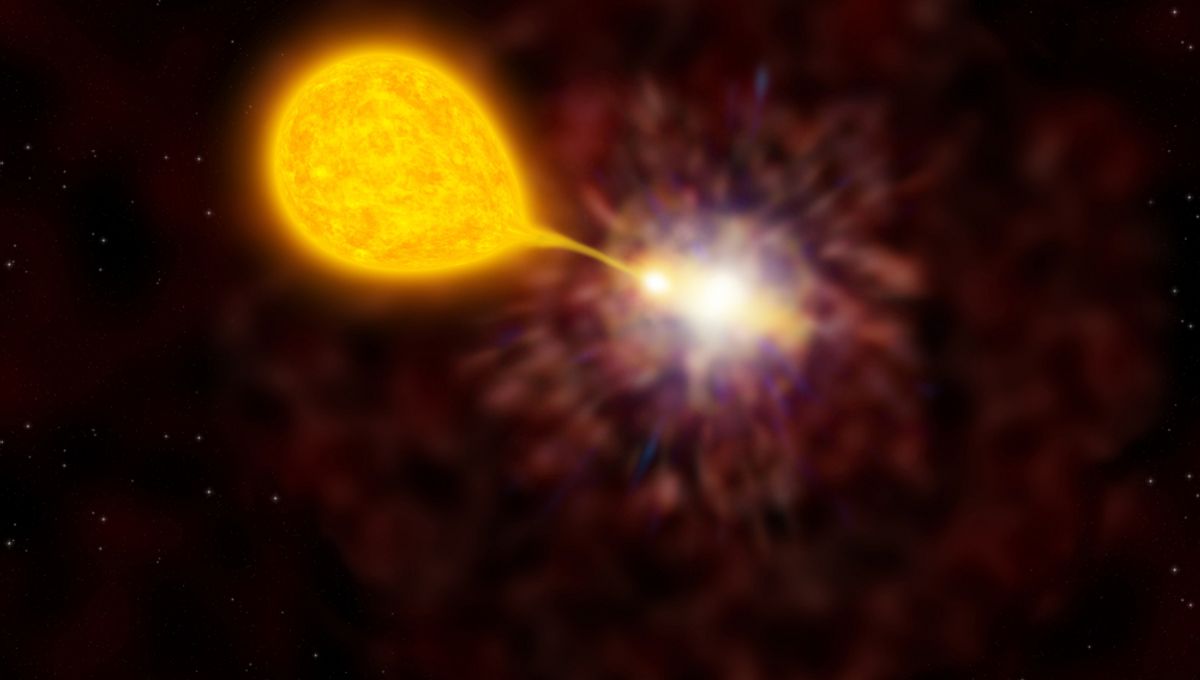
Most of the universe’s stars exist in pairs, sometimes after the more massive one completed its life cycle and became a white dwarf. This evolution changes the dance between the two, at least if they were fairly close to start off, as the dwarf’s powerful gravitational field draws the outer layers of the main sequence star to it, causing the two to orbit ever closer.
When enough material is transferred in this way, the pair become a cataclysmic variable (CV). The name comes not from an impending Armageddon, but the brief flashes of light these stars release when enough hydrogen is drawn onto the white dwarf to unleash nuclear fusion. The astronomers who first observed these events didn’t know the cause but concluded something enormous must be responsible. This type of object accounts for the majority of novae – stars called new because they suddenly brighten enough to become visible.
The newly discovered ZTF J1813+4251 system, reported in Nature, has an orbital period of just 51 minutes, the shortest time ever observed for this combination of star types to orbit each other. That alone would interest astronomers, but ZTF J1813+4251 is important for another reason – the pair eclipse each other as seen from Earth, allowing observers to measure their properties in unusual detail.
Astronomers have previously predicted a transition should occur as CVs draw closer to each other, reaching the point where the white dwarf has accreted, or captured, all the hydrogen from its companion and is now drawing helium.
Helium-accreting CVs have been detected and astronomers suspect they evolved from more conventional CVs, but since the process would have occurred tens or hundreds of millions of years ago, this has been unconfirmed.
“This is a rare case where we caught one of these systems in the act of switching from hydrogen to helium accretion,” said Dr Kevin Burdge of MIT in a statement. “People predicted these objects should transition to ultrashort orbits, and it was debated for a long time whether they could get short enough to emit detectable gravitational waves. This discovery puts that to rest.”
Burdge and co-authors found ZTF J1813+4251 by analyzing sky surveys covering more than 1.2 billion stars and looking for those that brightened and dimmed on very short timescales. The brightening comes not from fusion outbursts on the white dwarf – those are much rarer and less regular – but from the eclipsing process where one star blocks out the other’s light.
Confident only a binary pair, and probably a CV, would show a cycle like this, Burdge and co-authors got time on two of the world’s great telescopes to observe the light cycle in detail. They concluded the system is around 3,000 light years away and we can see it clearly enough to measure both the mass and radius of each component.
The white dwarf has about half the Sun’s mass, but in the nature of such burnt-out stars is a great deal smaller. Its companion has about 0.12 solar masses and is similar in size to Jupiter.
A sunlike star that was still mostly hydrogen could not have such a short orbit: Burdge said anything less than about eight hours would be impossible. Having lost most of its hydrogen to the white dwarf, however, the star in ZTF J1813+4251 has been reduced almost to its helium core, whose higher density makes shorter orbits possible.
Projecting forwards, the authors predict ZTF J1813+4251 will reach an orbit of just 18 minutes some 75 million years in the future when the system will be fully helium-accreting. Surprisingly, the stars will not then collide, but instead slowly move apart and the donor star will cool.
The authors expect to be able to detect the orbit shortening within a decade and to detect gravitational waves from the system using forthcoming instruments. This will allow astronomers to test Einstein’s predictions of the slowing produced by a gravitational wave of a particular size.
Although more than 1,000 CVs are known, only 12 have orbits shorter than 75 minutes. Consequently, ZTF J1813+4251 is not only a record-setter, but it also doesn’t have a lot of close counterparts that could be used for similar observations.
“This is a special system,” Burdge said. “We got doubly lucky to find a system that answers a big open question, and is one of the most beautifully behaved cataclysmic variables known.”
The paper is published in Nature.
Source Link: "Cataclysmic" Pair Of Stars With Shortest Known Orbit Discovered