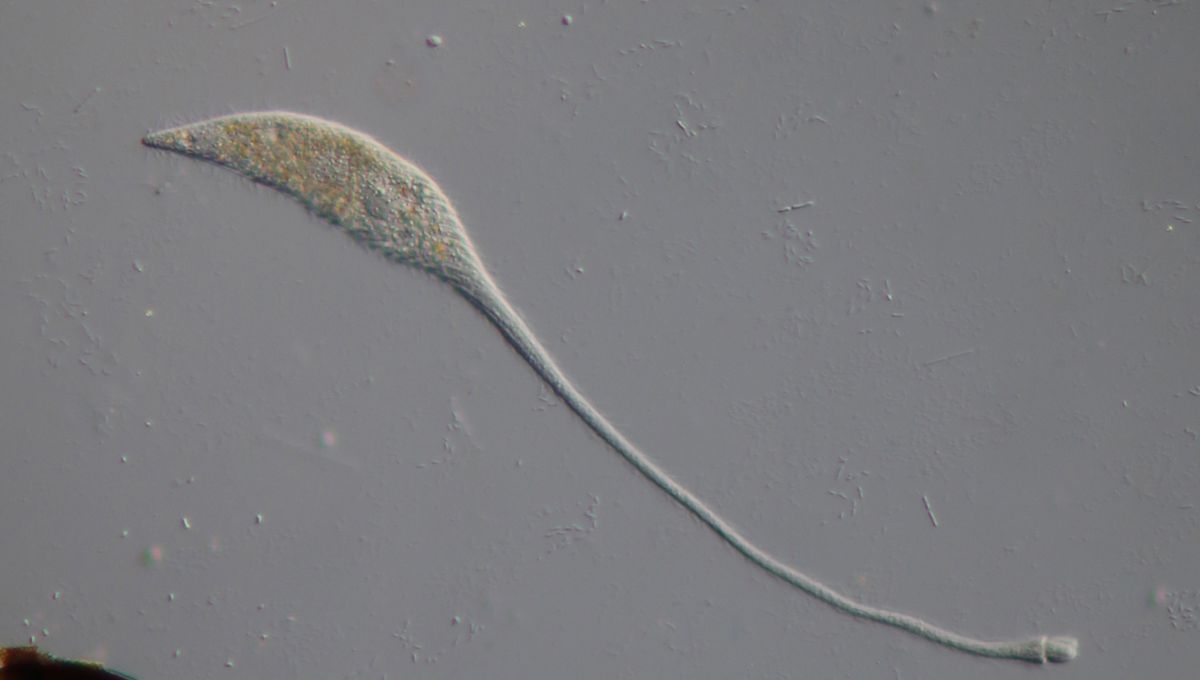
For a one-cell organism with no nervous system, Lacrymaria olor is a pretty impressive predator. Extending a long, wiggling neck from its pear-shaped body, L. olor hunts down prey to chomp on in the ponds where it lives. Just how it manages this remained a bit of a mystery, but a pair of determined scientists have now completed a seven-year study proving it’s down to the first observed case of cellular “origami”.
From the first viewing, associate professor of engineering Manu Prakash was enthralled by the antics of the single-celled protist L. olor. “There are some things in life you can watch and then never unwatch. It’s … just … it’s mesmerizing,” Prakash – who first observed the creature using the Foldscope paper microscope he helped develop – told the Stanford Report. This playfulness is central to Prakash’s approach to research, which he calls recreational biology, or “old-school science”.
You can see the fascinating display for yourself in the video below. Despite having no nervous system, and so none of the usual ways of responding to its environment through complex behaviors, L. olor can extend its swan-like neck more than 30 times its original body length in just 30 seconds.
In human terms, that would be like a 1.8-meter-tall (6-foot-tall) person extending their head more than 60 meters (200 feet).
Many have observed this wondrous behavior, but until Prakash and graduate student Eliott Flaum launched an in-depth investigation, it was unclear how it happened. “We started with a puzzle. Ellie and I asked a very simple question: Where does this material come from? And where does it go?”
Now, they have discovered the answer in a previously unknown geometric mechanism.
“This is the first example of cellular origami,” Prakash said. “We’re thinking of calling it lacrygami.”
Specifically, L. olor is making use of curved-crease origami. Thin microtubules in a helical shape are wrapped up inside the cell’s membrane and encased in a delicate, curved shroud. Each L. olor cell has 15 of these which can coil and uncoil to project and retract the neck – think of an accordion being pulled out and in. Because the very fine membrane is folded into pleats, you can store “an infinite amount of material,” said Flaum. “Biology has figured this out.”
Prakash and Flaum were able to observe all this cellular machinery using transmission electron microscopy.
Even more incredible is the fact that one L. olor individual will perform this process flawlessly more than 20,000 times during its life. “L. olor is bound by its geometry to fold and unfold in this particular way,” Flaum explained.
The point at which the folded membrane begins to unfold is known mathematically as a singularity. At this precise point, the structure is both folded and unfolded at the same time. Prakash and Flaum observed that the singularity in L. olor travels the exact same path every single time it extends and retracts its neck – all 20,000 of them – and in this way acts as a controller of the mechanism.
It’s this that makes L. olor so unique, even among organisms that are closely related to it. “This is the first time a geometric controller of behavior has been described in a living cell,” Prakash said.
As a bioengineer, Prakash is already considering the possible applications of this discovery in bioinspired technologies, including microrobots and new ways of building structures in space. In a summary of their paper, Prakash and Flaum conclude: “The blueprints we have been looking for to bring agency and embedded control in microrobotics might be hidden in plain sight in the geometrical diversity of protists.”
The study is published in Science.
Source Link: First-Of-Its-Kind “Origami” Solves Mystery Of This Single-Celled Critter’s Impressive Neck