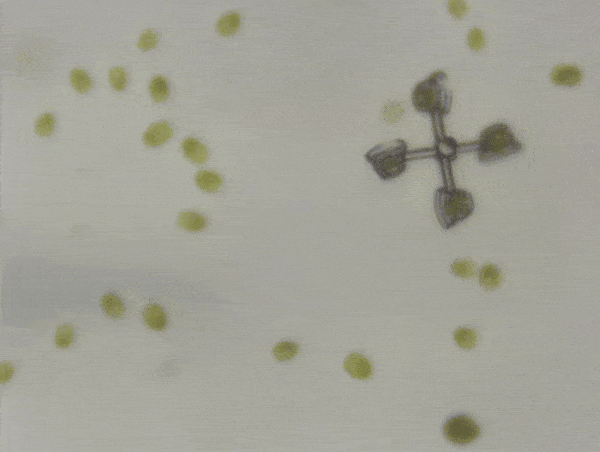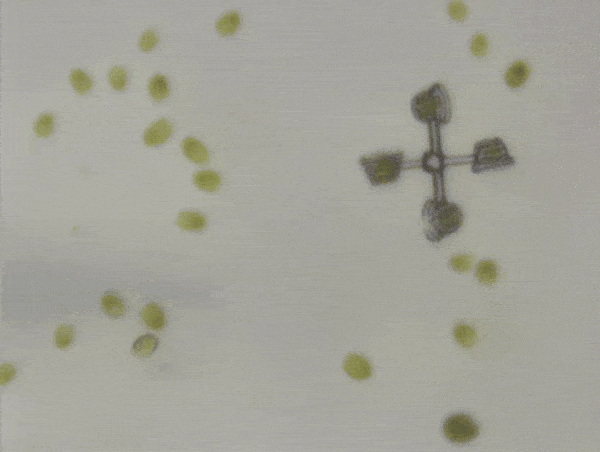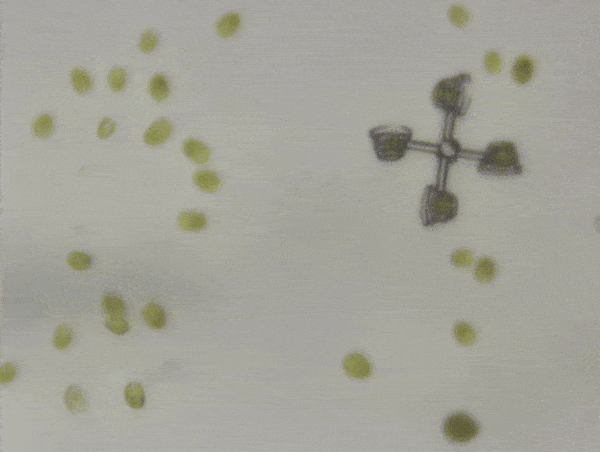
Powered by a crew of four algae, the rotator moved at 20-40 micrometers per second.
Image credit: © 2024 The Shoji Takeuchi Research Group at the University of Tokyo
Being able to build a biohybrid machine that can move forward linearly has been more of a challenge. Previous designs (using different biological microorganisms) had used ratchets to align the motion, but this limited the movement of the machines. In comes the scooter.
The scooter looks more like a podracer from Star Wars. Two algae face the same way and can propel the small vehicle forward, ideally in a straight line. The scooter behavior was more surprising as the algae pushed it to twist, turn, and tumble. This is probably due to it not being tethered in place (like the rotator) and uneven forces produced by the two drivers.
