Whether it’s the classic nightmare about having to take a test you haven’t studied for, or the surprisingly common one about all your teeth falling out, dreaming is an almost universal human experience. But while we might know quite a bit about what goes on in the brains of slumbering mammals, birds have so far been more of a mystery. A new study has started to remedy this by investigating sleep in pigeons, and found some surprising evidence that they might be dreamers too.
In humans, our most vivid and memorable dreams happen during the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of sleep, when the brain is at its most active. It is during the less active, non-REM sleep that the brain gets rid of waste products by flushing its ventricles with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Scientists wanted to find out whether these same processes are common to other groups of animals, as well as trying to better understand how the dynamics of CSF flow change during the transition from non-REM to REM sleep. Since birds were already known to experience periods of REM sleep, as well as having dense, cell-packed brains that are likely to generate a lot of waste products, they seemed like the perfect model animal to address these questions.
The study included 15 specially trained pigeons, which underwent functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and video-recorded pupillometry (measurement of eye movements) while asleep and awake.
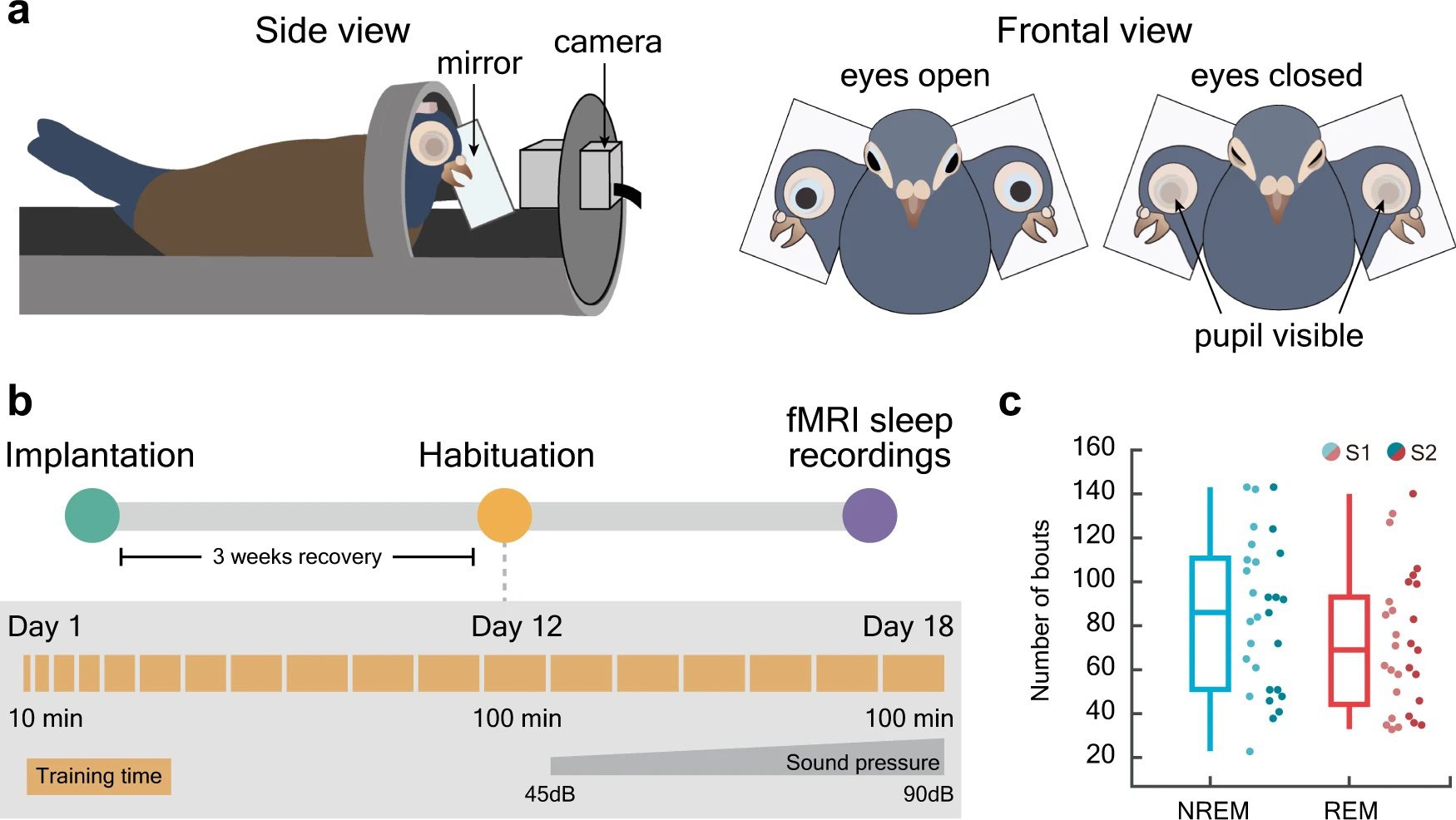
This graphic summarizes the experimental setup, including (a) the scanning and pupillometry, and (b) the training phase that took place before the sleep recordings were made. The graph in (c) shows data on the number of REM and non-REM phases each bird experienced.
“We were able to observe whether one or both eyes were open or closed, and to track eye movements and changes in pupil size through the pigeons’ transparent eyelids during sleep,” explained study co-author Mehdi Behroozi in a statement. The fMRI, meanwhile, was tracking activation patterns and CSF flow through the brain.
The CSF flow did increase during non-REM sleep, just like it does in humans, but the more surprising finding was that the flow decreased substantially during REM sleep. This had never been observed in any animal before.
What did happen during REM sleep was a spike in activity in brain regions associated with visual processing and wing movements, opening up the tantalizing possibility that the pigeons might have been dreaming of taking flight. The amygdala was also activated, which according to co-author Gianina Ungurean “suggests that if birds experience something similar to our human dreams, pigeons’ dreams might include emotions as well.”
Putting these observations together, the researchers propose an explanation for the dramatic decrease in CSF flow when the brain transitions to a REM state.
“We think that the increased flood of blood into the brain during REM sleep, which supports the elevated brain activity, might block the [CSF] from moving from the ventricles into the brain,” said senior author Niels Rattenborg. “This suggests that REM sleep and its functions might come at the expense of waste removal from the brain.”
However, it is possible that switching between REM and non-REM, which birds do particularly often during sleep, could help contribute to more efficient waste removal. As Ungurean explained, “At the onset of REM sleep, the influx of blood increases vessel diameter. This might force [CSF] that entered the space surrounding the vessels during non-REM sleep to flow into the brain tissue, and enhance the outflow of fluids carrying waste products.”
In the future, this research might take an even more fascinating turn. “We hope to train birds to report if and what they just saw upon awakening from REM sleep,” Ungurean said. “That would be an essential step towards establishing whether they dream.”
So, as well as learning more about all the important ways sleep affects our brains, we could one day ask the pigeons themselves, not only if they dream of flight, but maybe even where their slumberland journeys take them.
The study is published in Nature Communications.
Source Link: Do Pigeons Dream Of Electric Sheep? No, But They Might Dream About Flying