Even science is prone to the occasional case of mistaken identity, particularly when it comes to figuring out what’s in a fossil. When Colombian priest Padre Gustavo Huertas found two small, round rocks with leaf-like patterns sometime between the 1950s and 70s, he classified them as fossilized plants. But on more recent examination, it was revealed the rocks weren’t the remains of ancient plant life after all – they were baby turtle shells.
Huertas originally deemed the fossils to be specimens of the plant species Sphenophyllum colombianum. This was odd; the fossils dated to the Early Cretaceous, but other members of this plant’s genus were thought to have died out more than 100 million years before that time.
Upon closer inspection of one of the fossils, researchers Fabiany Herrera and Héctor Palma-Castro noticed key plant features, such as its shape and veins, were missing. Instead, it looked more like bone. Palaeontologist Edwin-Alberto Cadena confirmed this was indeed the case – and that bone was the shell of a tiny turtle.
“They sent me the photos, and I said, ‘This definitely looks like a carapace’ – the bony upper shell of a turtle,” said Cadena. It also turned out that the visible part of the fossil was the underside of the turtle shell, which could explain why it was misidentified.
What Huertas may have thought to be leaves and stems were instead the rib bones and vertebrae making up the shell. The more typically identifiable marks that could be used to compare to other turtles, both modern and fossilized, are found on the outside of the shell.
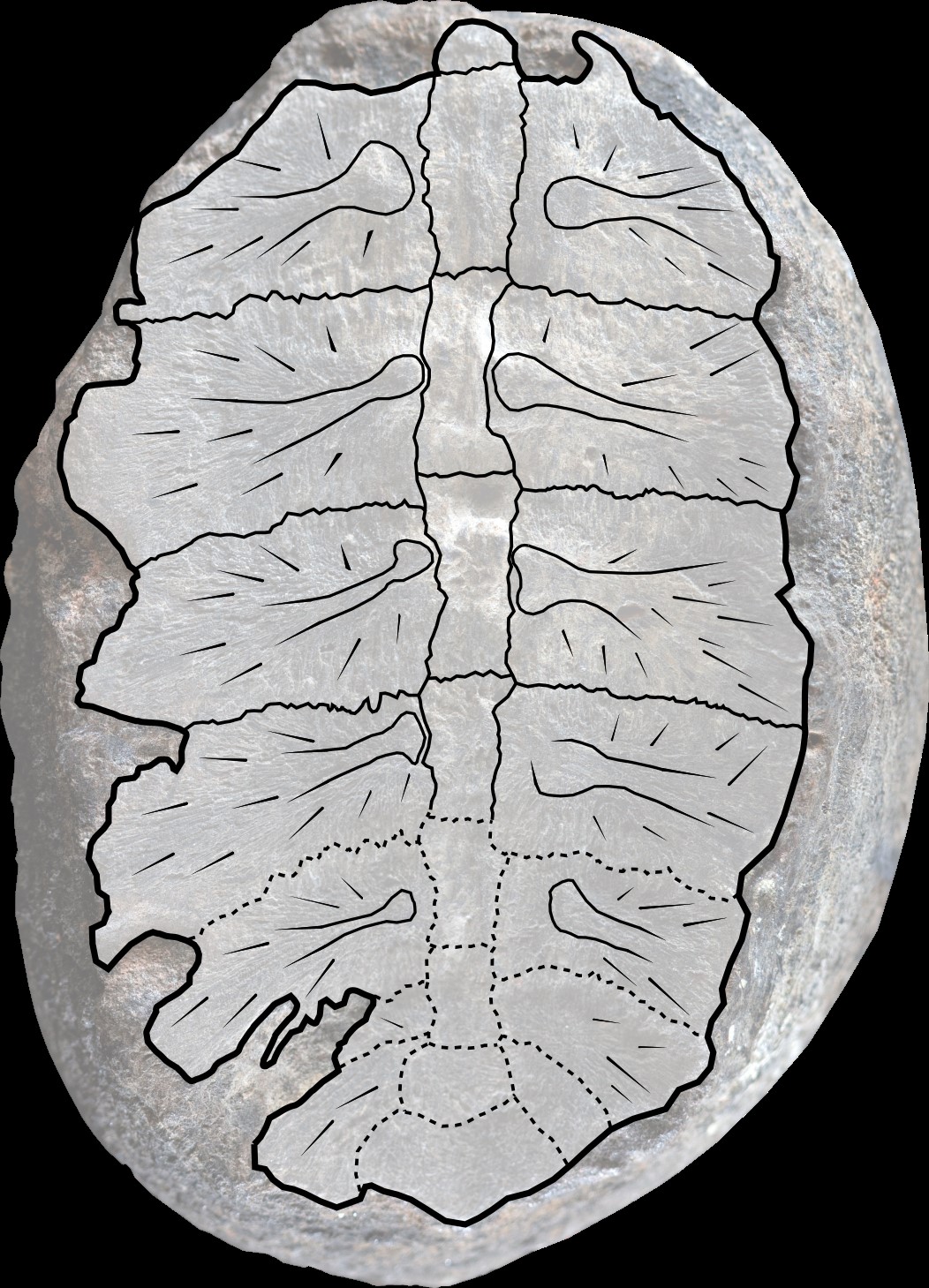
The turtle fossil with rib and back bones superimposed.
Image credit: Photo by Fabiany Herrera and Héctor Palma-Castro; drawing by Edwin-Alberto Cadena and Diego Cómbita-Romero
Given the size of the turtles, this was something of a rare discovery. As Cadena explained, the bone in the shells of young turtles is very thin and so can be easily destroyed. As a result, there aren’t many fossils of turtle hatchlings around.
The researchers determined that this particular turtle was somewhere between 0 and 1 year old when it died, with a slightly developed carapace. They also nicknamed it “Turtwig”, after the small, turtle-esque starter Pokémon that has a leafy twig on its head.
As well as potentially providing insight into turtle development during the Cretaceous – some grew up to 4.5 meters (15 feet) – the researchers hope their discovery will have a wider impact on the field. “We resolved a small paleobotanical mystery, but more importantly, this study shows the need to re-study historical collections in Colombia,” said Herrera.
“Discoveries like these are truly special because they not only expand our knowledge about the past but also open a window to the diverse possibilities of what we can uncover,” Palma-Castro added.
The study is published in Palaeontologia Electronica.
Source Link: Fossil Plant Turns Out To Be Over 100-Million-Year-Old Baby Turtle