A coronal mass ejection from the Sun may end up ruining one of the most anticipated astronomical events of the year.
It’s been a tense few months for astronomy fans hoping to see Comet C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan–ATLAS) coming up to its closest approach to Earth on October 12. Back in July, analysis by one astronomer showed that the comet was showing signs of possible disintegration as it moved closer to the Sun, potentially robbing the Earth of a view of the comet’s unusual tail, if it survived the encounter at all.
Thankfully, the comet did survive its encounter, and everything looked rosy again. But now, it looks like comet may be back off the menu, after a significant coronal mass ejection was hurled by the Sun towards it, and Earth, on Monday.
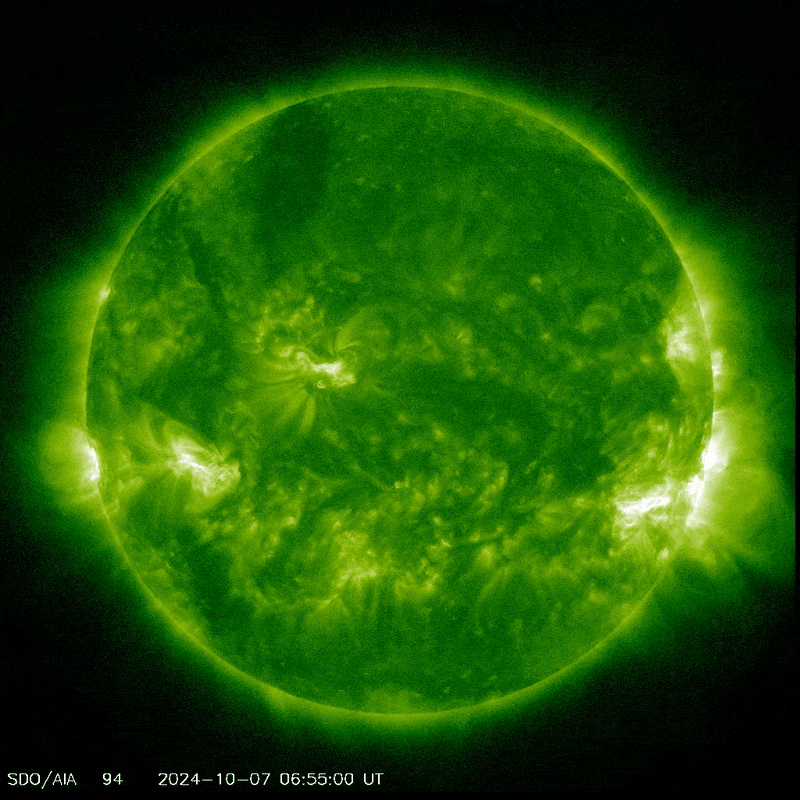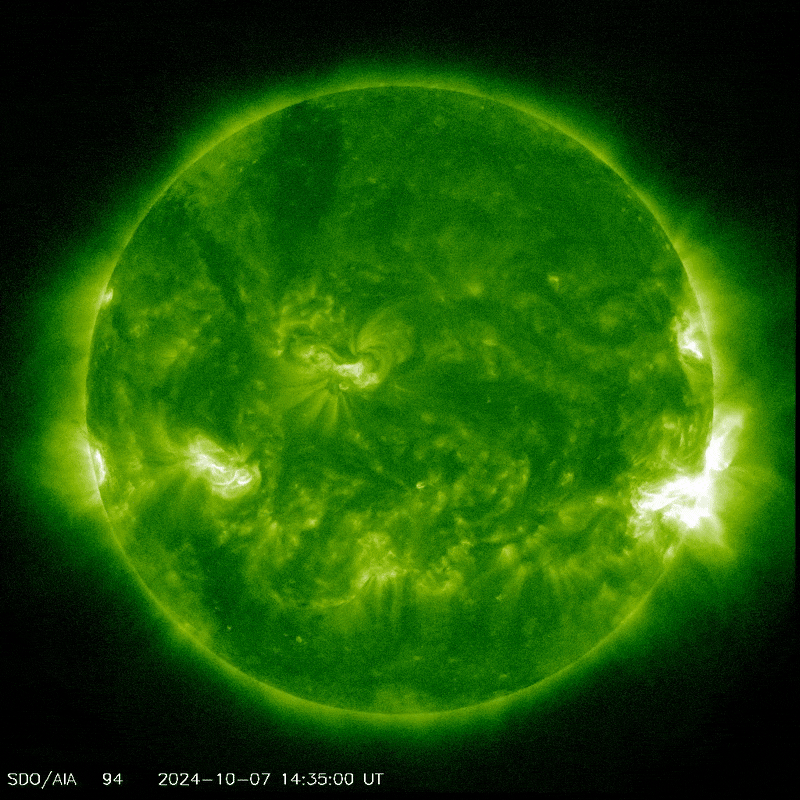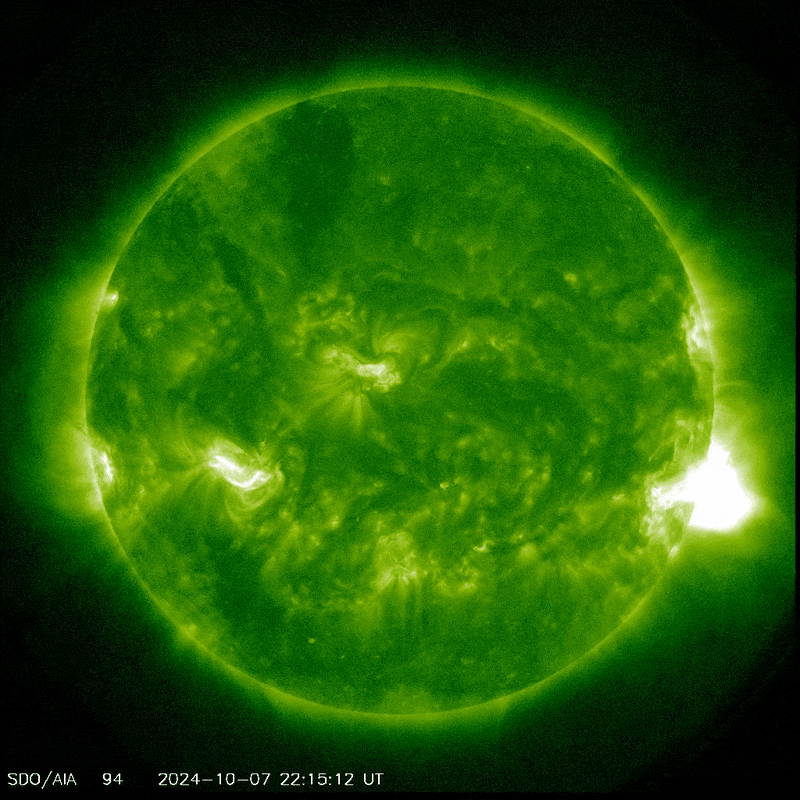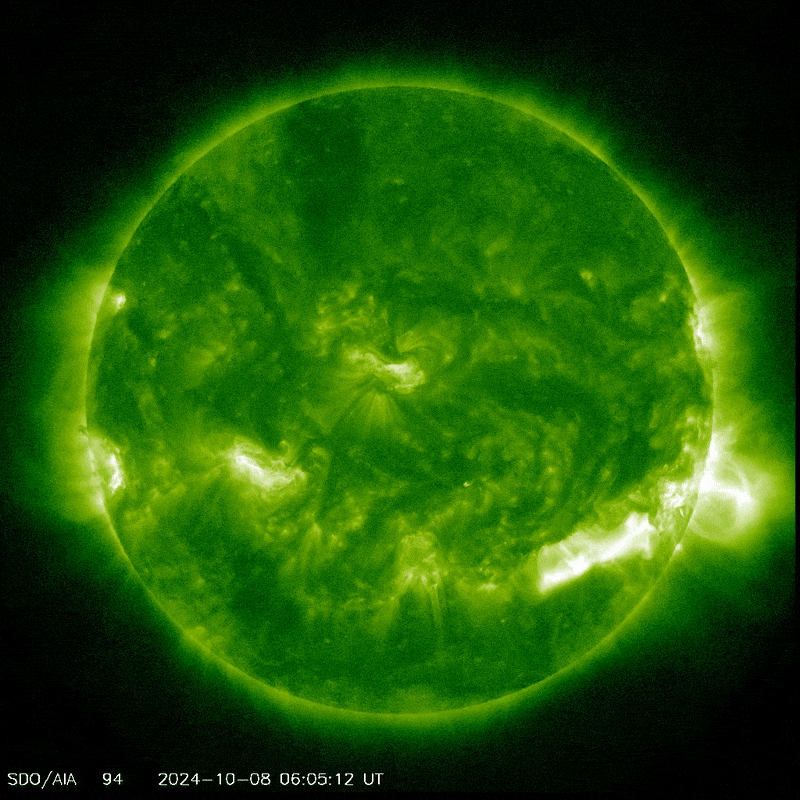
Sunspot AR3842 producing a coronal mass ejection.
Image credit: NASA/SDO
The Sun has been pretty active lately, around the peak of the 11-year solar cycle, sending geomagnetic storms our way and all the aurora and radio blackouts that they entail. On Monday, active sunspot AR3842 erupted, unleashing a massive solar flare that caused strong radio blackouts on Earth, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Space Weather Prediction Center.
The flare – a large burst of radiation coming from the release of magnetic energy – was associated with a coronal mass ejection, and it is this that may cause problems for Comet Tsuchinshan–ATLAS.
“Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) are large expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun’s corona. They can eject billions of tons of coronal material and carry an embedded magnetic field (frozen in flux) that is stronger than the background solar wind interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) strength,” the NOAA explains. “CMEs travel outward from the Sun at speeds ranging from slower than 250 kilometers [155 miles] per second (km/s) to as fast as near 3,000 km/s [1,864 miles per second]. The fastest Earth-directed CMEs can reach our planet in as little as 15-18 hours. Slower CMEs can take several days to arrive.”
The CME is predicted by a NASA model to graze Earth late on Wednesday or early on Thursday, with the Space Weather Prediction Center putting a G3 geomagnetic storm warning in place, indicating a strong geomagnetic storm.
“Infrastructure operators have been notified to mitigate any possible impacts,” the service explains on its website, adding that there is “some risk for controllable power fluctuations in the power grid” and there may be “possible slight risk of various satellite operations’ effects. Intermittent GPS degradation [is also] possible.”
While this is good news for aurora fans, as strong geomagnetic storms mean spectacular skies, it’s not looking great for Comet Tsuchinshan–ATLAS. The comet may be hit later today or early Wednesday by the CME, which could potentially rip off its tail. Fingers crossed that doesn’t happen, and we can get an even better view of the tail as it shoots off in front of the comet.
Source Link: Giant Coronal Mass Ejection May Hit Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS Before It Hits Earth