Tiny pollen grains too small to see have revealed that flowers are at least 123 million years old, more than 2 million years older than the previous oldest example. The date signals not just the origins of the things that bring color to our gardens but the most abundant clade of land plants on the planet today.
Flowering plants (angiosperms) are now so close to universal that they sometimes seem synonymous with plants to non-botanists. Conifers maintain their dominance in the forests of the far north, as well as providing the tallest trees on the planet, but otherwise non-flowering plants are represented by the humble mosses, and ferns that survive literally in flowering plants’ shadow.
Yet for almost three-quarters of the time since plants established themselves on land, there were no flowering plants at all. The development of pollen, and with it a vastly expanded range of options for conquering new territory, changed everything. However, even such an important innovation as this takes time to spread, so it was millions of years before the angiosperms were widespread enough to be obvious in the fossil record.
Examination of coastal sediments in what is now Portugal has revealed pollen grains just 0.02 millimeters (0.0008 Inches) wide, the oldest coming from sediments 123 million years ago. The grains could be found because, like most mammals, these pollens fluoresce under the right light. When a confocal laser scanning microscope was shone on some of the sediments four miniscule grains glowed in samples collected 27 kilometers (16 miles) apart.
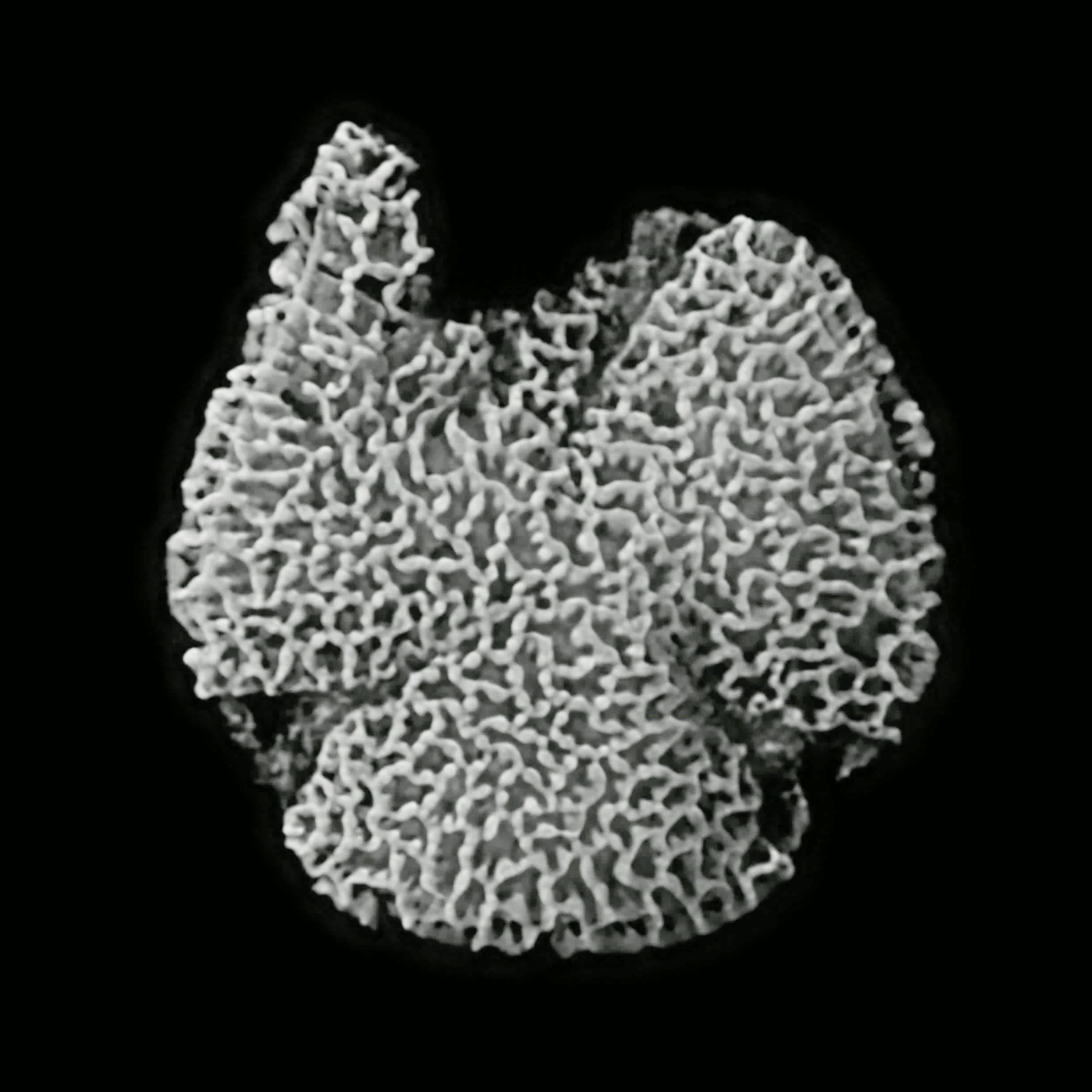
This 123-million-year-old tricolpate pollen grain recovered from Cretaceous sediments in Portugal is the oldest known evidence of a flowering plant.
Image Credit: Julia Gravendyck
Closer analysis revealed three small furrows on each grain’s outer walls, the identifying feature of tricolpate pollen, used by more than 70 percent of angiosperms today. It’s thought the grains fell into a river and were washed downstream and out to sea. Strontium isotope analysis of seashells buried in the same layer, considered to be an unusually precise method for dating fossils, established the age of the grains.
The previous oldest pollen grain was found on the Isle of Wight in 1990, and was estimated to be 120.4 million years old. Aside from being even smaller than the Portuguese pollen grains, that grain closely resembles the new discoveries. Several other pollen grains have been found that are hard to date, but might be equally old.
Whether this was the birthplace of angiosperms, or if they originated even earlier somewhere else can’t be known yet, but the discovery does prove the first flowers needed some upgrades to achieve their eventual dominance.
“The emergence of flowering plants altered the biological diversity considerably,” said Professor Ulrich Heimhofer of Leibniz University Hannover in a statement. “But exactly where and when this development began has been an enigma that Darwin already called an ‘abominable mystery,'” said first author Dr Julia Gravendyck of the University of Bonn.
The reason Darwin considered the mystery so abominable is that flowers appeared to go from nothing to 100 is such a short time in the fossil record. However, those few layers of rock that separated absence from domination represented millions of years, something Darwin couldn’t know at the time.
We also know little about what kind of plant it was that kicked off this world-changing innovation, although they certainly started small. The plants responsible for these grains were eudicots, angiosperms with two seed leaves when they germinate
Portugal was in the mid-latitudes in the early Cretaceous, as it is today, so the discovery calls into question the hypothesis that angiosperms first appeared in the tropics, although the authors say this “remains plausible”.
The study is published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Source Link: Flowers Have Been Blooming On Earth For 2 Million Years Longer Than We Thought