What gives a pink lake in Australia its bizarrely vibrant bubblegum coloration has been pondered since before bubblegum was even invented. In 1802, Matthew Flinders became the first to suggest Lake Hillier’s pink color came from its salinity, but in the few hundred years that have followed, science has revealed that this is just part of the story.
Western Australia is home to several pink lakes and lagoons, but Lake Hillier is perhaps one of the most peculiar, standing in stark contrast to the greenery that surrounds its defined edges. Being sat toward the coast of Middle Island, the pink lake looks – if possible – even pinker juxtaposed against the blue of the ocean (did you know lakes come in all sorts of weird colors?).
Research in 2022 decided to take a closer look at the pink lake, which is about 250 meters (820 feet) wide and eight times saltier than the ocean. Co-founder of the Extreme Microbiome Project Scott Tighe, and corresponding author on the paper about Lake Hillier, was inspired to take on the mystery behind its vibrancy after seeing it on TV.
“I thought, that’s amazing,” he told New Scientist. “I’ve got to get over there and grab samples and sequence the heck out of it.”
So sequence the heck out of it is what he did. With the help of Ken McGrath, of Brisbane microbial genomics company Microba, and a team of researchers, they collected samples and analyzed them using metagenomics. This approach effectively enables scientists to sort through the anonymity of crowded microbial environments, teasing out the separate genomes so that the entire ecosystem can be identified.
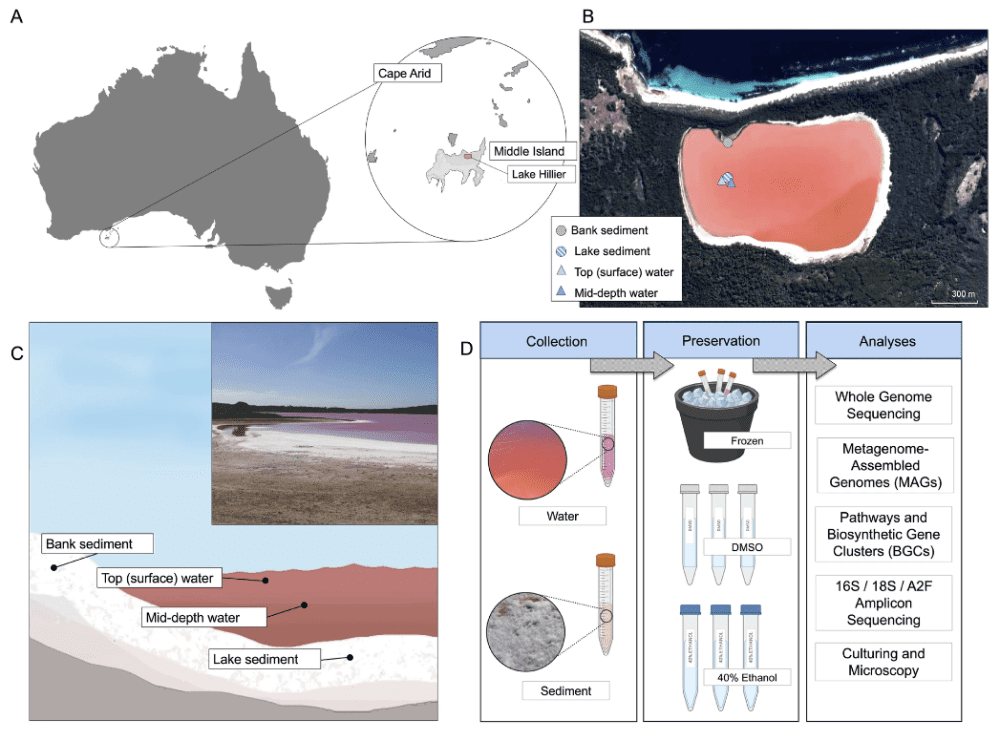
The tests revealed a rich roster of extremophiles, organisms that have adapted to survive in harsh conditions that would be inhospitable to other species. In the case of our salty pink Lake Hillier, many of the microbial species had evolved to tolerate high salt levels and the coloration of these went some way towards explaining the lake’s peculiar color.
“Lake Hillier is composed of a diverse set of microorganisms including archaea, bacteria, algae, and viruses,” the study authors concluded. “Our data indicate that the microbiome in Lake Hillier is composed of multiple pigment-producer microbes, including Dunaliella, Salinibacter, Halobacillus, Psychroflexus, [and] Halorubrum.”
The colors of these microbial species range from blue, to orange, and through to red, which they believe could explain why the end result is a very peculiarly pink lake. These colors come from the carotenoids they contain, which are thought to provide some protection against high saline environments – so Flinders wasn’t entirely wrong when he said the pink was because of the saltiness.
Science aside, Western Australia’s pink lake is a breathtaking sight to see, set against the untouched islands of the Recherche Archipelago Nature Reserve that’s home to seals, dolphins, and migrating whales.
Marine mammals and bubblegum-pink lakes? Don’t mind if we do.
Source Link: How This Pink Lake In Australia Gets Its Bubblegum Color