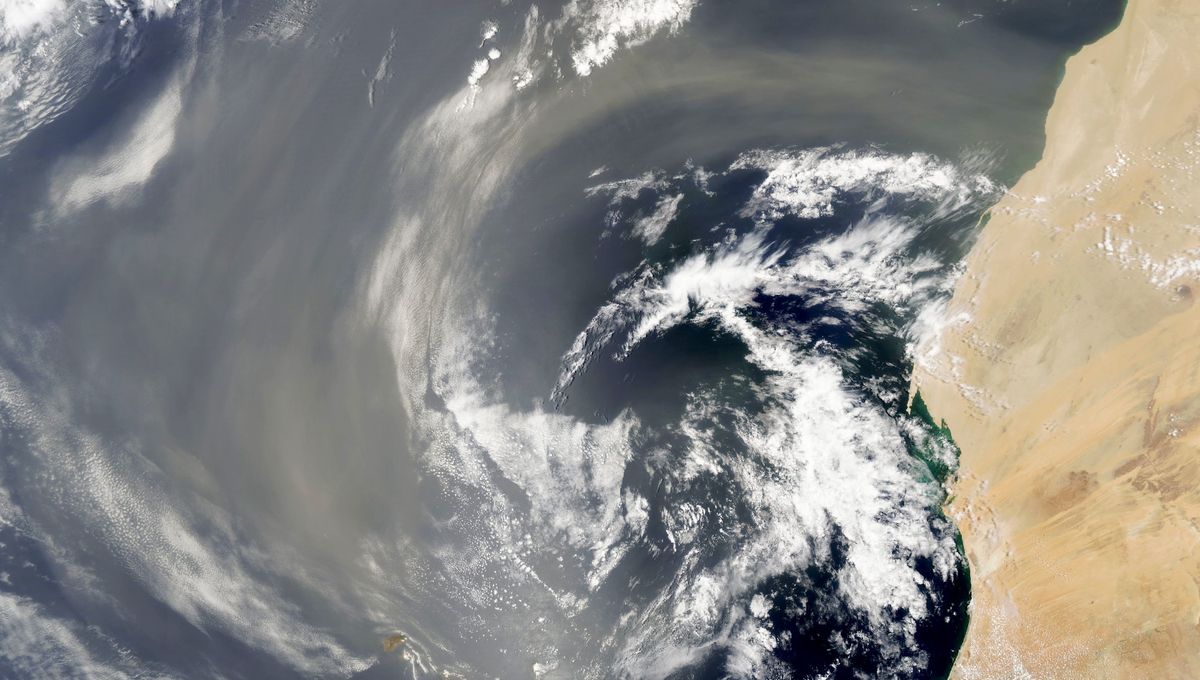
Parts of the US are preparing for dust storms this week as a large mass of dry, dusty air is set to make landfall after traveling across the Atlantic from the Sahara Desert – but how is it able to make this over 8,000-kilometer (5,000-mile) journey?
It’s all down to seasonal changes in the wind, which is why the arrival of long-distance dust in the US isn’t actually an unusual event – Saharan dust makes this voyage every summer.
An uptick in winds in the Sahara, peaking in late June to mid-August, picks up dust and injects it into the troposphere, the lowest layer of Earth’s atmosphere. There, it forms into the Saharan Air Layer, a 3 to 4-kilometer (2 to 2.5-mile) thick plume of extremely dry and dusty air, starting around 1.6 kilometers (1 mile) above the surface.
And when we say dry, we mean dry – the Saharan Air Layer has around 50 percent less moisture than you’d usually expect in the atmosphere over tropical regions.
Then, every three to five days at its peak, the trade winds – the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds over the equator – blow the layer across the Atlantic Ocean towards the US, where it can have all kinds of impacts.
One of the main ways the Saharan Air Layer can make its mark is in the weather.
“The dry air can really suppress afternoon clouds and help cool things down,” Jason Dunion, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)’s Hurricane Program Field Director and a meteorologist, told Space.com. It can also help to weaken tropical storms by promoting downdrafts, “but you can still get storms popping in the late afternoon,” Dunion added.
The downside of storm suppression, the meteorologist explains, is that it can also “make for some of your hottest days when these dust outbreaks come overhead in places like Texas and Alabama.”
Then there’s the potential health effects; at a low enough altitude, the presence of dust drops the air quality and can make conditions involving the lungs, like asthma, worse than usual.
The issue is that, while dust storms have a role to play in Earth’s biogeochemical cycles, their frequency is also on the up, which is of concern to officials because of the effects they can have on people’s health, economies and infrastructure, and the environment.
According to the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), around 2 billion tons of sand and dust end up in the atmosphere each year – the same weight as 350 Great Pyramids of Giza.
Around 25 percent of that matter is thought to stem from human activity, which the UN is hoping to target by dedicating the next decade to combating sand and dust storms, with an annual awareness day each July 12. This year’s awareness day, the first ever, marks the launch of a policy guide that aims to help governments adapt to the problems of sand and dust storms.
“The Policy Guideline will support countries to develop and implement sand and dust storms-related initiatives, improve land use and management, enhance food security, and build resilience to climate change,” said Lifeng Li, Director of the Land and Water Division at the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization, in a statement.
All “explainer” articles are confirmed by fact checkers to be correct at time of publishing. Text, images, and links may be edited, removed, or added to at a later date to keep information current.
Source Link: How Can Dust And Sand Travel 5,000 Miles?