As the Moon orbits the Earth, the Earth orbits the Sun, and the Sun orbits the center of the Milky Way, oscillating up and down relative to the galactic plane as it does so. But this might have consequences, with a group of physicists suggesting that this motion of our star through the galaxy potentially takes us through regions of space that could affect our planet’s climate.
According to the study detailing their findings, the Solar System may have passed through an interstellar cloud so dense that it could have interfered with the flow of the solar wind, potentially cooling the planets.
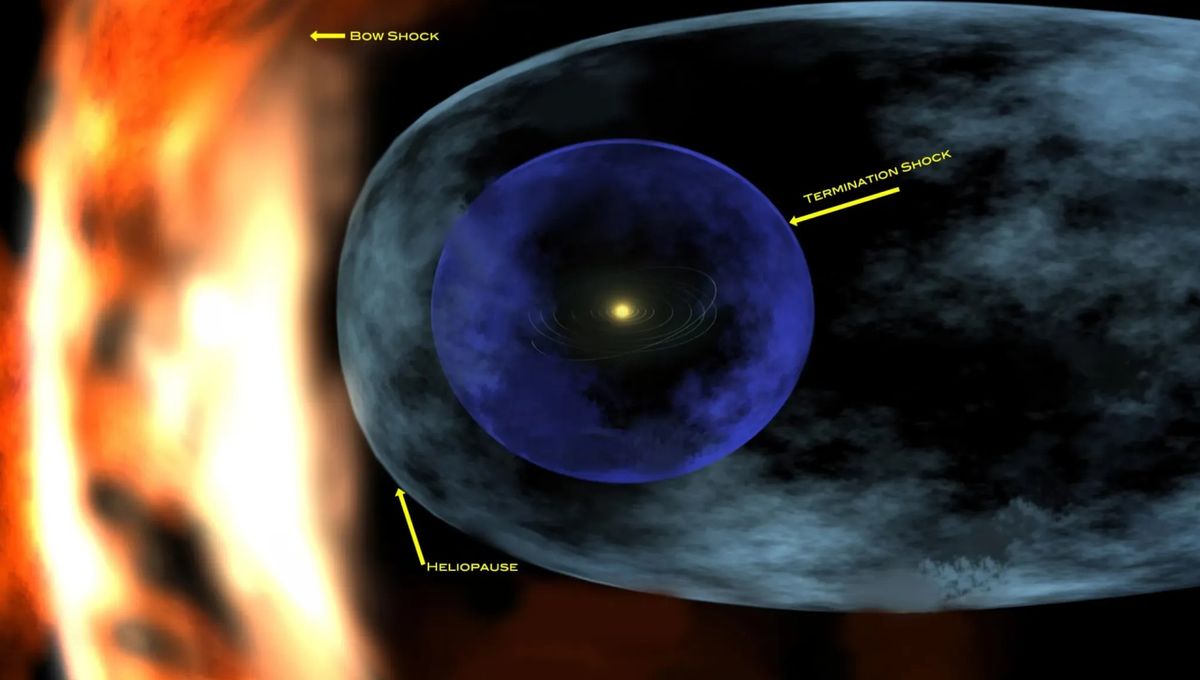
The Solar System is protected, to some extent, from the interstellar medium (ISM) by our heliosphere.
“The Sun sends out a constant flow of charged particles called the solar wind, which ultimately travels past all the planets to some three times the distance to Pluto before being impeded by the interstellar medium,” NASA explains. “This forms a giant bubble around the Sun and its planets, known as the heliosphere.”
The Solar System is currently in a 1,000-light-year-wide “Local Bubble“, or “local interstellar cloud” (LIC). This “bubble” is a lot less dense than typical interstellar space, with 0.001 particles per cubic centimeter compared to the typical 0.1 atoms per cubic centimeter. The Solar System will leave this sparse region of space in the next few thousand years and head once more into the interstellar medium.
Looking at the Solar System’s path, and mapping the Local Ribbon of Cold Clouds, the team found we have likely traveled through denser regions in the past.
“In the ISM that the Sun has traversed for the last couple of million years, there are cold, compact clouds that could have drastically affected the heliosphere,” the team explains in their paper. “We explore a scenario whereby the Solar System went through a cold gas cloud a few million years ago.”
Though research on the effects of traversing such regions has been sparser than atoms in the Local Bubble, the team believes it could have contracted our heliosphere, which in turn had an effect on our climate. Our heliosphere is protective, and as it contracted some of the material in these denser regions could reach Earth.
“Large amounts of neutral hydrogen as a result of an encounter with cold clouds with densities above 1,000 cm−3 will alter the chemistry of Earth’s atmosphere,” the team writes. “Very few works have investigated the climatic effects of such encounters quantitatively in the context of encounters with dense giant molecular clouds. Some argue that such high densities would deplete the ozone in the mid-atmosphere (50–100 km [31–62 miles]) and eventually cool the Earth.”
The team says that geological evidence of increased amounts of 60Fe (iron 60) and 244Pu (plutonium 244) isotopes found in ice cores, the oceans, Antarctic snow, and samples of the Moon, could be evidence of these particles reaching Earth as we traversed the Local Lynx of Cold Cloud 2 million years ago.
These isotopes are spat out by supernovas and neutron star mergers, which then become trapped by interstellar dust. These isotopes in the geological record have previously been explained as being sent here by a close supernova, but the current team believes they could be explained better by particles trapped in the cloud, as a close-by supernova would collapse the heliosphere to distances of 1 AU (the distance between the Earth and the Sun), while a further afield supernova would not deposit enough 60Fe on Earth.
“This paper is the first to quantitatively show there was an encounter between the Sun and something outside of the solar system that would have affected Earth’s climate,” space physicist at Boston University, Merav Opher, said in a statement, later adding, “but as soon as the Earth was away from the cold cloud, the heliosphere engulfed all the planets, including Earth.”
The contraction of the heliosphere could have lasted from hundreds of years to a million years, according to the team, and it is likely we will encounter another such heliosphere-contracting cloud within another million years or so.
While interesting, there is a lot more to find out.
“This work should be revisited with modern atmospheric modelling,” the team writes. “It has been suggested that climate changes around this time could have affected human evolution. The hypothesis is that the emergence of our species Homo sapiens was shaped by the need to adapt to climate change. With the shrinkage of the heliosphere, the Earth was exposed directly to the ISM.”
The study is published in Nature Astronomy.
An earlier version of this article was published in June 2024.
Source Link: Earth's Past Ice Ages Could Have Been Triggered By Our Movement Through The Galaxy