As the planet heats up, glaciers worldwide are in retreat, and one above all others worries oceanographers. Scientists from the British Antarctic Survey have published two new papers observing conditions at the base of Antarctica’s Thwaites Glacier to establish the factors driving its melting and its effect on global sea level rise.
They found that enough of the glacier is vulnerable that, were it to collapse, sea levels would rise 65 centimeters (25 inches) worldwide, something that could happen within a century. On its own, such an event could make some low-lying cities such as Miami effectively uninhabitable. Combined with inevitable melting elsewhere, it would turn serious problems into catastrophes.
To reach this conclusion, the authors drilled access holes through almost 600 meters (1,900 feet) of ice downstream of the Thwaites Glacier’s grounding line, where the glacier stops sitting directly on bedrock and starts floating. Through the hole, they measured ocean temperature, salinity, melt rate, and the glacier’s speed. One paper describes observations made using a fixed mooring at the bottom of the hole. The other reports on observations made using an underwater vehicle, which could also study the shape of the underside of the ice.
The water at the bottom was found to be a warm (by Antarctic standards) 2.5°C (36°F) year-round. It is also stratified by salinity levels, which limits melting, as the ice is only in contact with the freshest, coldest water. Consequently, the bulk of the area studied is melting more slowly than expected, but certain hotspots are making up for it, losing ice terrifyingly fast.
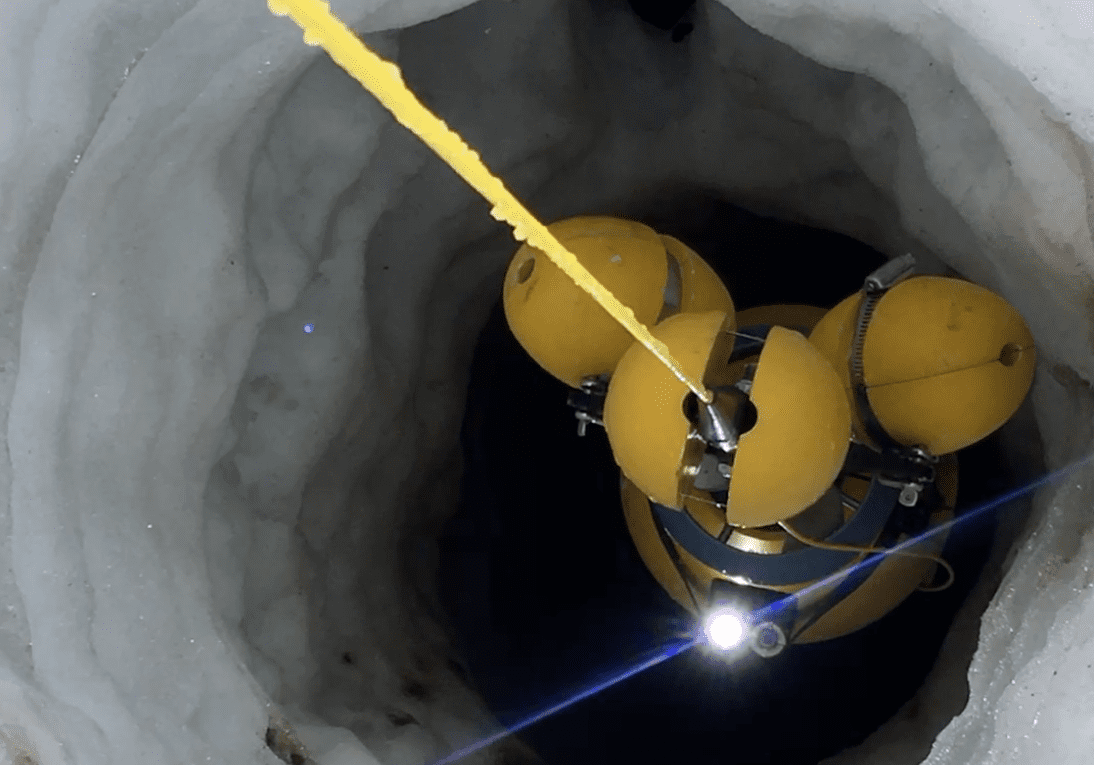
The undersea vehicle Icefin being pulled up through the borehole that was used to allow it to reach the water under the Thwaites Glacier. Image credit: Icefin/ITGC/Schmidt
Thwaites Glacier is part of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS), and has been long considered a major threat to sea levels worldwide because it is both big and unstable. Thwaites drains around a tenth of the WAIS and contains enough water to make vulnerable low-lying islands uninhabitable and cause the poisoning of some of the world’s richest agricultural lands with salt.
Moreover, the even larger components of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet are considered resistant to anything short of a major rise in global temperatures. Meanwhile, Thwaites sits on below-sea-level bedrock that gets deeper inland; prime conditions for a swift collapse, and indeed it has probably done so during humanity’s lifespan.
When humans were mobile hunter-gatherers with a population of a few million, the consequences of previous collapses were probably subtle. Now, as billions of us cluster around the coast, things are different.
Moreover, the collapse of Thwaites is considered a risk factor for exposing nearby glaciers to seawater, potentially triggering a domino effect that could cause sea levels to rise by 3 meters (10 feet).
