The idea of a pterosaur even the size of those in Jurassic Park III is terrifying enough, but now imagine one that’s 3.5 meters (11.5 feet) tall and with a wingspan longer than a London bus. We’re sorry to tell you, but that creature was real – and it may well be the largest animal ever to have taken to the skies.
Dubbed “Dracula” by scientists (for reasons that are about to become obvious), this giant pterosaur was uncovered by scientists in Transylvania, Romania. While its exact species is unclear, it’s believed to be a member of Azhdarchidae, a family of pterosaurs that lived during the Late Cretaceous and are well-known for being big.
Dracula’s size has led some to wonder whether or not it was capable of flight – if it was, then it may have been the largest flying creature to ever grace the planet.
However, the pterosaur’s remains were found fragmented, which means it’s hard to come up with a reliable answer, though some recent research suggests that even some of the biggest pterosaurs could most likely fly.

Dracula on display in Germany.
Image credit: Axel Schmidt, Altmühltal Dinosaur Museum
The other important question is how Dracula “oh lawd he comin” the pterosaur, and others of its kind, were able to get so big. Weirdly, for animals best known for being airborne, it comes down to their ability to walk well.
That’s according to a new study published in the journal Current Biology led by researchers at the University of Leicester, who examined the evolutionary history of pterosaurs through the lens of the ancient creatures’ fossilized hands and feet.
In doing so, the team revealed a distinct shift in the mid-Jurassic, at which point the anatomy of pterosaurs’ hands and feet became more similar to that of animals living on the ground.
“In early pterosaurs the hind limbs were connected by a flight membrane which severely impeded walking and running,” said study co-author Dr David Unwin in a statement sent to IFLScience.
“In later, more advanced pterosaurs, this membrane became separated along the midline, allowing each hind limb to move independently. This was a key innovation that, combined with changes to their hands and feet, greatly improved pterosaurs’ mobility on the ground.”
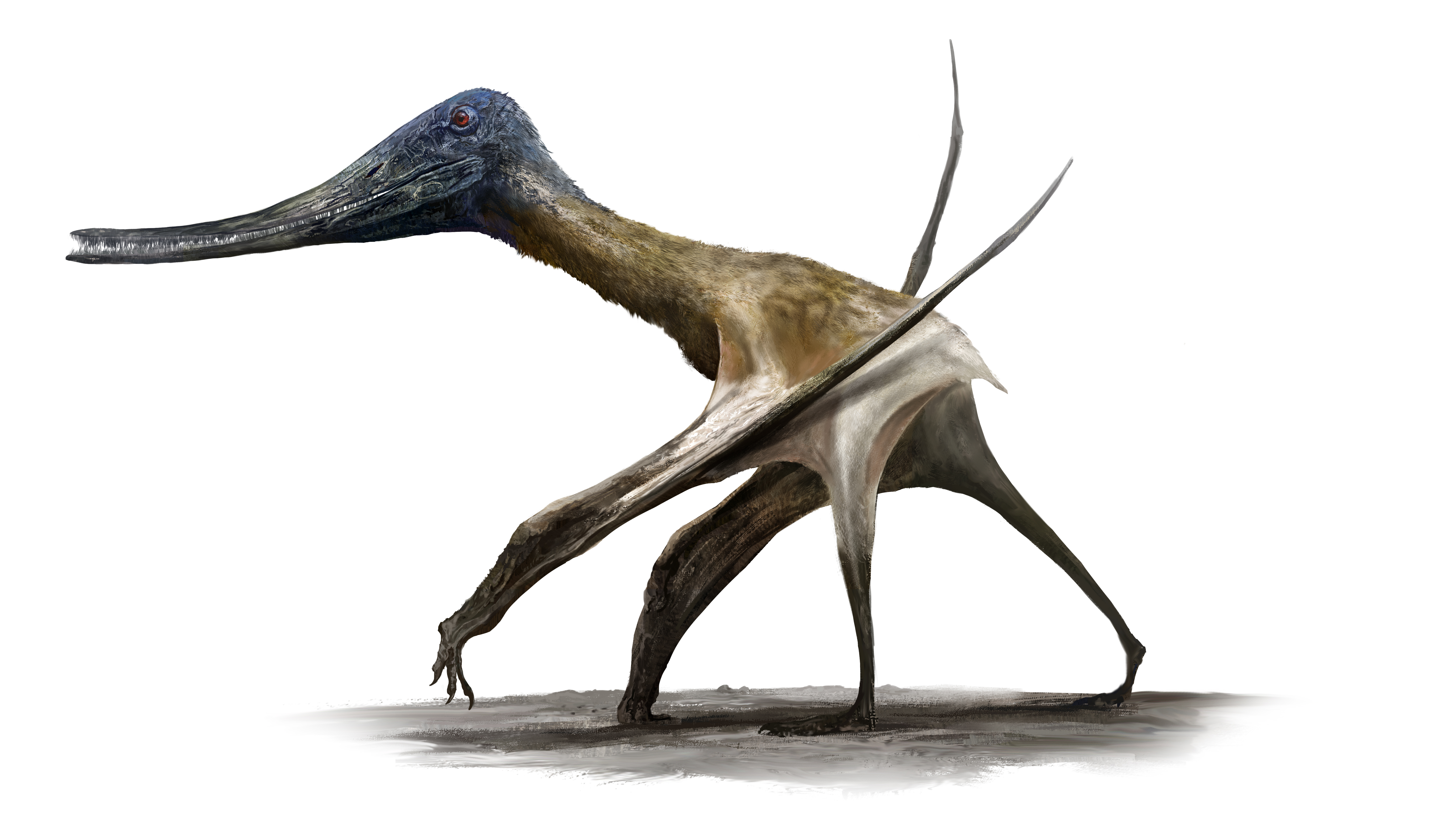
Get Balaenognathus on a runway, ASAP.
Image credit: Rudolf Hima
This was the key to unlocking bigger bodies, explained Unwin. “Freed from the constraints of climbing, these later pterosaurs could grow to enormous sizes, with some species becoming true giants of the Mesozoic.”
The study’s findings are an example of why looking beyond the obvious features is often one of the best ways to make new discoveries.
“That pterosaurs could fly is only one part of their story,” said lead author Robert Smyth. “By exploring how they lived in the trees or on the ground, we can begin to understand the roles that they played in ancient ecosystems.”
[H/T: Atlas Obscura]
Source Link: "Dracula" May Have Been The Largest Flying Creature The World Has Ever Seen