Planetary scientists believe they have found an enormous deposit of water ice near the Mars equator. Almost two decades ago, researchers discovered some peculiar deep deposits underneath the Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF). The latest data suggest these deposits are extremely rich in ice.
The MFF is made of many wind-sculpted features and has an area of about one-fifth of the continental United States. It is believed to be the biggest single source of dust on Mars and it extends all the way to Gale Crater, which NASA’s Curiosity is exploring.
Data from the European Space Agency’s Mars Express suggest that there is so much ice there, that if it were to melt it would cover Mars in a layer of water 1.5 to 2.7 meters ( 4.9 to 8.6 feet) deep. That’s the amount of water found in the whole Red Sea on Earth.
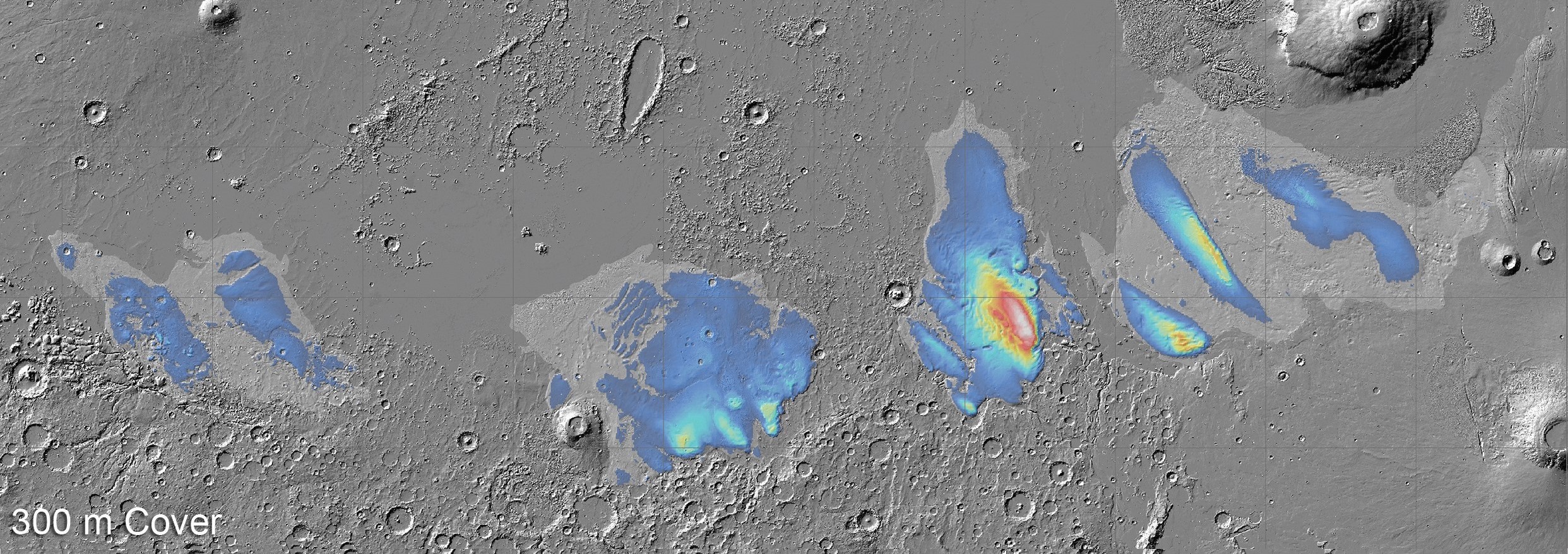
Map of potential ice thickness in the MFF.
Image Credit: ESA
“We’ve explored the MFF again using newer data from Mars Express’s MARSIS radar, and found the deposits to be even thicker than we thought: up to 3.7 km [2.3 miles] thick,” Dr Thomas Watters of the Smithsonian Institution, USA, lead author of both the new research and the initial 2007 study, said in a statement sent to IFLScience.
“Excitingly, the radar signals match what we’d expect to see from layered ice, and are similar to the signals we see from Mars’s polar caps, which we know to be very ice-rich.”
Since the initial observations, researchers considered the possibility that the deposit was rich in ice. It was relatively transparent to radar and low in density, so it was certainly not hard rock, but they couldn’t rule out that it could be a giant deposit of dust, volcanic ash, or sediments.
“Here’s where the new radar data comes in! Given how deep it is, if the MFF was simply a giant pile of dust, we’d expect it to become compacted under its own weight,” said co-author Andrea Cicchetti of the National Institute for Astrophysics, Italy. “This would create something far denser than what we actually see with MARSIS. And when we modelled how different ice-free materials would behave, nothing reproduced the properties of the MFF – we need ice.”
The current view sees the MFF as made of vast layers of ice and dust, topped by a final protective layer of dust or ash several hundred meters thick. This is what has kept the ice protected. Although scientists are unsure for how long.
“This latest analysis challenges our understanding of the Medusae Fossae Formation, and raises as many questions as answers,” said Colin Wilson, ESA project scientist for Mars Express and the ESA ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO).
“How long ago did these ice deposits form, and what was Mars like at that time? If confirmed to be water ice, these massive deposits would change our understanding of Mars climate history. Any reservoir of ancient water would be a fascinating target for human or robotic exploration.”
A paper about this research is published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
Source Link: Enormous Ice Deposit Nearly 4 Kilometers Thick Discovered Under Mars’s Equator