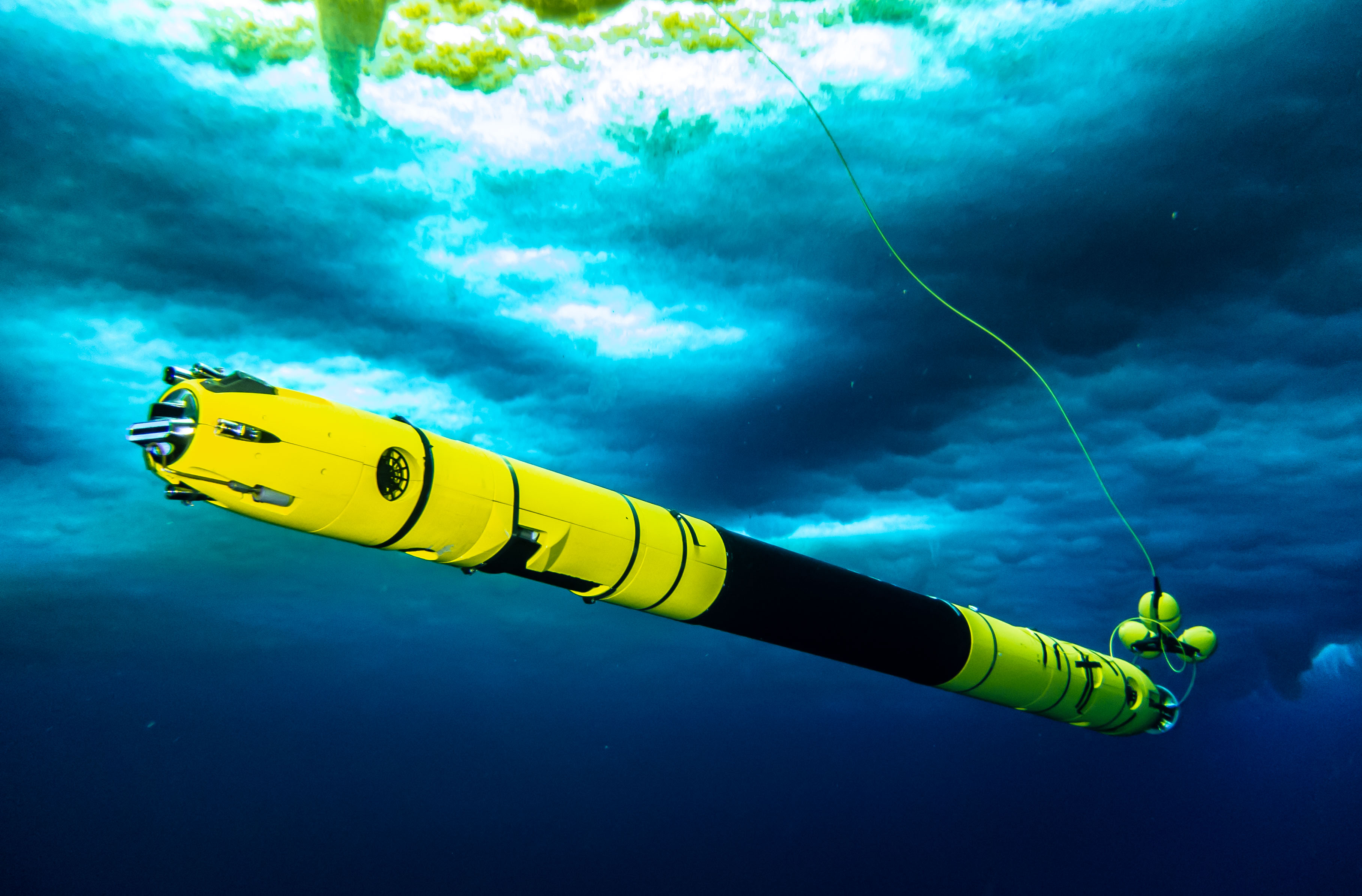
The underwater vehicle Icefin photographed under the ice near McMurdo Station. Image credit: Rob Robbins USAP Driver
Crucially, the underwater vehicle, Icefin, revealed the glacier melts fast when ice is sharply sloped at the point where it meets the ocean, and much more slowly when it is flat, making future melting hard to predict. One steep section of the glacier is melting six times faster than flat regions. Moreover, the main trunk of the glacier is more steeply sloped than the area studied here, suggesting melt rates could be higher.
Consequently, the hole was drilled in an area that not too long ago was still anchored to land – the grounding line has retreated 14 kilometers (8 miles) since the 1990s.
“Our results are a surprise but the glacier is still in trouble. If an ice shelf and a glacier is in balance, the ice coming off the continent will match the amount of ice being lost through melting and iceberg calving. What we have found is that despite small amounts of melting there is still rapid glacier retreat, so it seems that it doesn’t take a lot to push the glacier out of balance,” said Dr Peter Davis of the British Antarctic Survey in a statement.
United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres warned this week that sea level rise could cause a “mass exodus on a biblical scale”. The Thwaites Glacier could be key to whether that occurs.
The papers are published in Nature, and are available here and here.
Source Link: Collapse Of Thwaites “Doomsday” Glacier Depends On Small Areas Of Accelerated Melting