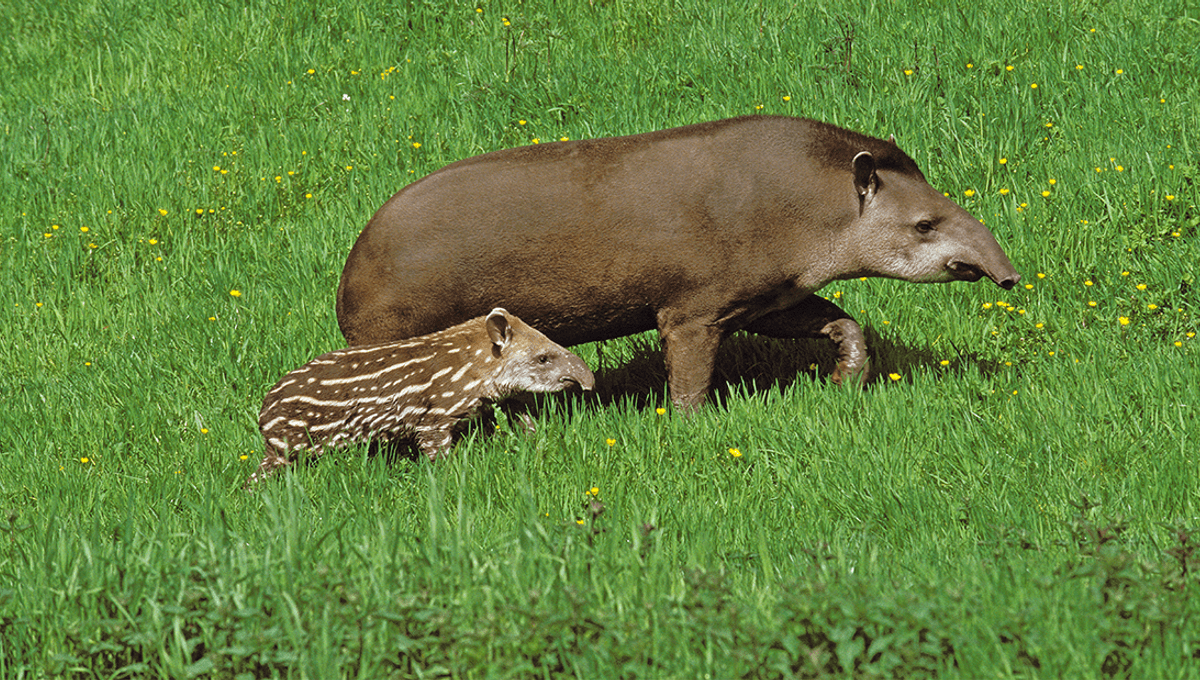
Tapirs might be one of the largest land mammals in South America clocking in at an impressive 300 kilograms (661 pounds), but they have been noticeably absent from a region in Brazil for over 100 years. Now, thanks to camera trap technology, the first images and videos of these iconic animals returning to the region have been captured.
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
As reported by g1, it’s been 110 years since the last confirmed sighting of a South American or lowland tapir (Tapirus terrestris) in the state of Rio de Janeiro. The IUCN describes populations as having “great variation in density” and while it is hard to get an accurate picture of the overall population in South America because of their naturally shy and elusive nature, they are currently listed as Vulnerable.
A combination of factors is thought to have been behind their decline, including deforestation, urbanization, and hunting. The animals also suffer from becoming roadkill after collisions.
However, recent years have seen attempts to reintroduce the lowland tapir to its native habitat – but its return to this particular area appears to be spontaneous. The new sightings come from camera traps in Cunhambebe State Park (PEC) and show potentially four individuals, including a mother and calf, within the protected area. Footage of the tapirs can be found on the park’s Instagram profile.
For an animal thought to be extinct in the area, this spontaneous return highlights the importance of protected reserves.
“The spontaneous return of the tapirs is a sign that the forests of Rio de Janeiro are capable of sustaining large mammals again,” Marcelo Cupello, a biologist with Rio de Janeiro’s State Environmental Institute (INEA-RJ), told g1. “This demonstrates functional ecological connectivity, as these animals are using natural forest corridors. In other words, the local fauna still maintains a certain capacity for movement and dispersion.”
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
Tapirs are important members of the ecosystems, helping to spread the seeds of many plant species throughout the rainforests they inhabit. Using their prehensile snouts, they remove plant material and distribute seeds through their own internal fertilization system (poop). Often called the “forest gardener“, this ability can help the biodiversity of an area improve, providing benefits for other species in turn.
Source Link: Good News: Tapirs Are Back In Rio De Janeiro State After More Than 100 Years