Nearly seven months after declaring a re-emergence of the New World screwworm fly in Costa Rica, a state of emergency was declared in the country on February 7 as the flesh-eating insect population continues to rise.
New World screwworm (NWS) flies (Cochliomyia hominivorax), which are a species of blowfly (family Calliphoridae), are native to much of North and South America and have been popping up and wreaking havoc across the continents for centuries. Having been known to decimate live-stock populations, as well as infecting domestic pets and even humans, the fly lays its eggs inside the open wounds of any mammal (and sometimes bird) species. Once hatched, the larvae burrow deep inside the living tissue, causing painful infections, tissue loss, and even death.
Despite best efforts to keep the population under control in Costa Rica, the numbers reportedly continued to rise. As of March this year, the first case of human infection was reported by the Ministry of Health and SENASA, marking the country’s inaugural case of human infestation.
However, due to a decades-long eradication campaign by the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) which saw the first successful eradication of NWS in North America in the 1960s, it is hoped that through combined government efforts they can once again “prevent, control, and eradicate” Costa Rica’s NWS population.
What is a new world screwworm?
Screwworms, of which there are two species, are obligate parasites during their larval stages. The New
World screwworm, or true screwworm, is indigenous to much of North and South America. However, due to eradication efforts, they are presently found just in the northern countries of South America, northern Chile, and northern Argentina. However, imported cases have been observed in Mexico, the US, and even the UK.
NWS life cycles can fluctuate depending on temperatures, taking as long as three months to complete in colder climates, and as short as 18 days when the temperature averages 29°C (35.6°F).
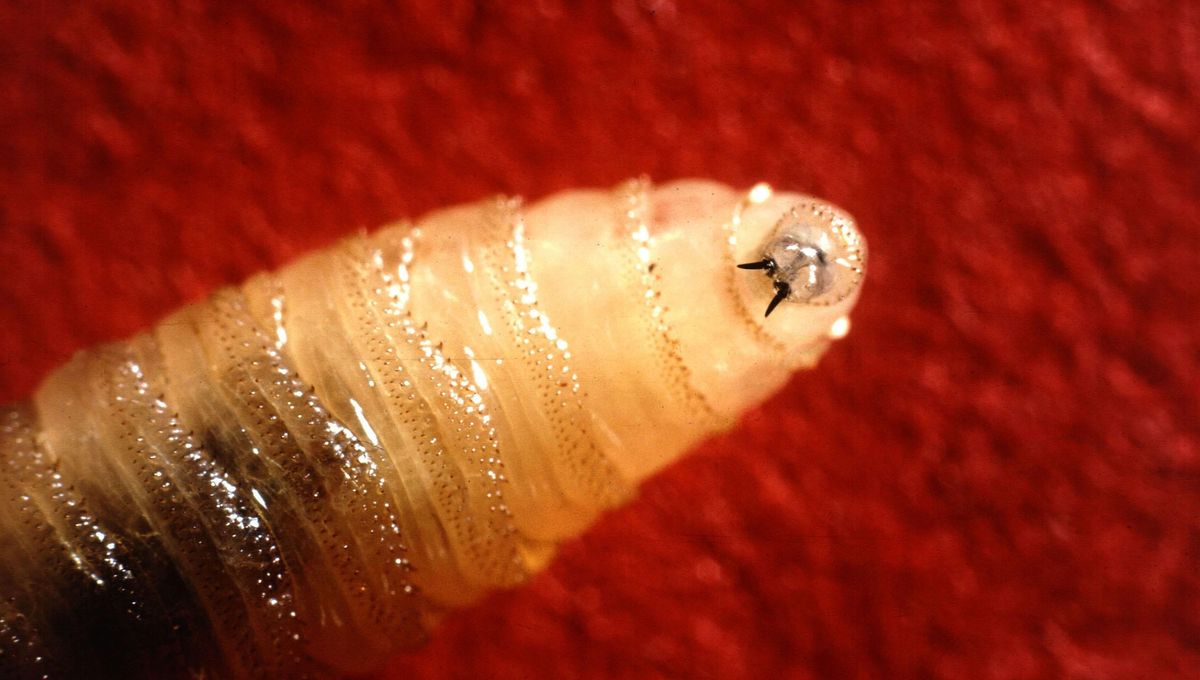
What makes the screwworm unusual and particularly dangerous is that, unlike most blowflies, screwworms prefer to lay their eggs on the wounds of living mammals as opposed to carrion. The screwworm fly will seek out any wound or orifice and will lay between 100 and 350 eggs around the edge of the opening.
In less than 24 hours, these eggs will hatch and burrow as a group downwards into the wound. The infestation spreads quickly throughout groups of animals as the smell from a larvae-infested wound is attractive to other egg-carrying females, drawing more screwworm flies to the area.
After about a week from hatching, the larvae, which have now grown from 2 millimeters (0.07 inches) to 1.5 centimeters (0.6 inches), will stop feeding and fall to the ground where they burrow and pupate. They emerge between seven and 60 days later, depending on the climate, to continue the whole disgusting cycle again.
Screwworm infestations are further complicated by the increased chance of different larval fly species entering the wound, increasing the chances of infection. If untreated, screwworm infestations can kill an animal within one to two weeks, with naval wound infestations in newborns being the deadliest.
Eradication strategy
Such an unusual species requires some unusual tactics to keep the population under control, and efforts implemented by the USDA have proved extremely successful.
The method for eradication, called the sterile insect technique (SIT), sees millions of captive male NWS sterilized using radiation. These males are then dropped into the existing wild populations, at a rate of approximately 3 million sterile flies twice a week in one affected Florida Keys area by the USDA during the eradication period. As female NWS mate once in their lifespan, mating with a sterile male prevents the female from laying viable eggs.
First carried out in the US in 1958 due to infestations decimating live-stock populations in Florida, and the technique proved successful. It has subsequently been used often to tackle NWS outbreaks throughout the Americas and has helped tackle other invasive species too.
Scientists Dr Raymond Bushland and Dr Edward Knipling from the USDA were awarded the 1992 World Food Prize for their work developing the SIT, and it’s hoped this creative method will once again liberate Costa Rica from the threats of NWS.
Source Link: Burrowing, Flesh-Eating Fly Larvae Outbreak Sparks National Emergency In Costa Rica