![]()
Electromagnetic waves are packets of energy travelling all around us. Some of these waves have lots of energy, and some have less.
We call the lowest energy electromagnetic waves radio waves. There’s a good chance radio waves are moving around you right now, shining out of wifi routers, laptops and mobile phones.
The most powerful electromagnetic waves are gamma rays, though you will never have had these anywhere near you unless you’ve spent time hanging around exploding stars or the inside of a nuclear reactor.
And there are some electromagnetic waves that we can actually see. This is visible light – the light we can see all around us.
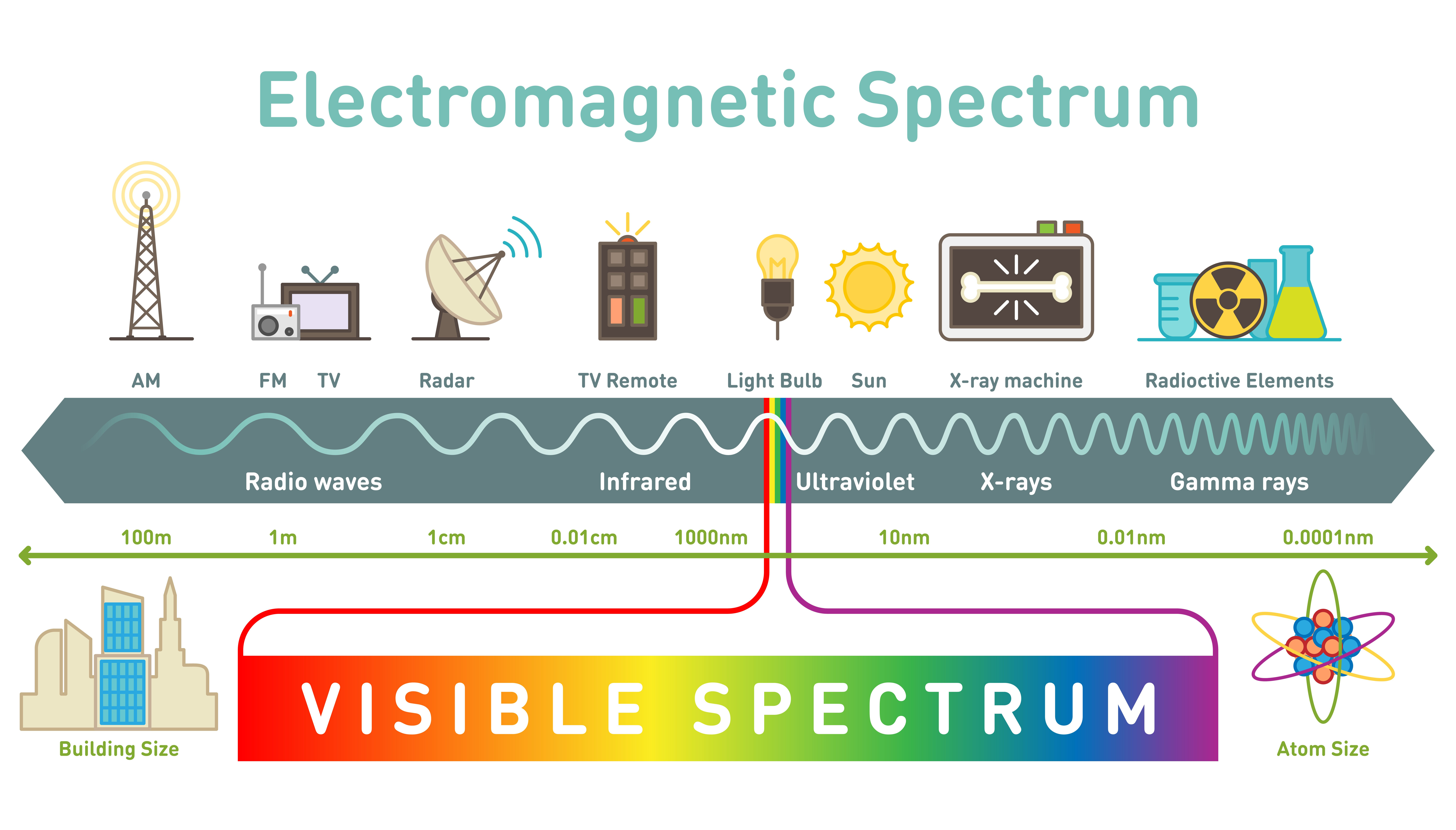
The electromagnetic spectrum, from low energy radio waves to high energy gamma rays.
Image credit: VectorMine/Shutterstock.com
Most electromagnetic waves around you just pass by without you ever noticing them, but some of them are perceived by your brain and form a very important part of your everyday experience of the world.
Brain – and body
But your brain can’t detect them on its own. Instead, it has to make sense of information about the electromagnetic waves that has been detected by other parts of your body.
A large part of the human brain is dedicated to making sense of a type of electromagnetic wave that we call “visible light”. This type of electromagnetic wave bounces off objects and into our eyes.
At the back of the human eye there are millions of tiny cells that produce electrical signals when they are hit by an electromagnetic wave with a particular amount of energy. Some of these cells are designed to detect an amount of energy that we call the colour “red”. Others are specialised for another amount of energy that we call the colour “green”, or another that we call “blue”.
The eye then sends electrical signals to your brain to describe the type of electromagnetic wave that it has detected – what colour the light was and where it came from. Finally, through a tremendously complicated sequence of electrical signals, a sighted person has the experience of “seeing”.
The fact that human eyes can detect visible light but not other types of electromagnetic wave is just the way that human eyes have evolved. Other animals’ eyes have evolved differently. For example, butterflies can see a slightly higher energy electromagnetic wave that our eyes can’t detect, but which we call ultraviolet. Some flowers reflect a lot of ultraviolet waves, which makes it easier for butterflies to find them for food.
Invisible waves
Another type of electromagnetic wave that our brain indirectly perceives is called infrared. We can sense this as heat.
When you stand near to a bonfire, your skin detects the fire’s infrared electromagnetic waves. It then sends electrical signals to the brain to tell it that there is something hot nearby. The brain couldn’t detect this wave by itself.
But the human body has no way to detect radio waves, so our brain is completely unaware of them as they pass around us. But we can use technology – like a radio, or wifi – to convert the electrical energy in radio waves into something we can detect, such as the music playing on a radio station.
We also use technology to detect x-rays, another type of electromagnetic wave. X-rays are used in hospitals to look inside bodies – for instance, to see if a bone is broken. If you have an x-ray taken, hospital specialists send the x-rays through your body, and a machine can pick up how easily the x-rays travelled through different parts of your body. Areas that are more difficult for the x-ray to pass through, such as bone, show up as white.
Even though your brain is ridiculously clever, it would know nothing without the information that it receives from the rest of your body. You and all your experiences come from your body, your organs, and your senses detecting the world around you, and sending that information to your brain.
An enormously complicated set of tiny electrical signals later and you have a conscious experience of being you, inside your body, and in a world literally full of electromagnetic waves.![]()
Damian Cruse, Associate Professor in the School of Psychology, University of Birmingham
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Source Link: Can Our Brains Sense Electromagnetic Waves?