Ancient predatory worms dating back around 518 million years have been discovered in North Greenland, where a treasure trove of Early Cambrian fossils lay in wait in the Sirius Passet Lagerstätte. The new-to-science animals have been named Timorebestia, Latin for “terror beasts”, and their discovery reveals new insights into a curious group of predatory worms that are still alive today.
Arrowworms, also known as chaetognaths, are extant marine predators that hunt for tiny zooplankton in the ocean. Today they’re relatively small animals ranging from about 3 to 100 millimeters (0.118 to 4 inches), but their newly discovered Timorebestia koprii relatives were comparative monsters at around 30 centimeters (11.8 inches).
Found in a fossil locality that dates back more than 518 million years, it’s believed these giant terror worms may be some of the earliest carnivorous animals hunting in the water column in the Early Cambrian. They were peculiar-looking critters, with long antennae and an impressive set of jaws inside their heads. This separates them from arrowworms, whose jaws are on the outside.
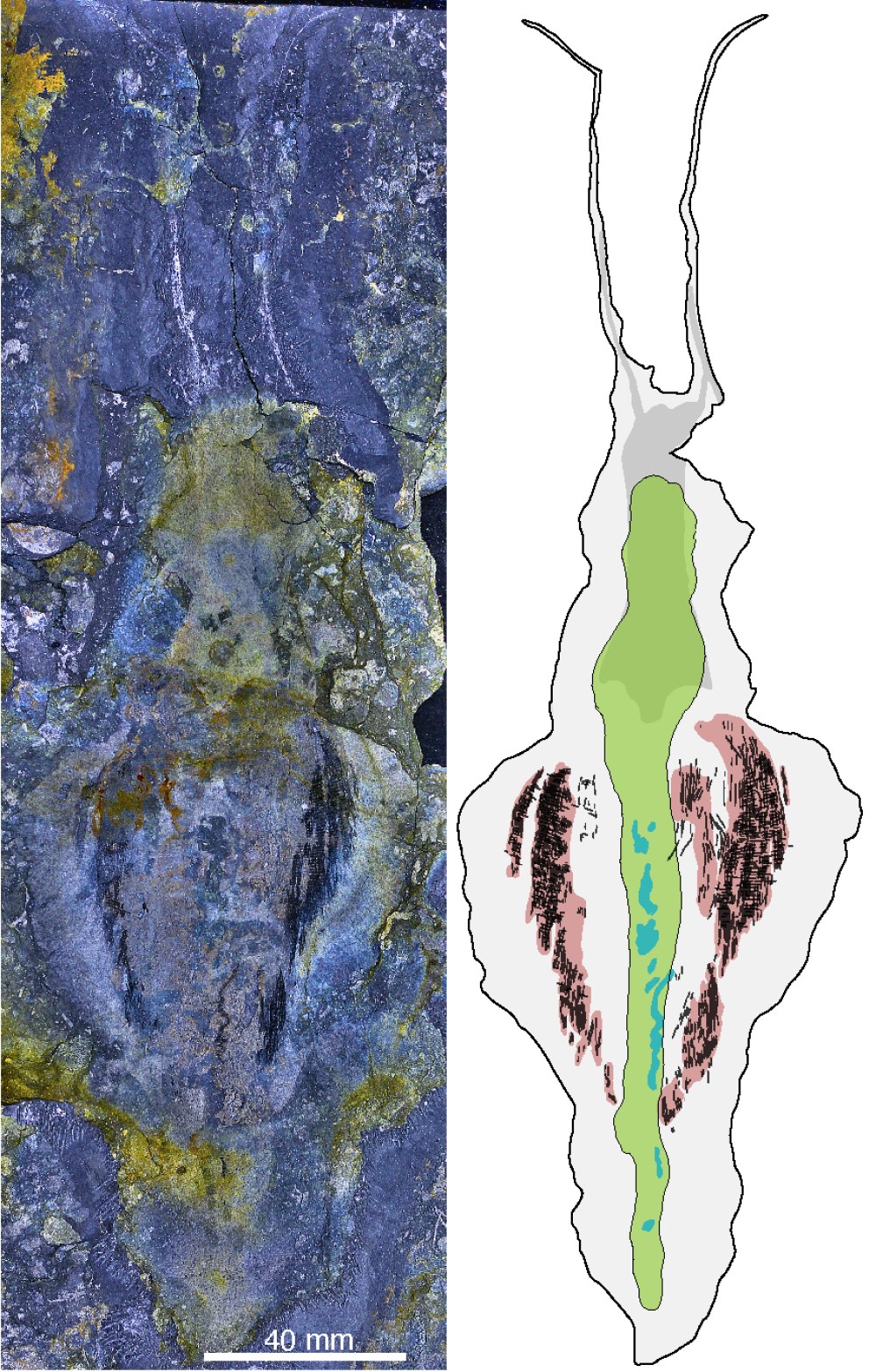
Timorebestia koprii and its distinctive long antennae. This is the largest known specimen at almost 30 centimeters or 12 inches.
