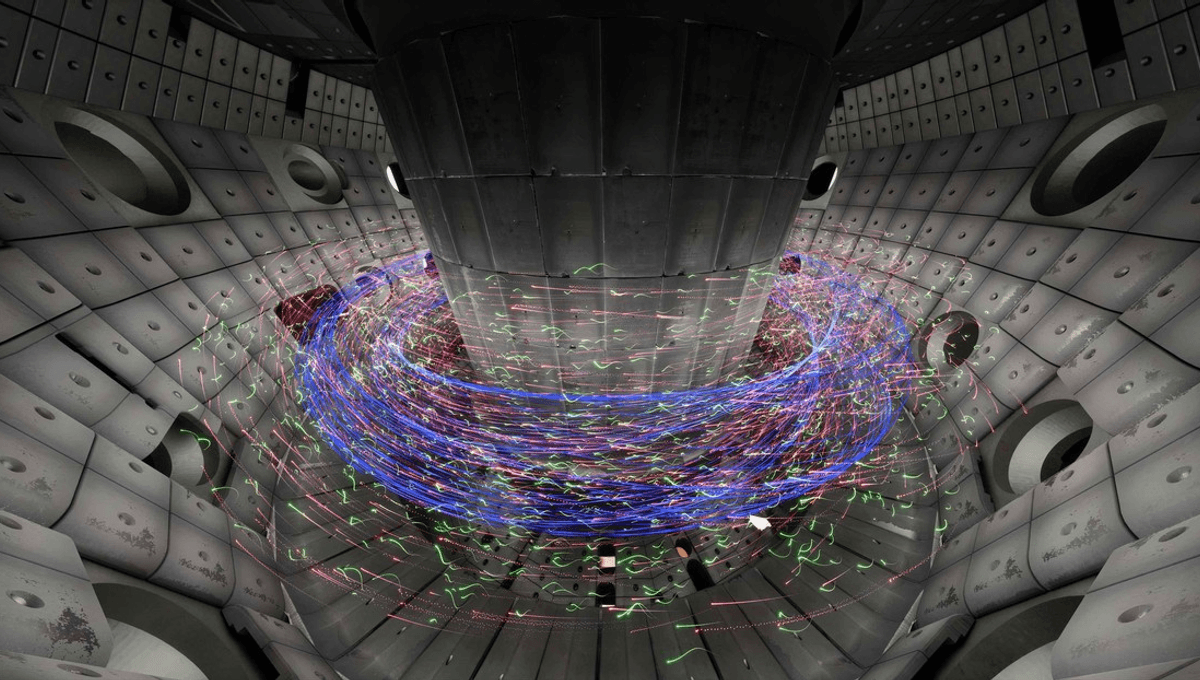
Researchers have been able to turn simulation and observational data from a fusion reactor into an incredible 3D simulation. It provides a view of what it would be like to fly through the plasma, and gives insights into how the reactor behaves at such extreme temperatures.
The modeled reactor is a faithful reproduction of EPFL’s variable-configuration tokamak (TCV). A tokamak is a donut-shaped reactor. Plasma at a temperature of over 100 million degrees flows through it and fusion takes place. The team at the Laboratory for Experimental Museology (EM+), part of the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, recreated this 30-year-old machine and provided us with a unique way to look inside.
“We used a robot to generate ultra-high-precision scans of the reactor interior, which we then compiled to produce a 3D model that replicates its components right down to their texture,” Samy Mannane, a computer scientist at EM+, said in a statement. “We were even able to capture the wear and tear on the graphite tiles lining the reactor walls, which are subject to extremely high temperatures during test runs of the TCV.”
Flying through the fusion reactor is cool for everyone, but scientists can use it to actually learn how to improve the design and make the reaction more efficient. The simulation delivers the position of thousands of particles and their effects, shifting about 60 times per second. A special computing setup with five computers and 10 GPUs in total delivered this incredible visualization.
“We were able to build our system thanks to advances in infographics technology,” explained Sarah Kenderdine, the professor who heads EM+. “It would’ve been impossible even just five years ago.”
The visualization shows the particles involved in the reaction. Electrons are in red; protons are in green; and blue lines indicate the magnetic field. They swirl around and interact, just as they would in the actual tokamak.
“The physics behind the visualization process is extremely complicated,” added Paolo Ricci, director of the Swiss Plasma Center. “Tokamaks have many different moving parts: particles with heterogenous behavior, magnetic fields, waves for heating the plasma, particles injected from the outside, gases, and more. Even physicists have a hard time sorting everything out. The visualization developed by EM+ combines the standard output of simulation programs – basically, tables of numbers – with real-time visualization techniques that the lab uses to create a video-game-like atmosphere.”
The visualization is not just a pretty video. It’s accurate, it’s coherent, and it’s realistic.
Source Link: Fly Inside A Nuclear Fusion Reactor Thanks To This Spectacular Simulation