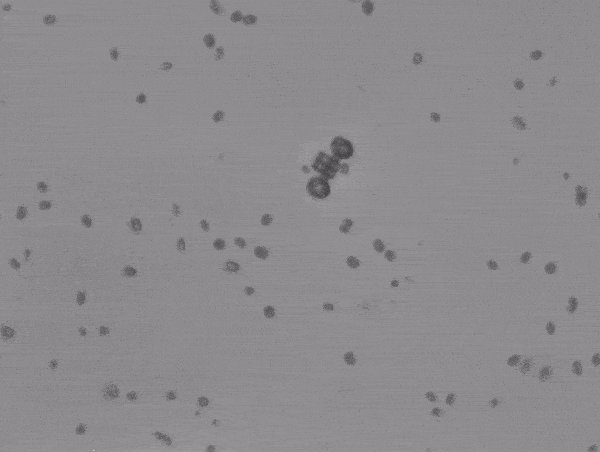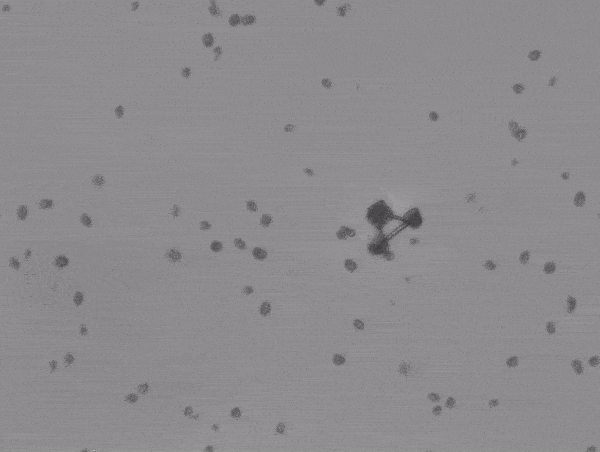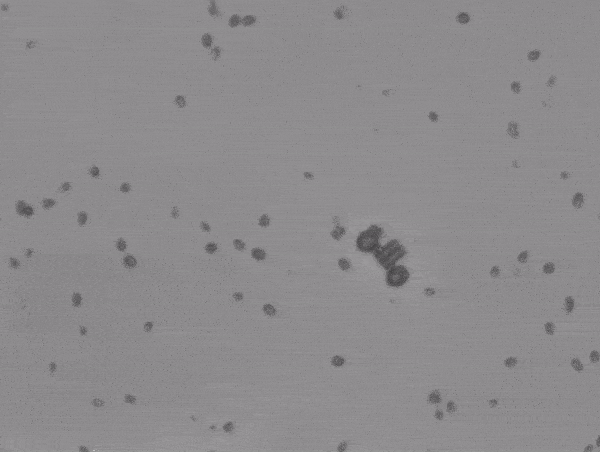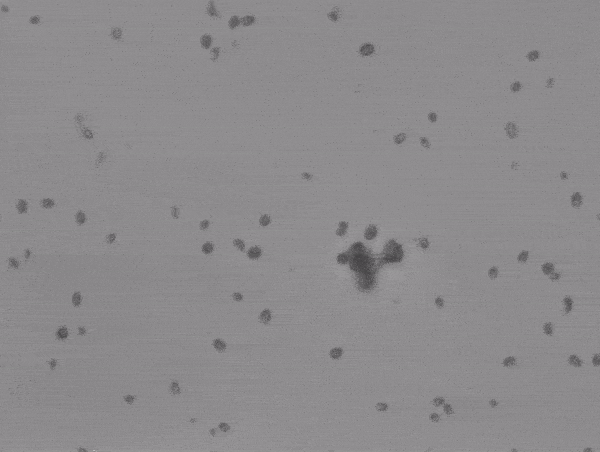
“[We] observed a range of erratic rolling and flipping motions,” commented lead author Haruka Oda.
Image credit: © 2024 The Shoji Takeuchi Research Group at the University of Tokyo
The two algae biohybrid machines are paving the way for new designs to create powerful vehicles. “These methods have the potential to evolve in the future into a technology that can be used for environmental monitoring in aquatic environments, and for substance transport using microorganisms, such as moving pollutants or nutrients in water,” said Professor Shoji Takeuchi from the Graduate School of Information Science and Technology at the University of Tokyo, senior author on the study, in a press release.
This study is published in the journal Small.
Source Link: Buckle Up! Microscopic Algae Are Driving Tiny "Scooters"