In February 1987, a star went supernova in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of the small galaxies that orbit around our own galaxy, the Milky Way. It was the closest known supernova since 1604 and it has been studied with so many telescopes in so many different wavelengths. The latest taken to this task was JWST.
The space telescope brought a higher resolution to Supernova 1987A. Clearly visible is the central structure, known as the keyhole due to its shape. This is clumpy gas and dust ejected during the supernova, dense enough to foil the ability of the telescope to see through your usual nebula.
The keyhole is connected to the equatorial ring and this ring is connected to two wider outer rings. Due to the angle of the supernova, these are slightly slanted from our line of sight, creating an hourglass shape. The star that went supernova released for thousands of years material. This is a typical behavior for aging stars.
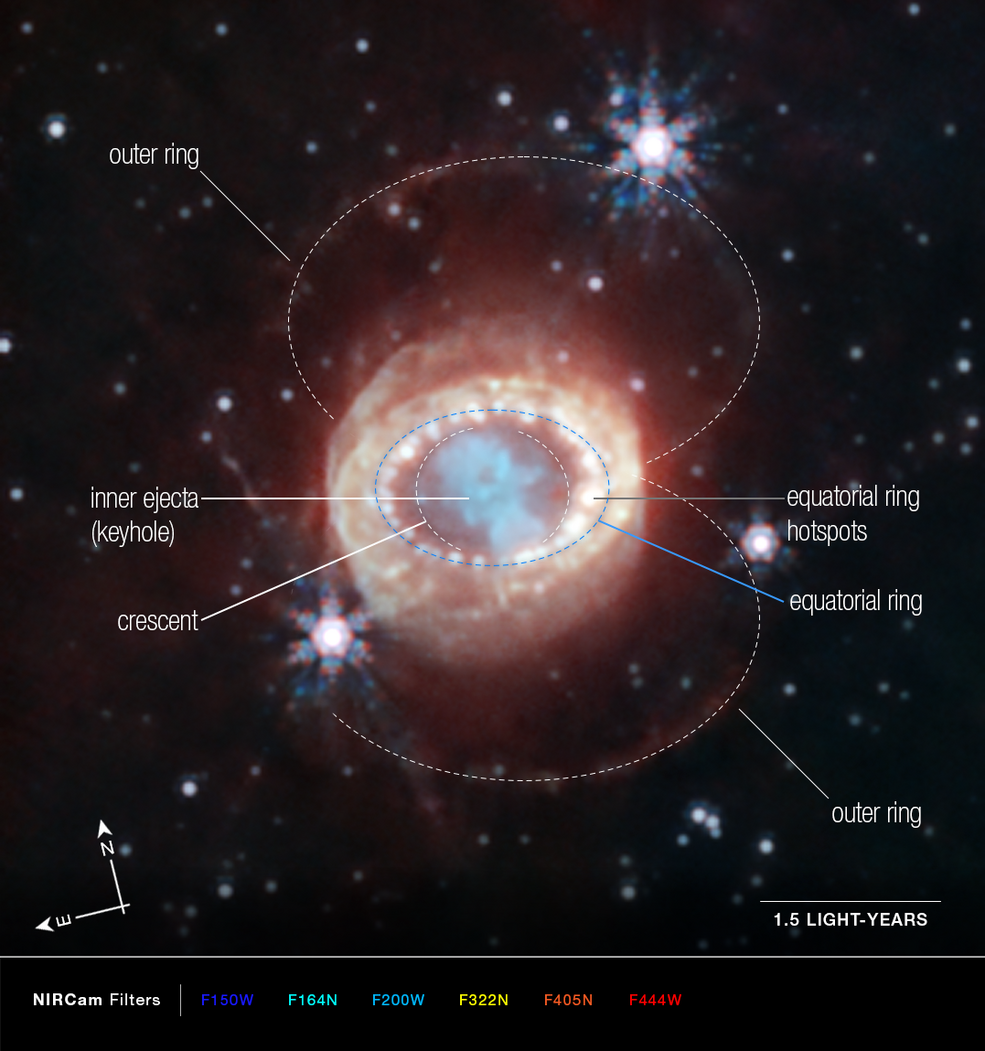
An annotated version of the JWST image of SN 1987A
Image Credits: NASA, ESA, CSA, M. Matsuura (Cardiff University), R. Arendt (NASA’s Goddard Spaceflight Center & University of Maryland, Baltimore County), C. Fransson (Stockholm University), and J. Larsson (KTH Royal Institute of Technology). Image Processing: A. Pagan
As the star went supernova, material was ejected at much higher velocities. Slamming into the older releases, it creates shocks that light up the equatorial ring like a string of pearls. In the JWST image, we can see shocks even on the external portion of the ring.
But the exquisite resolution of JWST has revealed another structure deep within the supernova remnant. Crescent structures flanking the keyhole within the interior of the equatorial ring have appeared in this photo. They appear to be the outer layer of gas released by the supernova as it exploded.
The team is intrigued by them, but they want to know more. They are quite bright, but the team is not sure if that is due to the presence of a lot of material or due to an optical effect. Something called limb brightening could make it appear that an expanding shell in three dimensions is chunkier when flattened out in a photograph.
JWST will continue to study this fascinating object for sure. Many mysteries continue to surround this supernova, and researchers are keen to solve them. Chiefly among them is the end product of this stellar explosion. Astronomers believe a neutron star should have been left behind from this cataclysmic event but it is yet to be detected.
A possibility based on the observations suggests that the neutron star is shrouded in a deep cover of dust. The new JWST observations are consistent with this scenario.
Source Link: Hidden Structure Of Iconic Supernova Seen By JWST