Image credit: Dr Jakob Vinther
While a chompy worm the length of a ruler might not sound all that intimidating to the modern Homo sapiens, it would’ve been a significant threat to animals sharing the water column in Timorebestia’s heyday.
“Our research shows that these ancient ocean ecosystems were fairly complex with a food chain that allowed for several tiers of predators,” said senior study author Dr Jakob Vinther, from the University of Bristol’s Schools of Earth Sciences and Biological Sciences, in a statement.
“Timorebestia were giants of their day and would have been close to the top of the food chain. That makes it equivalent in importance to some of the top carnivores in modern oceans, such as sharks and seals back in the Cambrian period.”
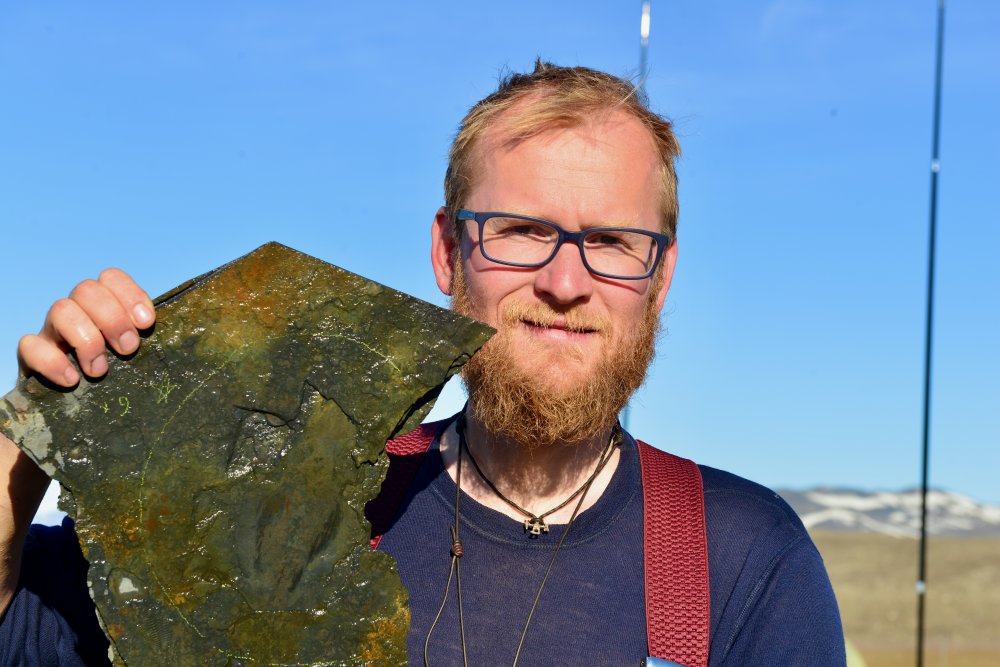

Timorebesta koprii fossil (left) and Dr Jakob Vinther for scale.
Image credit: Dr Jakob Vinther
Evidence of Timorebestia’s predatory prowess was found in its fossilized digestive system, where the remains of some unlucky Isoxys were found. Isoxys were a common swimming arthropod at the time whose defenses were apparently useless against Timorebestia.
“We can see these arthropods [were] a food source [for] many other animals,” added Morten Lunde Nielsen, a former PhD student at Bristol and part of the current study. “They are very common at Sirius Passet and had long protective spines, pointing both forwards and backwards. However, they clearly didn’t completely succeed in avoiding that fate, because Timorebestia munched on them in great quantities.”
Its success as a marine hunter adds a previously unrecognized dynasty of predators to our oceans’ history, as it seems Timorebestia and arrowworms were likely dominating the oceans before arthropods took off. Vinther estimates their reign may have lasted for 10 to 15 million years for they were superseded by more successful animals.
