Escherichia coli bacteria sometimes organize themselves into sets of four known as rosettes, a trait usually associated with multicellular organisms like ourselves, as a step towards becoming biofilms. The finding blurs what is considered perhaps the most important division among living things, and also raises questions about how we missed something so important in such a well-studied lifeform.
If you include university undergraduates, the scientific researchers who have studied E. coli probably run into the millions. It is, after all, the organism scientists use as a model for all bacteria, and to some extent, all single-celled organisms. We measure its abundance to track the health of our waterways, cherish beneficial strains for producing vitamin K2, and fight the varieties that are a major cause of food poisoning.
Most of all, scientists have studied E.coli’s evolution and genome in extraordinary depth, leading to modifications to produce vital drugs such as human insulin and proteins that are hard to obtain naturally. Yet, according to a paper in iScience, all this time we may have been looking at it wrong, treating each cell as entirely independent.
The fact E. coli, like many other unicellular organisms, can sometimes cooperate is well known. They form biofilms that protect them against outside attack, including from antibiotics and host immune systems. The biofilms depend on a sugar polymer that binds the bacteria to each other, whose product, the paper notes, “has a significant metabolic cost” and so requires powerful evolutionary drivers to be maintained.
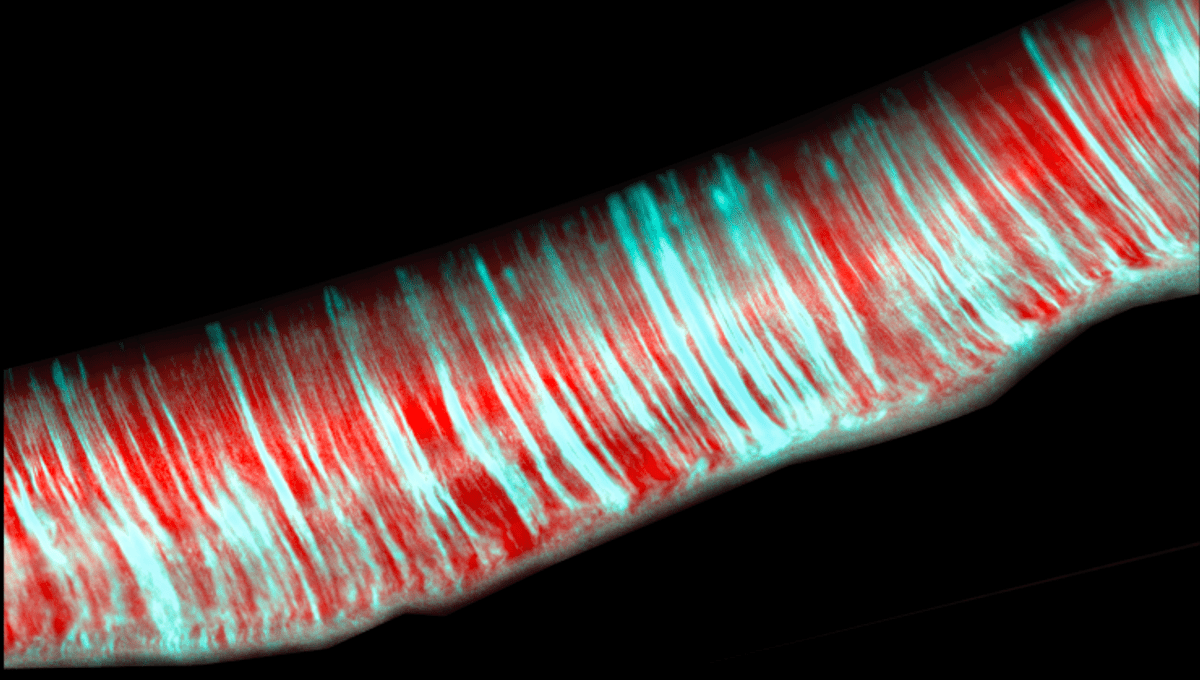
When Dr Kyle Allison of Georgia Tech and co-authors examined how biofilms form, they observed something new. Individual E. coli were joining into four cell structures known as rosettes, which in turn grew into parallel chains of constant width. After about 10 generations of cell division, the chains attached to surfaces and stopped growing.
The team even identified the gene, Ag43, that makes the rosette formation possible.
“Rosettes are rather significant in higher organisms, like mammals, because they initiate developmental processes like embryogenesis,” Allison said in a statement. The few cases where they had been seen in bacteria were considered rare exceptions.
“What we’re seeing here is bacteria maybe are not what we’ve considered in the past,” Allison said. “My suspicion is that what we found is far more common than we knew.”
The team also demonstrated chains are formed of clones of a single bacterium. When two chains from different bacteria come into contact, they keep to their own kind rather than mix or exchange.
All the observations were in the lab, so the authors acknowledge they don’t know how often E. coli practice this form of multicellularity in our large intestines or on plants. However, they saw the same behavior in a strain cultured over a century ago and one taken from a recent urinary tract infection (80 percent of which are caused by E. coli) so the capacity at least is widespread.
The full implications of the discovery could take a long time to explore. It may offer an explanation for how multicellularity first evolved, leading eventually to us. On a more practical level, biofilms are involved in an estimated 80 percent of bacterial infections – many of them specifically caused by E. coli. Understanding how they form could help treat them.
The authors also think we can use biofilms to our advantage, for example when encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria to keep pathogens out of the human body.
The paper is Open Access in iScience.
Source Link: E. coli, The Archetypal Single-Celled Organism, Has A Secret Multicellular Lifestyle