You should always wash your hands if you touch public surfaces, because they might be covered in dangerous pathogens. While one should wash hands regularly anyway, it would be so much easier if dangerous microbes simply did not stay on trays, seats, handles, and toilets. That dream could soon be a reality thanks to a new coating.
Scientists at the University of Nottingham, together with company Indestructible Paint, have developed a paint-on resin that incorporates chlorhexidine. This substance is often used in dentistry to treat mouth infections and perform pre-surgical cleaning. Mixed with the resin, it can be painted on a range of plastic and hard non-porous surfaces to provide an antimicrobial coating.
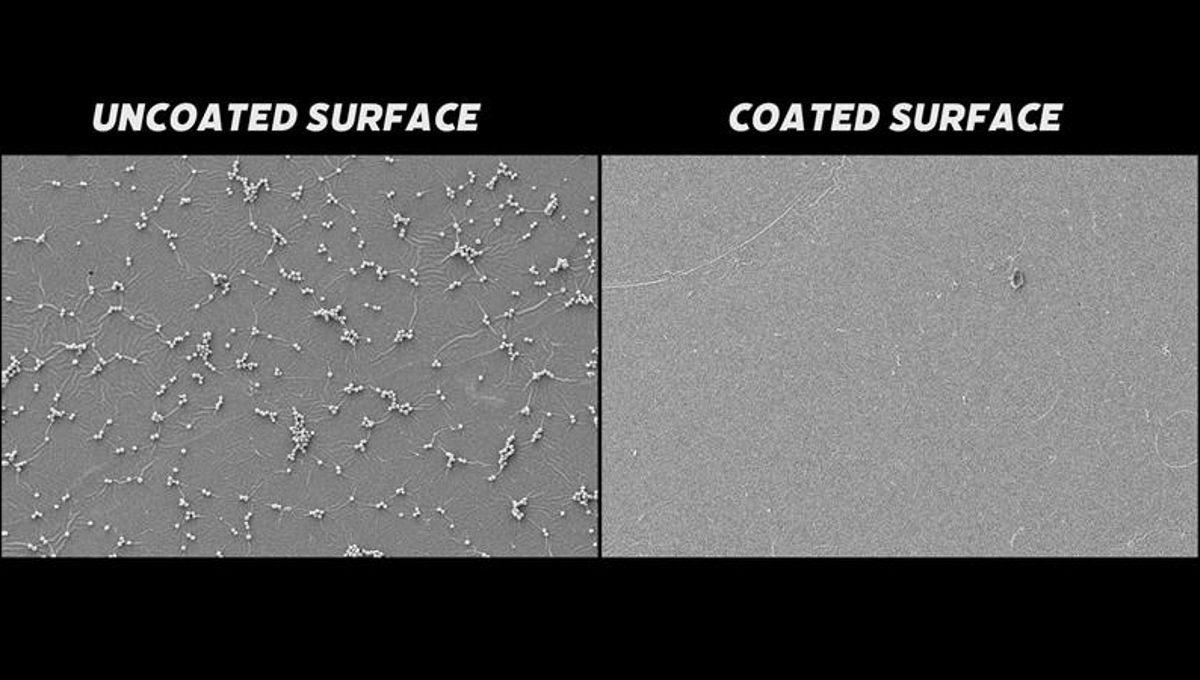
Adding chlorhexidine doesn’t affect the adhesion of the epoxy to the surface. Its microbial effect has been demonstrated against dangerous pathogens such as E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and even the fungus Candida albicans. None of these pathogens were found on coated surfaces in lab tests.
“It’s hugely exciting to see this research being applied in a practical way. In our initial research we incorporated the disinfectant into the polymer to create a new antimicrobial paint which has excellent efficacy, it also doesn’t spread into the environment or leach from the surface when touched,” lead author Dr Felicity de Cogan, Associate Professor in Pharmaceutical Science of Biological Medicines, said in a statement.
“This new study showed clearly that surfaces with this paint applied had no bacteria and as soon as it dries it is active. By adding this to paint we can create an effective bacteria killing coating that is easy to apply and cost effective.”
The antimicrobial effect is long-lasting, and chlorhexidine has been shown to be effective against certain flu viruses and even SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID-19. This could be a revolutionary weapon in our arsenal against dangerous infections, especially in a hospital setting.
“Paint is widely used as it is a versatile, cheap and durable material, it can be applied to any surface. These plastic and metal surfaces found widely in public spaces do have drawbacks,” Dr de Cogan explained.
“Research has shown that contaminated surfaces, can act as a reservoir of antimicrobial resistance genes, encouraging the spread of antimicrobial resistance across bacterial species through horizontal gene transfer despite deep cleaning practices. It is paramount that new technologies such as this antimicrobial paint are developed to prevent the spread of pathogenic microorganisms to vulnerable patients and address the ever-increasing threat of antimicrobial resistance.”
The study is published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Source Link: Bug-Busting Antimicrobial Paint Can Make Surfaces Pathogen-Proof – From Staph to E. coli