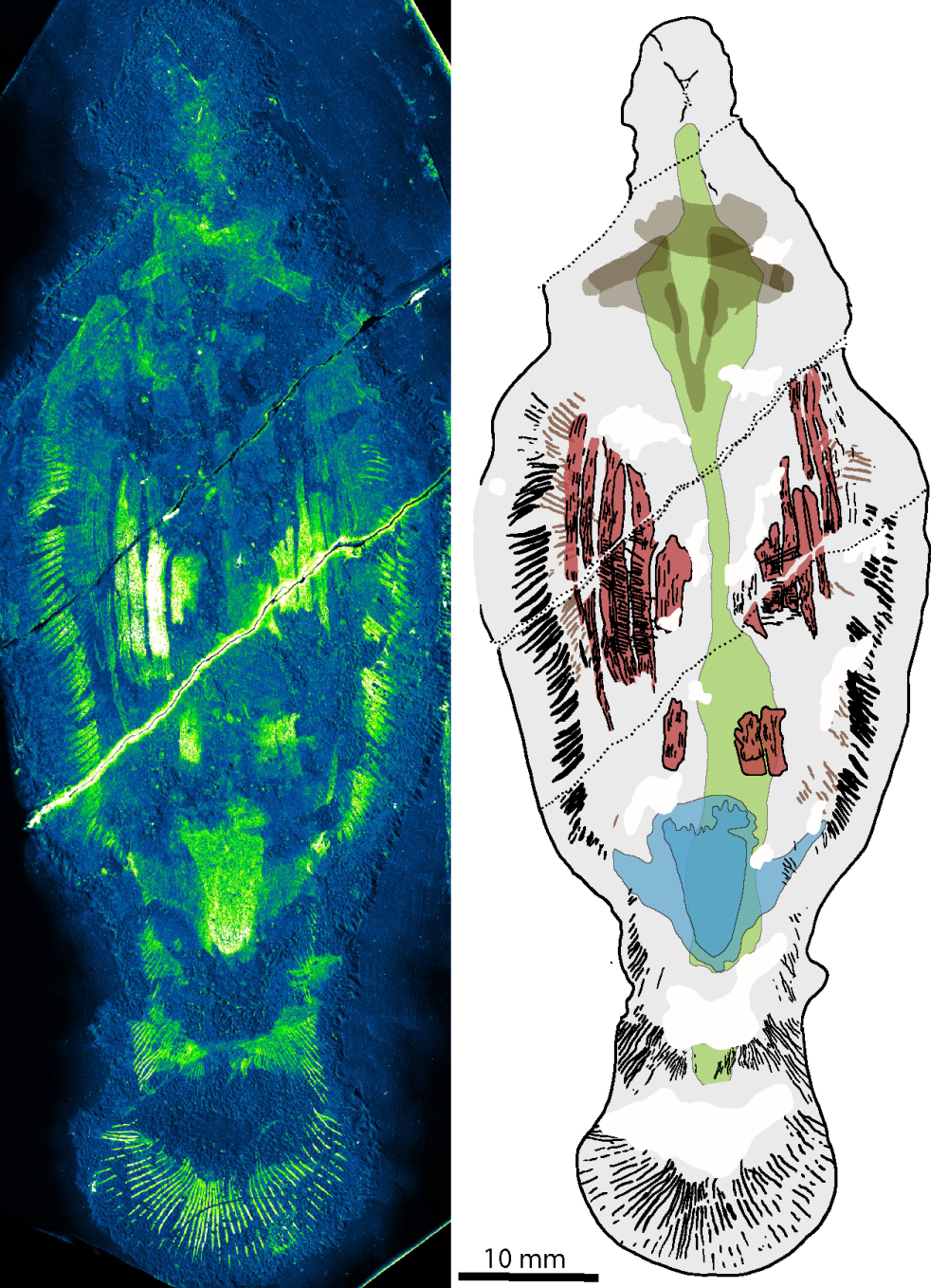
The team used an electron microprobe to map the carbon in the fossils out, revealing anatomical features such as fin rays and muscle systems.
Image credit: Dr Jakob Vinther
“We are very excited to have discovered such unique predators in Sirius Passet,” concluded Tae Yoon Park from the Korean Polar Research Institute, the other senior author and field expedition leader. “Over a series of expeditions to the very remote Sirius Passet in the furthest reaches of North Greenland more than 82.5˚ north, we have collected a great diversity of exciting new organisms. Thanks to the remarkable, exceptional preservation in Sirius Passet we can also reveal exciting anatomical details including their digestive system, muscle anatomy, and nervous systems.”
“We have many more exciting findings to share in the coming years that will help show how the earliest animal ecosystems looked like and evolved.”
The study is published in Science Advances.
Source Link: Giant Predatory Worms Dating Back 518 Million Years Found In Greenland